Abstract
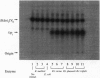
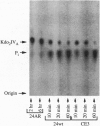
Lipid A from several strains of the N2-fixing bacterium Rhizobium leguminosarum displays significant structural differences from Escherichia coli lipid A, one of which is the complete absence of phosphate groups. However, the first seven enzymes of E. coli lipid A biosynthesis, leading from UDP-GlcNAc to the phosphorylated intermediate, 2-keto-3-deoxyoctulosonate (Kdo2)-lipid IVA, are present in R. leguminosarum. We now describe a membrane-bound phosphatase in R. leguminosarum extracts that removes the 4' phosphate of Kdo2-lipid IVA. The 4' phosphatase is selective for substrates containing the Kdo domain. It is present in extracts of R. leguminosarum biovars phaseoli, viciae, and trifolii but is not detectable in E. coli and Rhizobium meliloti. A nodulation-defective strain (24AR) of R. leguminosarum biovar trifolii, known to contain a 4' phosphatase residue on its lipid A, also lacks measurable 4' phosphatase activity. The Kdo-dependent 4' phosphatase appears to be a key reaction in a pathway for generating phosphate-deficient lipid A.
Full text
PDF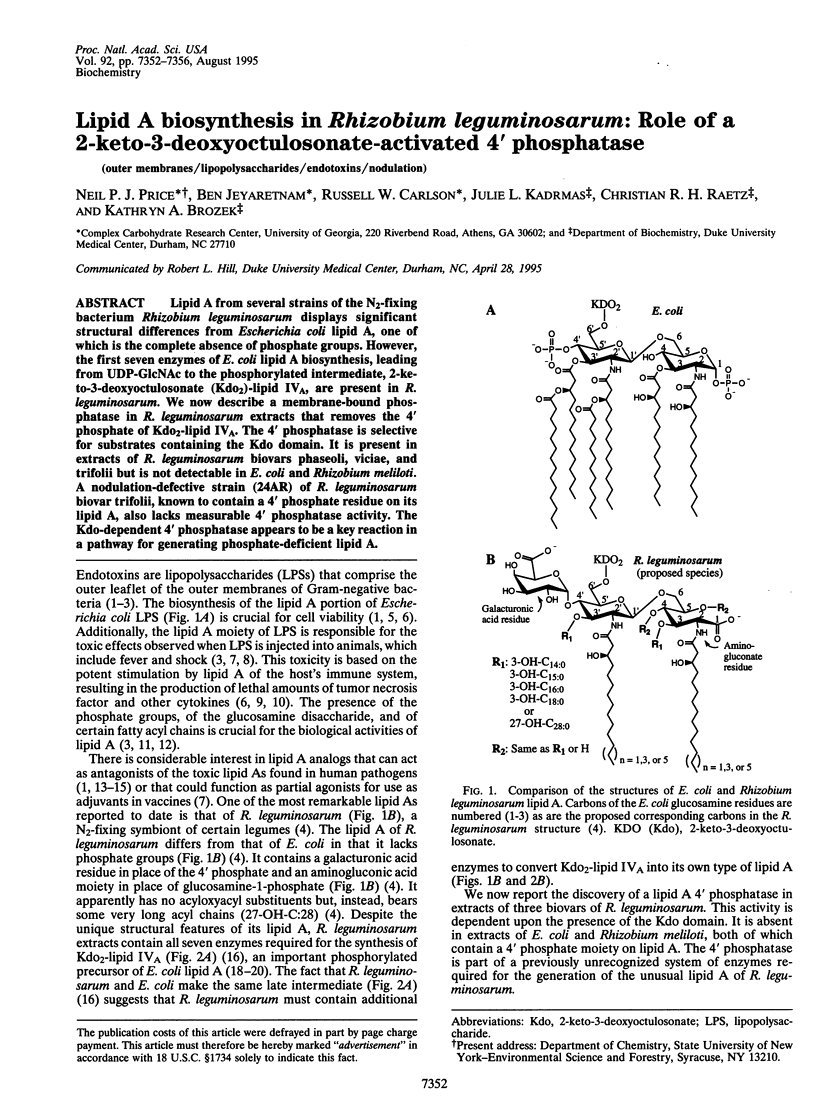




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. S., Bull H. G., Galloway S. M., Kelly T. M., Mohan S., Radika K., Raetz C. R. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli. The first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19858–19865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belunis C. J., Raetz C. R. Biosynthesis of endotoxins. Purification and catalytic properties of 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid transferase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9988–9997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat U. R., Forsberg L. S., Carlson R. W. Structure of lipid A component of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli lipopolysaccharide. Unique nonphosphorylated lipid A containing 2-amino-2-deoxygluconate, galacturonate, and glucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14402–14410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozek K. A., Hosaka K., Robertson A. D., Raetz C. R. Biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli. Cytoplasmic enzymes that attach 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid to lipid A. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6956–6966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brozek K. A., Raetz C. R. Biosynthesis of lipid A in Escherichia coli. Acyl carrier protein-dependent incorporation of laurate and myristate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15410–15417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cava J. R., Elias P. M., Turowski D. A., Noel K. D. Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genetic regions encoding lipopolysaccharide structures essential for complete nodule development on bean plants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.8-15.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementz T., Raetz C. R. A gene coding for 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic-acid transferase in Escherichia coli. Identification, mapping, cloning, and sequencing. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9687–9696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway S. M., Raetz C. R. A mutant of Escherichia coli defective in the first step of endotoxin biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6394–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Hampton R. Y., Qureshi N., Takayama K., Raetz C. R. Lipid A-like molecules that antagonize the effects of endotoxins on human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19490–19498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Raetz C. R. Lipid A 4'-kinase from Escherichia coli: enzyme assay and preparation of 4'-32P-labeled probes of high specific radioactivity. Methods Enzymol. 1992;209:466–475. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)09057-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst O., Borowiak D., Weckesser J., Mayer H. Structural studies on the phosphate-free lipid A of Rhodomicrobium vannielii ATCC 17100. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 1;137(1-2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. E., Weckesser J., Mayer H., Fromme I. Isolation and characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Chromatium vinosum. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert R. E., Weckesser J., Tharanathan R. N., Mayer H. Isolation and characterization of the lipopolysaccharide of Thiocapsa roseopersicina. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):241–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchens R. L., Ulevitch R. J., Munford R. S. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) partial structures inhibit responses to LPS in a human macrophage cell line without inhibiting LPS uptake by a CD14-mediated pathway. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):485–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R., Staskawicz B. J. Prokaryotic plant parasites. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):921–935. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90271-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Brade H., Dürrbaum I., Dinarello C. A., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Flad H. D. IL-1 induction-capacity of defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3229–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson D. K., Weintraub A., Pohlman T. H., Maier R. V. Human endothelial cell adhesiveness for neutrophils, induced by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide in vitro, is inhibited by Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):3025–3030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natanson C., Hoffman W. D., Suffredini A. F., Eichacker P. Q., Danner R. L. Selected treatment strategies for septic shock based on proposed mechanisms of pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med. 1994 May 1;120(9):771–783. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-120-9-199405010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima M., Raetz C. R. Membrane lipid biogenesis in Escherichia coli: identification of genetic loci for phosphatidylglycerophosphate synthetase and construction of mutants lacking phosphatidylglycerol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7837–7844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T. Chemical structure of lipid A from Porphyromonas (Bacteroides) gingivalis lipopolysaccharide. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 11;332(1-2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80512-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrillo J. E. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 20;328(20):1471–1477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305203282008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price N. P., Kelly T. M., Raetz C. R., Carlson R. W. Biosynthesis of a structurally novel lipid A in Rhizobium leguminosarum: identification and characterization of six metabolic steps leading from UDP-GlcNAc to 3-deoxy-D-manno-2-octulosonic acid2-lipid IVA. J Bacteriol. 1994 Aug;176(15):4646–4655. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.15.4646-4655.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radika K., Raetz C. R. Purification and properties of lipid A disaccharide synthase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14859–14867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Bacterial endotoxins: extraordinary lipids that activate eucaryotic signal transduction. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5745–5753. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5745-5753.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Dowhan W. Biosynthesis and function of phospholipids in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1235–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R., Ulevitch R. J., Wright S. D., Sibley C. H., Ding A., Nathan C. F. Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Sep;5(12):2652–2660. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Brade H. Bacterial endotoxins. Sci Am. 1992 Aug;267(2):54–61. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0892-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietschel E. T., Kirikae T., Schade F. U., Mamat U., Schmidt G., Loppnow H., Ulmer A. J., Zähringer U., Seydel U., Di Padova F. Bacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):217–225. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.2.8119492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub A., Zähringer U., Wollenweber H. W., Seydel U., Rietschel E. T. Structural characterization of the lipid A component of Bacteroides fragilis strain NCTC 9343 lipopolysaccharide. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;183(2):425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]