Abstract
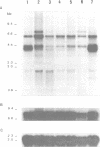
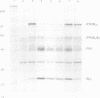
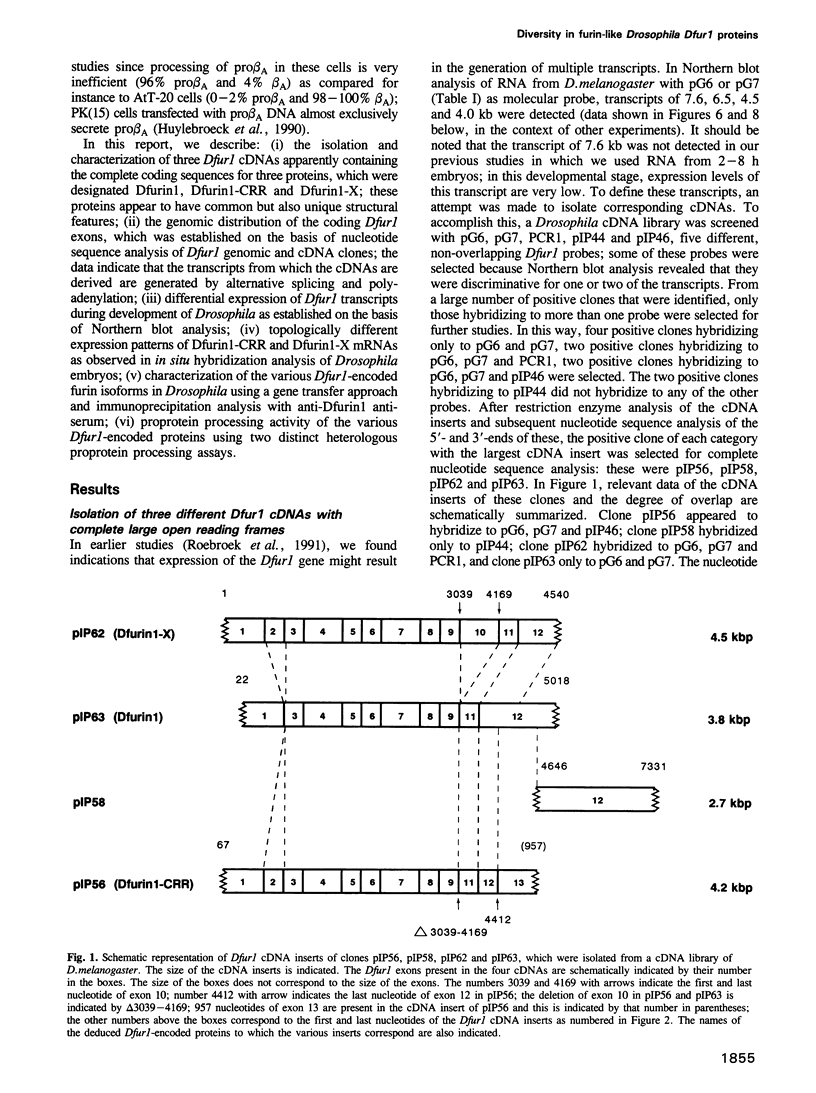
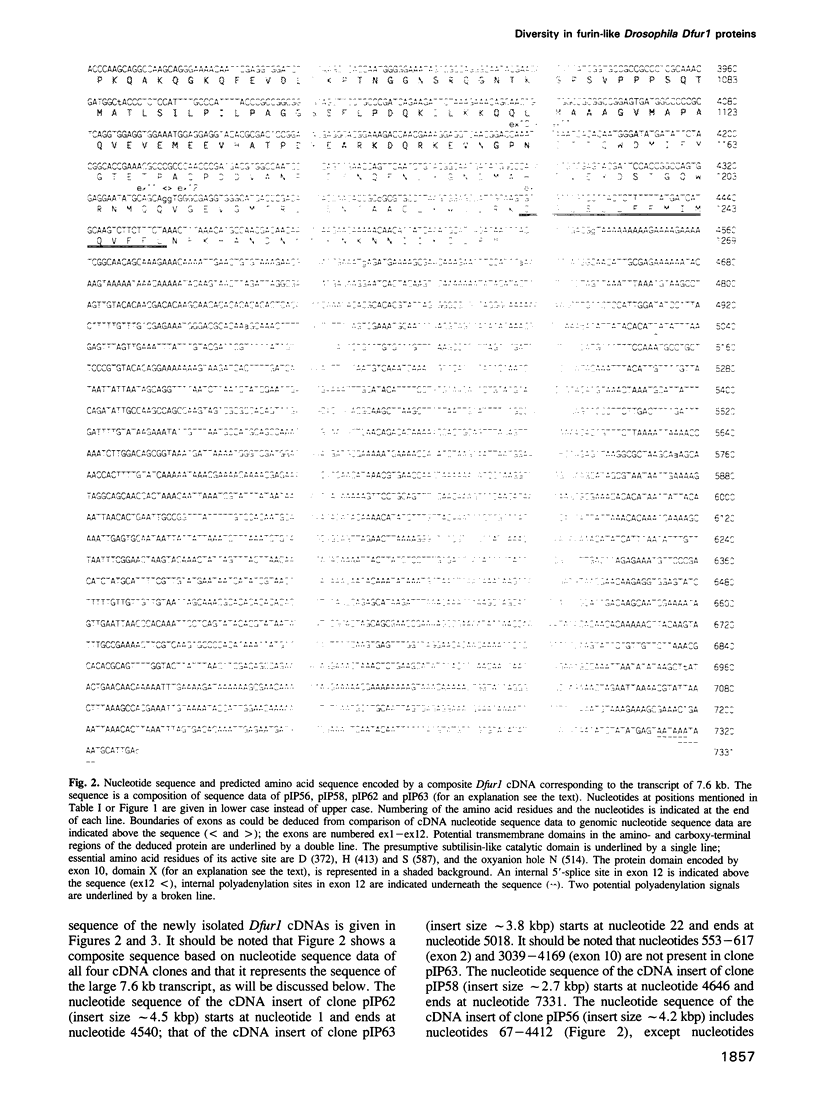
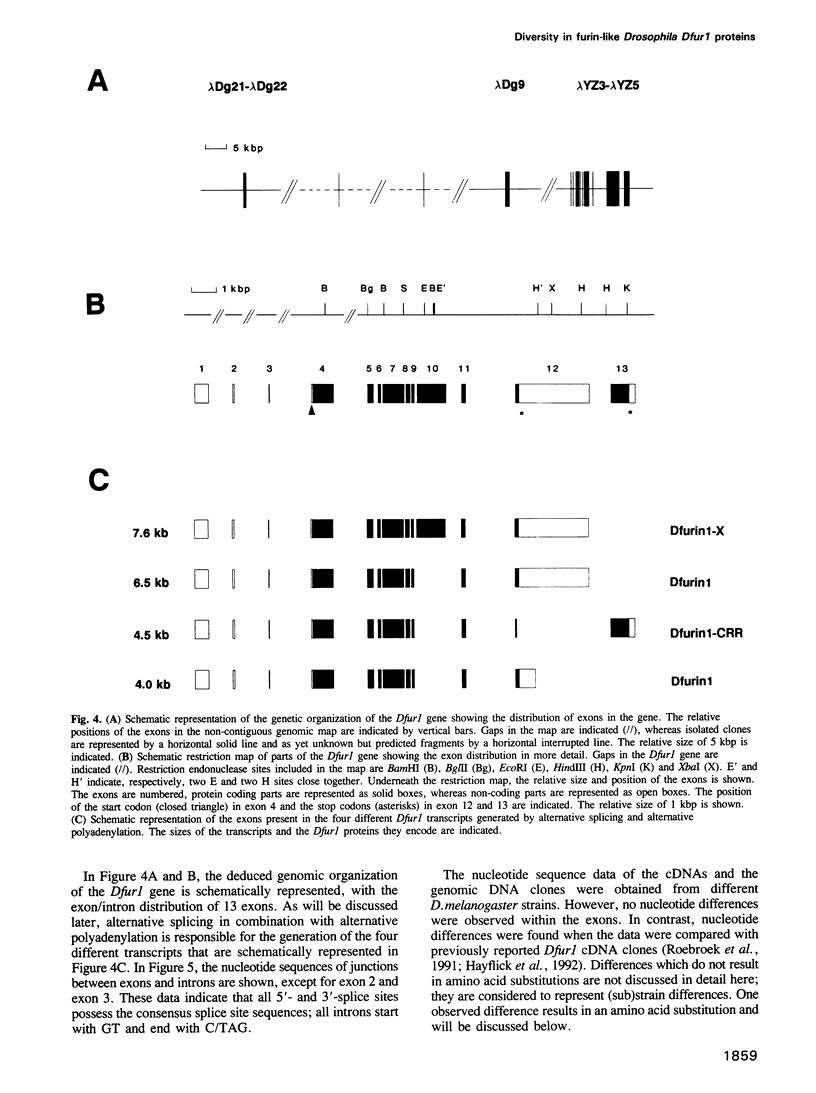
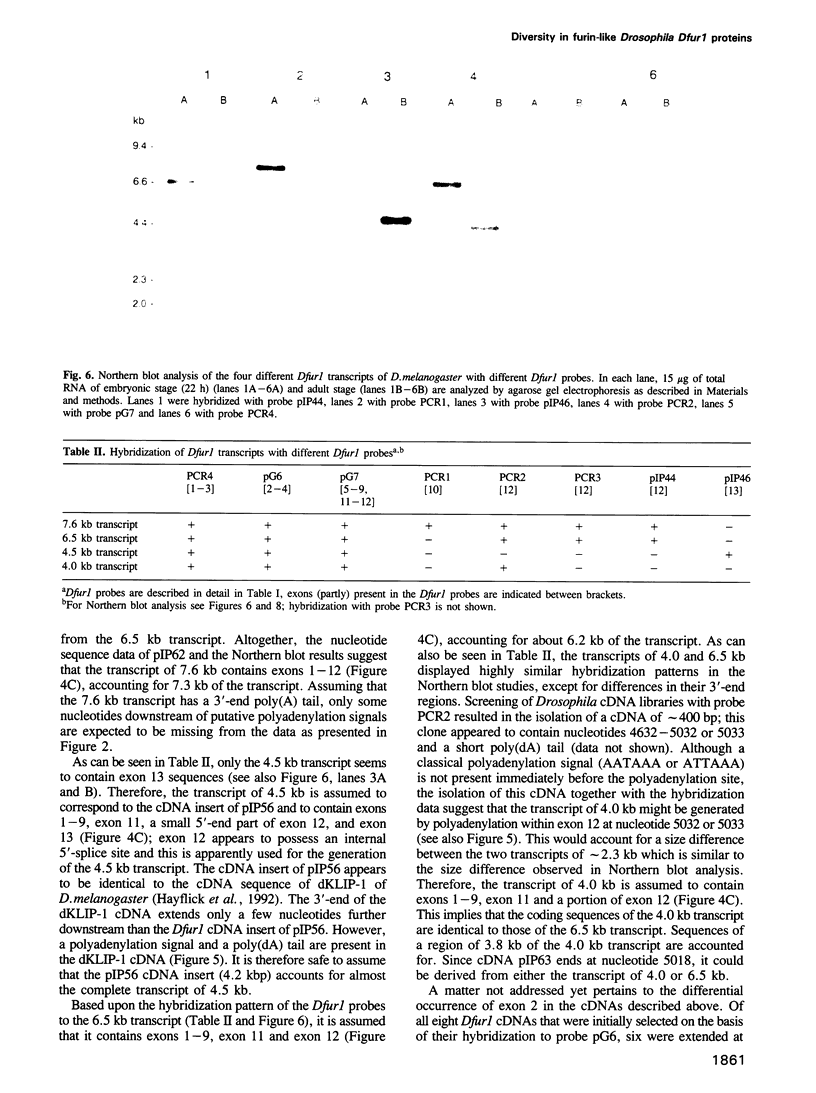
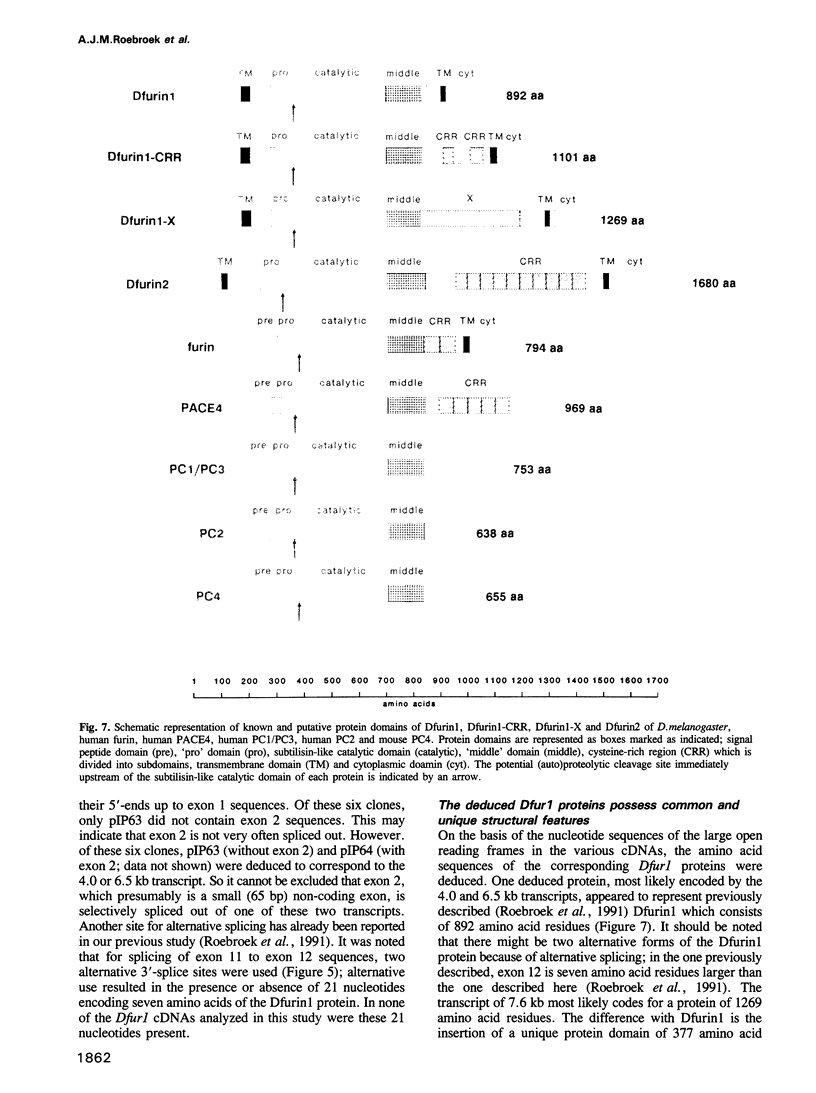
To investigate whether or not alternative splicing might be a mechanism by which in Drosophila melanogaster diversity is generated in endoproteases of the novel eukaryotic family of subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzymes, we determined structural and functional characteristics of the Dfur1 gene. Northern blot analysis revealed Dfur1 transcripts of 7.6, 6.5, 4.5 and 4.0 kb. By comparative nucleotide sequence analysis of Dfur1 genomic and cDNA clones, 10 coding exons were identified and, together with Northern blot analysis using exon-specific probes, evidence was obtained that the four transcripts are generated by alternative splicing and polyadenylation. The apparently complete open reading frames of three Dfur1 cDNAs revealed that these coded for three furin-like proteins, Dfurin1 (892 residues), Dfurin1-CRR (1101 residues) and Dfurin1-X (1269 residues), which possessed common but also unique structural domains. These various isoforms of furin in Drosophila were characterized in gene transfer studies using immunoprecipitation analysis. Differential expression of Dfur1 transcripts was found in Northern blot analysis of RNA from various developmental stages of Drosophila. RNA in situ hybridization experiments revealed that the Dfurin1-X and Dfurin1-CRR isoforms are expressed in non-overlapping sets of tissues during Drosophila embryogenesis. In gene transfer experiments in which the Dfurin1, Dfurin1-CRR and Dfurin1-X proteins were expressed at high levels together with the precursor of the beta A-chain of activin-A, a member of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) superfamily, or the precursor of von Willebrand factor, all three proteins appeared capable of processing these substrates. Our studies indicate that the Dfur1 gene encodes structurally different subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzymes with distinct physiological functions in Drosophila.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasson K. I., Tam W. W., Feurst T. O., Moss B., Loh Y. P. Production of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) by a vaccinia virus transient expression system and in vitro processing of the expressed prohormone by POMC-converting enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J., Mason O. B., Landsberg K. E., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J. cDNA and gene structure for a human subtilisin-like protease with cleavage specificity for paired basic amino acid residues. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;10(5):319–328. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan P. A., Leduc R., Thomas L., Thorner J., Gibson H. L., Brake A. J., Barr P. J., Thomas G. Human fur gene encodes a yeast KEX2-like endoprotease that cleaves pro-beta-NGF in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2851–2859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Oliva A. A., Jr, LaMendola J., Grens A., Bode H., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the prohormone convertase gene family in metazoa: analysis of cDNAs encoding a PC3-like protein from hydra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creemers J. W., Roebroek A. J., Van de Ven W. J. Expression in human lung tumor cells of the proprotein processing enzyme PC1/PC3. Cloning and primary sequence of a 5 kb cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 23;300(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80169-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Civelli O., Herbert E. Polyprotein gene expression: generation of diversity of neuroendocrine peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:665–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Enzymes required for yeast prohormone processing. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:345–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Molecular and enzymatic properties of furin, a Kex2-like endoprotease involved in precursor cleavage at Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):296–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J. S., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A., Thomas G. A unique Kex2-like endoprotease from Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in the central nervous system during early embryogenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):705–717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huylebroeck D., Van Nimmen K., Waheed A., von Figura K., Marmenout A., Fransen L., De Waele P., Jaspar J. M., Franchimont P., Stunnenberg H. Expression and processing of the activin-A/erythroid differentiation factor precursor: a member of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1153–1165. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-8-1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer M. C., Tucker J. E., Joh R., Landsberg K. E., Saltman D., Barr P. J. Identification of a second human subtilisin-like protease gene in the fes/fps region of chromosome 15. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;10(10):757–769. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marynen P., Devriendt K., Van den Berghe H., Cassiman J. J. A genetic polymorphism in a functional domain of human pregnancy zone protein: the bait region. Genomic structure of the bait domains of human pregnancy zone protein and alpha 2 macroglobulin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi Y., Oda K., Fujiwara T., Takami N., Tashiro K., Ikehara Y. Functional expression of furin demonstrating its intracellular localization and endoprotease activity for processing of proalbumin and complement pro-C3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16954–16959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama M., Ikemizu J., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Evidence that differentiates between precursor cleavages at dibasic and Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1991 Nov;110(5):806–811. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Kim W. S., Torii S., Hosaka M., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Baba T., Murakami K. Identification of the fourth member of the mammalian endoprotease family homologous to the yeast Kex2 protease. Its testis-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5897–5900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Creemers J. W., Pauli I. G., Kurzik-Dumke U., Rentrop M., Gateff E. A., Leunissen J. A., Van de Ven W. J. Cloning and functional expression of Dfurin2, a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme of Drosophila melanogaster with multiple repeats of a cysteine motif. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17208–17215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Pauli I. G., Zhang Y., van de Ven W. J. cDNA sequence of a Drosophila melanogaster gene, Dfur1, encoding a protein structurally related to the subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Bussemakers M. J., van Heerikhuizen H., Onnekink C., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Characterization of human c-fes/fps reveals a new transcription unit (fur) in the immediately upstream region of the proto-oncogene. Mol Biol Rep. 1986;11(2):117–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00364823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Leunissen J. A., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. Evolutionary conserved close linkage of the c-fes/fps proto-oncogene and genetic sequences encoding a receptor-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2197–2202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Oomen P. P., Wagenaar S. S., Debruyne F. M., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. fur gene expression as a discriminating marker for small cell and nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1545–1549. doi: 10.1172/JCI113240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Day R., Hamelin J., Gaspar A., Collard M. W., Chrétien M. Testicular expression of PC4 in the rat: molecular diversity of a novel germ cell-specific Kex2/subtilisin-like proprotein convertase. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1559–1570. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1448111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Gaspar L., Mion P., Marcinkiewicz M., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. cDNA sequence of two distinct pituitary proteins homologous to Kex2 and furin gene products: tissue-specific mRNAs encoding candidates for pro-hormone processing proteinases. DNA Cell Biol. 1990 Jul-Aug;9(6):415–424. doi: 10.1089/dna.1990.9.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Hamelin J., Gaspar A. M., Day R., Chrétien M. The cDNA sequence of the human pro-hormone and pro-protein convertase PC1. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 May;11(4):283–289. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Marcinkiewicz M., Benjannet S., Gaspar L., Beaubien G., Mattei M. G., Lazure C., Mbikay M., Chrétien M. Cloning and primary sequence of a mouse candidate prohormone convertase PC1 homologous to PC2, Furin, and Kex2: distinct chromosomal localization and messenger RNA distribution in brain and pituitary compared to PC2. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jan;5(1):111–122. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-1-111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Avruch A. S., LaMendola J., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F. Identification of a cDNA encoding a second putative prohormone convertase related to PC2 in AtT20 cells and islets of Langerhans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):340–344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeekens S. P., Steiner D. F. Identification of a human insulinoma cDNA encoding a novel mammalian protein structurally related to the yeast dibasic processing protease Kex2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2997–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sossin W. S., Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Cellular and molecular biology of neuropeptide processing and packaging. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1407–1417. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Ven W. J., Roebroek A. J., Van Duijnhoven H. L. Structure and function of eukaryotic proprotein processing enzymes of the subtilisin family of serine proteases. Crit Rev Oncog. 1993;4(2):115–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij C. L., Diergaarde P. J., Hart M., Pannekoek H. Full-length von Willebrand factor (vWF) cDNA encodes a highly repetitive protein considerably larger than the mature vWF subunit. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1839–1847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorberg J., Fontijn R., van Mourik J. A., Pannekoek H. Domains involved in multimer assembly of von willebrand factor (vWF): multimerization is independent of dimerization. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):797–803. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Nagahama M., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Sequence requirements for precursor cleavage within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8270–8274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. J., Barr P. J., Wong P. A., Kiefer M. C., Brake A. J., Kaufman R. J. Expression of a human proprotein processing enzyme: correct cleavage of the von Willebrand factor precursor at a paired basic amino acid site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9378–9382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. H., Seow K. T., Bahri S. M., Oon S. H., Chia W. Two Drosophila receptor-like tyrosine phosphatase genes are expressed in a subset of developing axons and pioneer neurons in the embryonic CNS. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying S. Y. Inhibins, activins, and follistatins: gonadal proteins modulating the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocr Rev. 1988 May;9(2):267–293. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijnhoven H. L., Creemers J. W., Kranenborg M. G., Timmer E. D., Groeneveld A., van den Ouweland A. M., Roebroek A. J., van de Ven W. J. Development and characterization of a panel of monoclonal antibodies against the novel subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme furin. Hybridoma. 1992 Feb;11(1):71–86. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1992.11.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Ven W. J., Voorberg J., Fontijn R., Pannekoek H., van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Roebroek A. J., Siezen R. J. Furin is a subtilisin-like proprotein processing enzyme in higher eukaryotes. Mol Biol Rep. 1990 Nov;14(4):265–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00429896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., van Duijnhoven H. L., Keizer G. D., Dorssers L. C., Van de Ven W. J. Structural homology between the human fur gene product and the subtilisin-like protease encoded by yeast KEX2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):664–664. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]