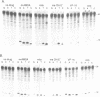
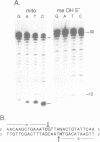
Abstract
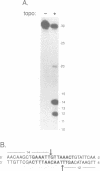
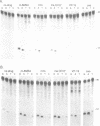
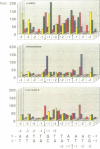
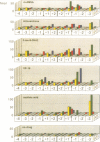
We have analyzed the DNA sequence requirements for cleavage of a 30 bp oligonucleotide that contains a strong bacteriophage T4 type II topoisomerase site. A novel method was used to generate substrates with each of the four nucleotides at 10 positions surrounding the cleavage site, and mutant substrates were also prepared for the four internal positions of the staggered cleavage site. The substrates were tested for cleavage in the presence of several inhibitors that induce enzyme-mediated cleavage: four antitumor agents of different classes (an aminoacridine, a substituted anthraquinone, an ellipticine derivative and an epipodophyllotoxin) and one antibacterial quinolone. At eight nucleotide positions flanking the cleavage site, the same preferred bases were found regardless of which inhibitor was present. These preferred bases show dyad symmetry with respect to the cleavage site, indicating that both protomers of the topoisomerase homodimer interact with DNA in an analogous manner. In addition, we found that the preferred bases on the 5' side of each cleaved phosphodiester bond are highly specific to the inhibitor used in the cleavage reaction. These results strongly suggest that the inhibitors interact directly with the DNA bases at the cleavage site, placing the inhibitor binding site precisely at the site of DNA cleavage.
Full text
PDF


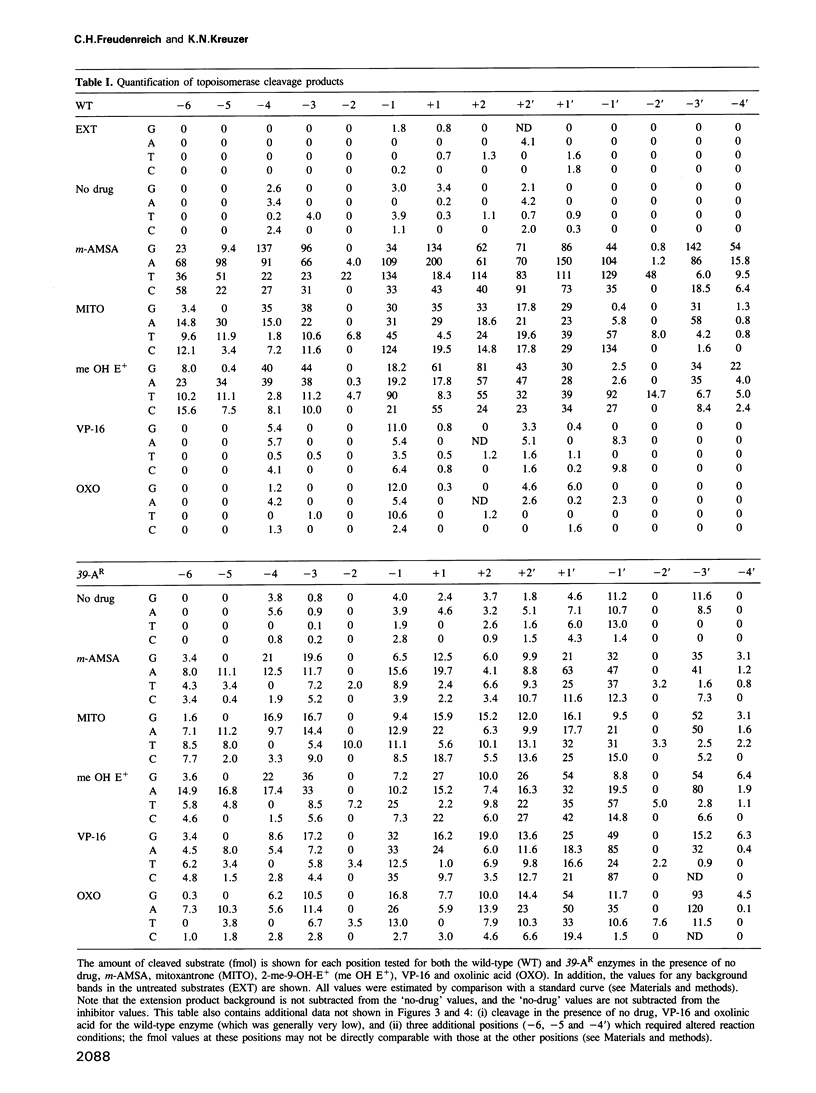
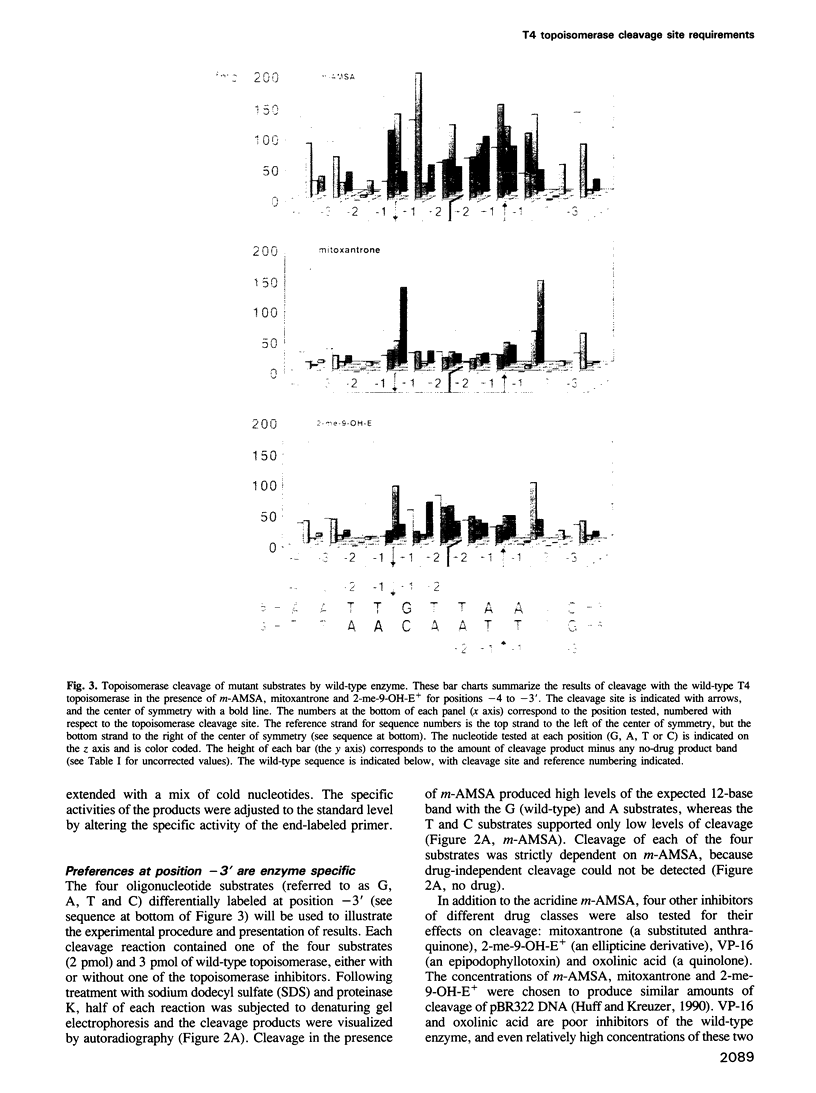







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baguley B. C., Holdaway K. M., Fray L. M. Design of DNA intercalators to overcome topoisomerase II-mediated multidrug resistance. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 Mar 7;82(5):398–402. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.5.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. A topoisomerase from Escherichia coli related to DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Local sequence requirements for DNA cleavage by mammalian topoisomerase II in the presence of doxorubicin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6611–6619. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capranico G., Zunino F., Kohn K. W., Pommier Y. Sequence-selective topoisomerase II inhibition by anthracycline derivatives in SV40 DNA: relationship with DNA binding affinity and cytotoxicity. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):562–569. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. X., Gresh N., Pullman B. A theoretical investigation on the sequence selective binding of mitoxantrone to double-stranded tetranucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3799–3812. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Joyce C. M., Beardsley G. P. Novel blunt-end addition reactions catalyzed by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 5;198(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9677–9686. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arpa P., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase-targeting antitumor drugs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 17;989(2):163–177. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. S., Mullinger A. M., Johnson R. T. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase II prevent chromatid separation in mammalian cells but do not prevent exit from mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8895–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Bacterial topoisomerases and the control of DNA supercoiling. Trends Genet. 1990 Dec;6(12):433–437. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90306-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Heck M. M. Localization of topoisomerase II in mitotic chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1716–1725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. M., Barot H. A., Cullen M. E. DNA gyrase complex with DNA: determinants for site-specific DNA breakage. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1411–1418. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossé P., René B., Le Bret M., Paoletti C., Saucier J. M. Sequence requirements for mammalian topoisomerase II mediated DNA cleavage stimulated by an ellipticine derivative. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2861–2868. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Stearns T., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II must act at mitosis to prevent nondisjunction and chromosome breakage. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):159–168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff A. C., Kreuzer K. N. Evidence for a common mechanism of action for antitumor and antibacterial agents that inhibit type II DNA topoisomerases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20496–20505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff A. C., Leatherwood J. K., Kreuzer K. N. Bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase is the target of antitumor agent 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide (m-AMSA) in T4-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1307–1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff A. C., Ward R. E., 4th, Kreuzer K. N. Mutational alteration of the breakage/resealing subunit of bacteriophage T4 DNA topoisomerase confers resistance to antitumor agent m-AMSA. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Mar;221(1):27–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00280363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkegaard K., Wang J. C. Mapping the topography of DNA wrapped around gyrase by nucleolytic and chemical probing of complexes of unique DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90435-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Alberts B. M. Site-specific recognition of bacteriophage T4 DNA by T4 type II DNA topoisomerase and Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5339–5346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., Jongeneel C. V. Escherichia coli phage T4 topoisomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:144–160. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. P., Sander M., Hsieh T. Nuclease protection by Drosophila DNA topoisomerase II. Enzyme/DNA contacts at the strong topoisomerase II cleavage sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21779–21787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Morris D. R. Sites of reaction of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase on pBR322 in vivo as revealed by oxolinic acid-induced plasmid linearization. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):63–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90324-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Hanstock C. C. High field 1H-NMR analysis of the 1:1 intercalation complex of the antitumor agent mitoxantrone and the DNA duplex [d(CpGpCpG)]. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Jun;2(6):1097–1106. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10507626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K., Andersen A. H., Christiansen K., Svejstrup J. Q., Westergaard O. Minimal DNA requirement for topoisomerase II-mediated cleavage in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13856–13863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D., Minner C., Bernstein H., Bernstein C. DNA elongation rates and growing point distributions of wild-type phage T4 and a DNA-delay amber mutant. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 5;106(4):963–981. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific cleavage of DNA by E. coli DNA gyrase. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufti S., Bernstein H. The DNA-delay mutants of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.860-871.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Mechanism of antitumor drug action: poisoning of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II on DNA by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)-methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1361–1365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y., Capranico G., Orr A., Kohn K. W. Local base sequence preferences for DNA cleavage by mammalian topoisomerase II in the presence of amsacrine or teniposide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5973–5980. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripley L. S., Dubins J. S., deBoer J. G., DeMarini D. M., Bogerd A. M., Kreuzer K. N. Hotspot sites for acridine-induced frameshift mutations in bacteriophage T4 correspond to sites of action of the T4 type II topoisomerase. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):665–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. J., Osheroff N. Stabilization of the topoisomerase II-DNA cleavage complex by antineoplastic drugs: inhibition of enzyme-mediated DNA religation by 4'-(9-acridinylamino)methanesulfon-m-anisidide. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2511–2515. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Rowe T., Glisson B., Yalowich J., Liu L. Role of topoisomerase II in mediating epipodophyllotoxin-induced DNA cleavage. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5857–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Chen G. L., Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. DNA damage by antitumor acridines mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):2021–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Kohlbrenner W. E., Weigl D., Baranowski J. Mechanism of quinolone inhibition of DNA gyrase. Appearance of unique norfloxacin binding sites in enzyme-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Mitscher L. A., Sharma P. N., O'Donnell T. J., Chu D. W., Cooper C. S., Rosen T., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: a cooperative drug--DNA binding model. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3886–3894. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A consensus sequence for cleavage by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5533–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan D. M., Latham M. D., Rowe T. C., Ross W. E. Purification and characterization of an altered topoisomerase II from a drug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5680–5687. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewey K. M., Chen G. L., Nelson E. M., Liu L. F. Intercalative antitumor drugs interfere with the breakage-reunion reaction of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9182–9187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewey K. M., Rowe T. C., Yang L., Halligan B. D., Liu L. F. Adriamycin-induced DNA damage mediated by mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):466–468. doi: 10.1126/science.6093249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yegian C. D., Mueller M., Selzer G., Russo V., Stahl F. W. Properties of the DNA-delay mutants of bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):900–919. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechiedrich E. L., Christiansen K., Andersen A. H., Westergaard O., Osheroff N. Double-stranded DNA cleavage/religation reaction of eukaryotic topoisomerase II: evidence for a nicked DNA intermediate. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6229–6236. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Hinds M., Chan D., Mayes J., Sie K. L., Parker E., Silberman L., Radcliffe A., Beran M., Blick M. Characterization of an amsacrine-resistant line of human leukemia cells. Evidence for a drug-resistant form of topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16411–16420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Michaels S., Kerrigan D., Pommier Y., Kohn K. W. Protein-associated deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks produced in mouse leukemia L1210 cells by ellipticine and 2-methyl-9-hydroxyellipticinium. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3261–3267. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90560-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]