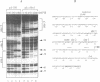
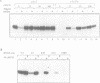
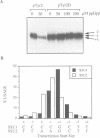
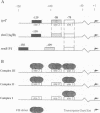
Abstract
The Escherichia coli DNA bending protein factor for inversion stimulation (FIS), is neither necessary nor responsible for the stimulation of transcription from the wild type promoter for the tyrT operon (encoding a species of tyrosine tRNA) that occurs upon resumption of exponential growth. This conclusion is unexpected given that the regulatory element required for optimal transcription of tyrT contains three binding sites for FIS protein. In addition, it is in apparent conflict with reports from other laboratories which have described FIS-dependent activation of the stable RNA promoters rrnB P1 and thrU(tufB) in vivo. However, tyrT transcription is stimulated in a FIS-dependent manner both in vivo and in vitro when promoter function is impaired by mutation of the promoter itself or by the addition of the polymerase effector guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate. These conditions, which expose a requirement for activation of stable RNA synthesis by FIS, suggest that FIS serves an adaptive role permitting high levels of stable RNA transcription on nutritional shift-up when RNA polymerase levels are depleted. In principle such a mechanism could confer a significant selective advantage thus accounting for the conservation of FIS binding sites in the regulatory regions of stable RNA promoters.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Friesen J. D. The nucleotide sequence of tufB and four nearby tRNA structural genes of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball C. A., Osuna R., Ferguson K. C., Johnson R. C. Dramatic changes in Fis levels upon nutrient upshift in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8043–8056. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8043-8056.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baracchini E., Bremer H. Determination of synthesis rate and lifetime of bacterial mRNAs. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer B. F., Kar E. G., Elford R. M., Holmes W. M. Sequence determinants for promoter strength in the leuV operon of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988;63(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. L., Landy A. Promoter mutations in the transfer RNA gene tyrT of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boles T. C., White J. H., Cozzarelli N. R. Structure of plectonemically supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):931–951. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80272-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. All three elements of the lac ps promoter mediate its transcriptional response to DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90329-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Gralla J. D. Supercoiling response of the lac ps promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):587–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch L., Nilsson L., Vijgenboom E., Verbeek H. FIS-dependent trans-activation of tRNA and rRNA operons of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Glasgow A. C., Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Fis binding to the recombinational enhancer of the Hin DNA inversion system. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):762–772. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M., Gallant J. Two compounds implicated in the function of the RC gene of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):838–841. doi: 10.1038/221838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon C., Philips J., Fu Z. Y., Squires C., Squires C. L. Comparison of the expression of the seven ribosomal RNA operons in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4175–4185. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05511.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drlica K. Control of bacterial DNA supercoiling. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(4):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel S. E., Johnson R. C. The Fis protein: it's not just for DNA inversion anymore. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3257–3265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal T., Gourse R. L. Guanosine 3'-diphosphate 5'-diphosphate is not required for growth rate-dependent control of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5533–5537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Regulation of ribosome production in Escherichia coli: synthesis and stability of ribosomal RNA and of ribosomal protein messenger RNA at different growth rates. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):335–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Egan J. B., Roth A., Messer W. The FIS protein binds and bends the origin of chromosomal DNA replication, oriC, of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4167–4172. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L. Visualization and quantitative analysis of complex formation between E. coli RNA polymerase and an rRNA promoter in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9789–9809. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourse R. L., de Boer H. A., Nomura M. DNA determinants of rRNA synthesis in E. coli: growth rate dependent regulation, feedback inhibition, upstream activation, antitermination. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. J., Raab C. In vivo synthesis of tRNA Tyr 1 and tRNA Tyr 2 : differences in "early" and "late log" E. coli MRE 600. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 24;46(6):2006–2011. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B., Reynolds R. P. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2343–2361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner P., Arber W. Mutational analysis of a prokaryotic recombinational enhancer element with two functions. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):577–585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübner P., Haffter P., Iida S., Arber W. Bent DNA is needed for recombinational enhancer activity in the site-specific recombination system Cin of bacteriophage P1. The role of FIS protein. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):493–500. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ball C. A., Pfeffer D., Simon M. I. Isolation of the gene encoding the Hin recombinational enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josaitis C. A., Gaal T., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Rudt F., Koch C., Mertens G. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu DNA is stimulated by a site within the invertase gene and a host factor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Vandekerckhove J., Kahmann R. Escherichia coli host factor for site-specific DNA inversion: cloning and characterization of the fis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4237–4241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrewa D., Granzin J., Stock D., Choe H. W., Labahn J., Saenger W. Crystal structure of the factor for inversion stimulation FIS at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 5;226(1):209–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpper H., Contreras R., Landy A., Khorana H. G. Promoter-dependent transcription of tRNAITyr genes using DNA fragments produced by restriction enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I. Supercoiling response of a bacterial tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):501–507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Genetically separable functional elements mediate the optimal expression and stringent regulation of a bacterial tRNA gene. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Requirement for an upstream element for optimal transcription of a bacterial tRNA gene. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):248–250. doi: 10.1038/305248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Travers A. A. Stringent control of bacterial transcription. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):6–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laundon C. H., Griffith J. D. Curved helix segments can uniquely orient the topology of supertwisted DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):545–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90467-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. H., Schleif R. F. In vivo DNA loops in araCBAD: size limits and helical repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):476–480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirmo S., Gourse R. L. Factor-independent activation of Escherichia coli rRNA transcription. I. Kinetic analysis of the roles of the upstream activator region and supercoiling on transcription of the rrnB P1 promoter in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):555–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClellan J. A., Boublíková P., Palecek E., Lilley D. M. Superhelical torsion in cellular DNA responds directly to environmental and genetic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8373–8377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlands J. T., Josaitis C. A., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Both fis-dependent and factor-independent upstream activation of the rrnB P1 promoter are face of the helix dependent. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):719–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierlich D. P. Regulation of bacterial growth, RNA, and protein synthesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:393–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.002141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Vanet A., Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. The role of FIS in trans activation of stable RNA operons of E. coli. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):727–734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Verbeek H., Vijgenboom E., van Drunen C., Vanet A., Bosch L. FIS-dependent trans activation of stable RNA operons of Escherichia coli under various growth conditions. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):921–929. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.921-929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninnemann O., Koch C., Kahmann R. The E.coli fis promoter is subject to stringent control and autoregulation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1075–1083. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsen K. L., Gralla J. D. Interrelated effects of DNA supercoiling, ppGpp, and low salt on melting within the Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA rrnB P1 promoter. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(16):2243–2251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. R., Woody A. Y., Haley B. E. Characterization of the guanosine-3'-diphosphate-5'-diphosphate binding site on E. coli RNA polymerase using a photoprobe, 8-azidoguanosine-3'-5'-bisphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):964–971. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaskon R. R., Wartell R. M. Sequence distributions associated with DNA curvature are found upstream of strong E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):785–796. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryals J., Little R., Bremer H. Control of rRNA and tRNA syntheses in Escherichia coli by guanosine tetraphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1261–1268. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1261-1268.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. J., Belagaje R., Brown E. L., Fritz H. J., Khorana H. G. A synthetic tyrosine suppressor tRNA gene with an altered promoter sequence. Its cloning and relative expression in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10803–10810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., SOLOMON A. K. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. I. Intracellular Na and K concentrations and net cation movement. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:355–369. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Colloms S. D., Collins J. F., Szatmari G., Sherratt D. J. xerB, an Escherichia coli gene required for plasmid ColE1 site-specific recombination, is identical to pepA, encoding aminopeptidase A, a protein with substantial similarity to bovine lens leucine aminopeptidase. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1623–1627. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Bujard H. Transcription from efficient promoters can interfere with plasmid replication and diminish expression of plasmid specified genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1399–1404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Landy A. Empirical estimation of protein-induced DNA bending angles: applications to lambda site-specific recombination complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9687–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. F., Moitoso de Vargas L., Koch C., Kahmann R., Landy A. Cellular factors couple recombination with growth phase: characterization of a new component in the lambda site-specific recombination pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. A tRNATyr promoter with an altered in vitro response to ppgpp. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 25;141(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Conserved features of coordinately regulated E. coli promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2605–2618. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Promoter sequence for stringent control of bacterial ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):973–976. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.973-976.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. To bend or...? Curr Biol. 1991 Jun;1(3):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90223-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. Modulation of RNA polymerase specificity by ppGpp. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Aug 19;147(2):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00267575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Baliko G., Bosch L. Potential binding sites of the trans-activator FIS are present upstream of all rRNA operons and of many but not all tRNA operons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Bosch L. FIS-induced bending of a region upstream of the promoter activates transcription of the E coli thrU(tufB) operon. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):713–718. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Bosch L. The mechanism of trans-activation of the Escherichia coli operon thrU(tufB) by the protein FIS. A model. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4077–4081. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagi K., Privé G. G., Dickerson R. E. Analysis of local helix geometry in three B-DNA decamers and eight dodecamers. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):201–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90620-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Wahli W., Adrian M., Stasiak A., Dubochet J. The apical localization of transcribing RNA polymerases on supercoiled DNA prevents their rotation around the template. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):667–672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05098.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Delft J. H., Mariñon B., Schmidt D. S., Bosch L. Transcription of the tRNA-tufB operon of Escherichia coli: activation, termination and antitermination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9515–9530. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]