Abstract
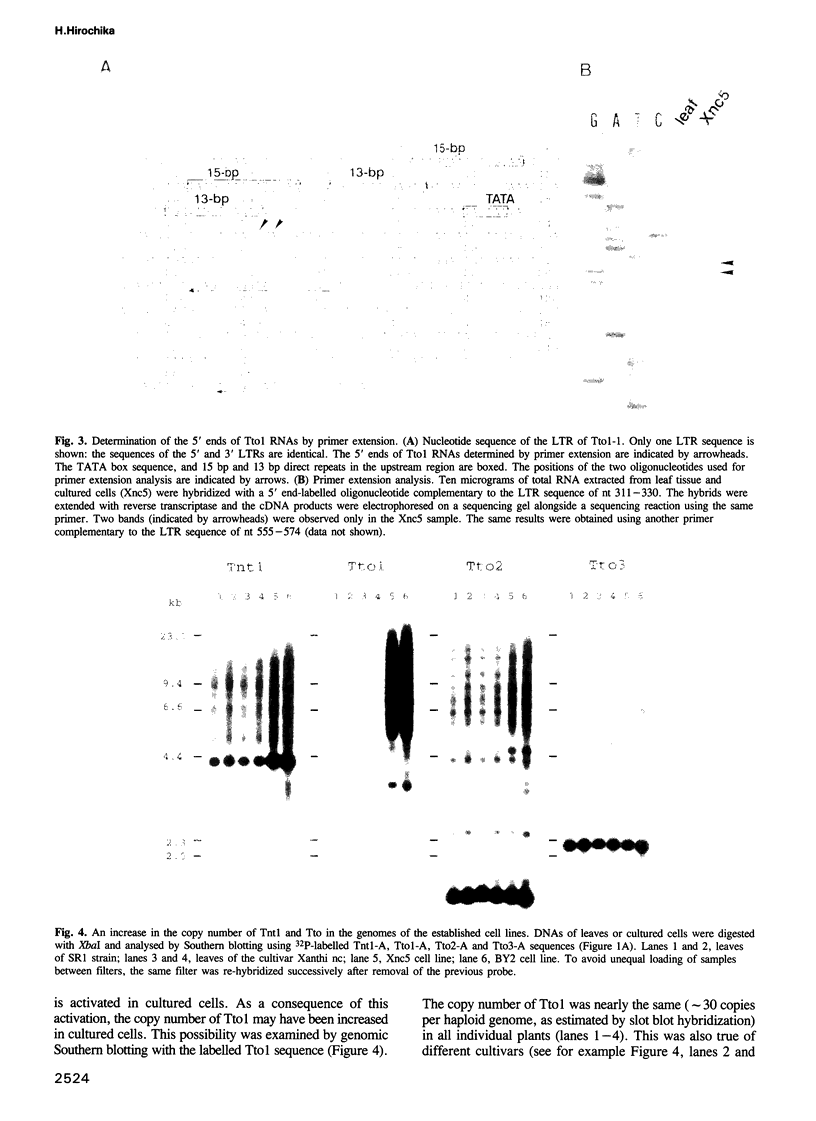
Sequences of at least three new families of retrotransposons (Tto1-Tto3) were amplified by PCR from cDNA prepared from protoplasts of an established tobacco cell line, based on the fact that certain amino acids are highly conserved in the reverse transcriptases encoded by retrotransposons. Structural analysis indicates that Tto1 is 5.5 kb long and has features typical of retrotransposons. Transcription of Tto1 starting in the long terminal repeat was active only in cultured cells. Protoplast formation enhanced the transcription. The copy number of Tto1 increased 10-fold in established cell lines; it also increased in plants regenerated from tissue cultures and in transgenic plants. These results indicate that Tto1 is activated during tissue culture. This is the first demonstration of activation of a plant retrotransposon by tissue culture. The copy number of Tto2 and a previously isolated transposon, Tnt1, also increased in established cell lines, indicating that these two retrotransposons may also be activated by tissue culture. These three retrotransposons are cryptic in normally propagated plants: no difference in the copy number was observed between individuals of the same cultivars or even between different cultivars.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradshaw V. A., McEntee K. DNA damage activates transcription and transposition of yeast Ty retrotransposons. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Sep;218(3):465–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00332411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. R., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):739–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1–30. doi: 10.1086/416128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. Drosophila retrotransposons: interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:33–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Dunbar E., Anderson R., Pearce S. R., Hartley R., Kumar A. Ty1-copia group retrotransposons are ubiquitous and heterogeneous in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 25;20(14):3639–3644. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.14.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Smith D. B. A Ty1-copia group retrotransposon sequence in a vertebrate. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):322–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00587596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell A. J., Smith D. B., Kumar A. Extreme heterogeneity of Ty1-copia group retrotransposons in plants. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jan;231(2):233–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00279796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A. Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet. 1992 Mar;8(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90198-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A., Spielmann A., Caboche M. Tnt1, a mobile retroviral-like transposable element of tobacco isolated by plant cell genetics. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):376–380. doi: 10.1038/337376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harberd N P, Flavell R B, Thompson R D. Identification of a transposon-like insertion in a Glu-1 allele of wheat. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):326–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00329661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Enhancers and trans-acting E2 transcriptional factors of papillomaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2599–2606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2599-2606.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Fukuchi A., Kikuchi F. Retrotransposon families in rice. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00587581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Hirochika R. Ty1-copia group retrotransposons as ubiquitous components of plant genomes. Jpn J Genet. 1993 Feb;68(1):35–46. doi: 10.1266/jjg.68.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Mottinger J., Freeling M. A low copy number, copia-like transposon in maize. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1093–1101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Voytas D. F., Cummings M. P., Ausubel F. M. A superfamily of Arabidopsis thaliana retrotransposons. Genetics. 1991 Apr;127(4):801–809. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliga P., Sz-Breznovits A., Márton L. Streptomycin-resistant plants from callus culture of haploid tobacco. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 4;244(131):29–30. doi: 10.1038/newbio244029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):792–801. doi: 10.1126/science.15739260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottinger J. P., Johns M. A., Freeling M. Mutations of the Adh1 gene in maize following infection with barley stripe mosaic virus. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):367–369. doi: 10.1007/BF00332775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuffer M. G. Stability of the suppressor element in two mutator systems at the a(1) locus in maize. Genetics. 1966 Mar;53(3):541–549. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima M., Itoh H., Matsuoka M., Murakami T., Ohashi Y. Analysis of stress-induced or salicylic acid-induced expression of the pathogenesis-related 1a protein gene in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell. 1990 Feb;2(2):95–106. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.2.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschke V. M., Phillips R. L., Gengenbach B. G. Discovery of transposable element activity among progeny of tissue culture--derived maize plants. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4828.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter S. S., Brorein W. J., Jr, Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Transposition of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouteau S., Huttner E., Grandbastien M. A., Caboche M. Specific expression of the tobacco Tnt1 retrotransposon in protoplasts. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1911–1918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. R., Kalitsis P., Joseph J. L., Sentry J. W. Plant retrotransposon from Lilium henryi is related to Ty3 of yeast and the gypsy group of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5015–5019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand D. J., McDonald J. F. Copia is transcriptionally responsive to environmental stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4401–4410. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel E., Dunsmuir P., Rubin G. M. Polymorphisms in the chromosomal locations of elements of the 412, copia and 297 dispersed repeated gene families in Drosophila. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Ausubel F. M. A copia-like transposable element family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):242–244. doi: 10.1038/336242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Cummings M. P., Koniczny A., Ausubel F. M., Rodermel S. R. copia-like retrotransposons are ubiquitous among plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7124–7128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weising K., Schell J., Kahl G. Foreign genes in plants: transfer, structure, expression, and applications. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:421–477. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun Y. D., Davis R. L. Copia RNA levels are elevated in dunce mutants and modulated by cAMP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8313–8326. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziarczyk P., Fourcade-Peronnet F., Simonart S., Maisonhaute C., Best-Belpomme M. Functional analysis of the long terminal repeats of Drosophila 1731 retrotransposon: promoter function and steroid regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8631–8644. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]