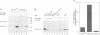Abstract
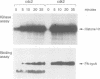
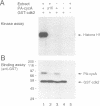
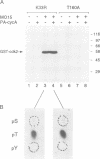
Activation of the cyclin-dependent protein kinases p34cdc2 and p33cdk2 requires binding with a cyclin partner and phosphorylation on the first threonine residue in the sequence THEVVTLWYRAPE. We present evidence that this threonine residue, number 160 in p33cdk2, can be specifically phosphorylated by a cdc2-related protein kinase from Xenopus oocytes called p40MO15. Binding to cyclin A and phosphorylation of this threonine are both required to activate fully the histone H1 kinase activity of p33cdk2. In cell extracts, a portion of p40MO15 is found in a high molecular weight complex that is considerably more active than a lower molecular weight form. Wild-type MO15 protein expressed in bacteria does not possess kinase activity, but acquires p33cdk2-T160 kinase activity after incubation with cell extract and ATP. We conclude that p40MO15 corresponds to CAK (cdc2/cdk2 activating kinase) and speculate that, like p33cdk2 and p34cdc2, p40MO15 requires activation by phosphorylation and association with a companion subunit.
Full text
PDF

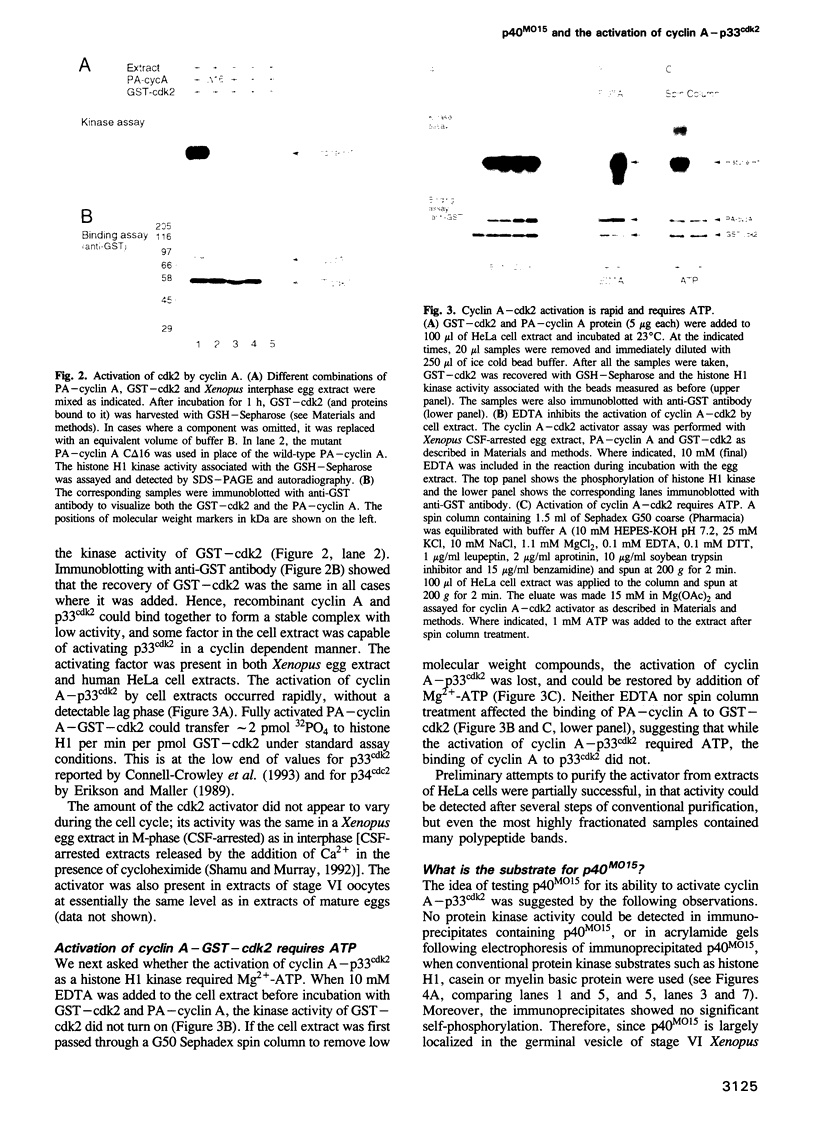
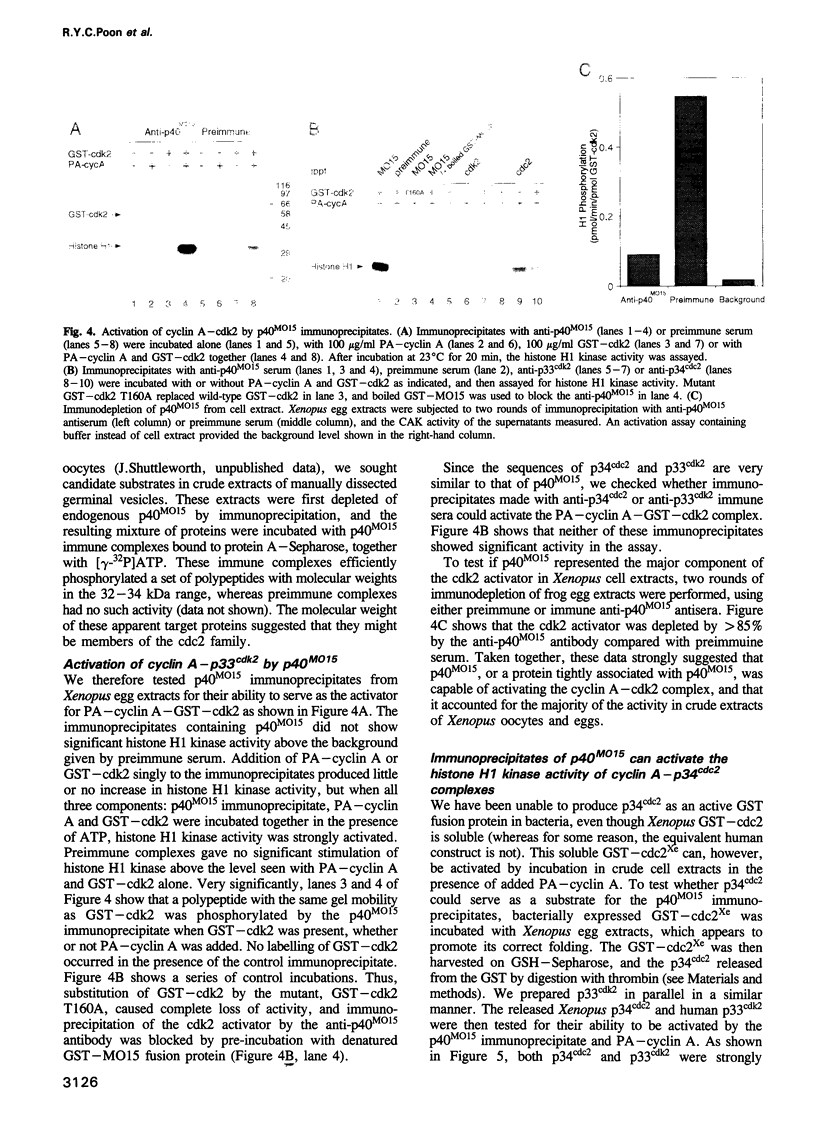
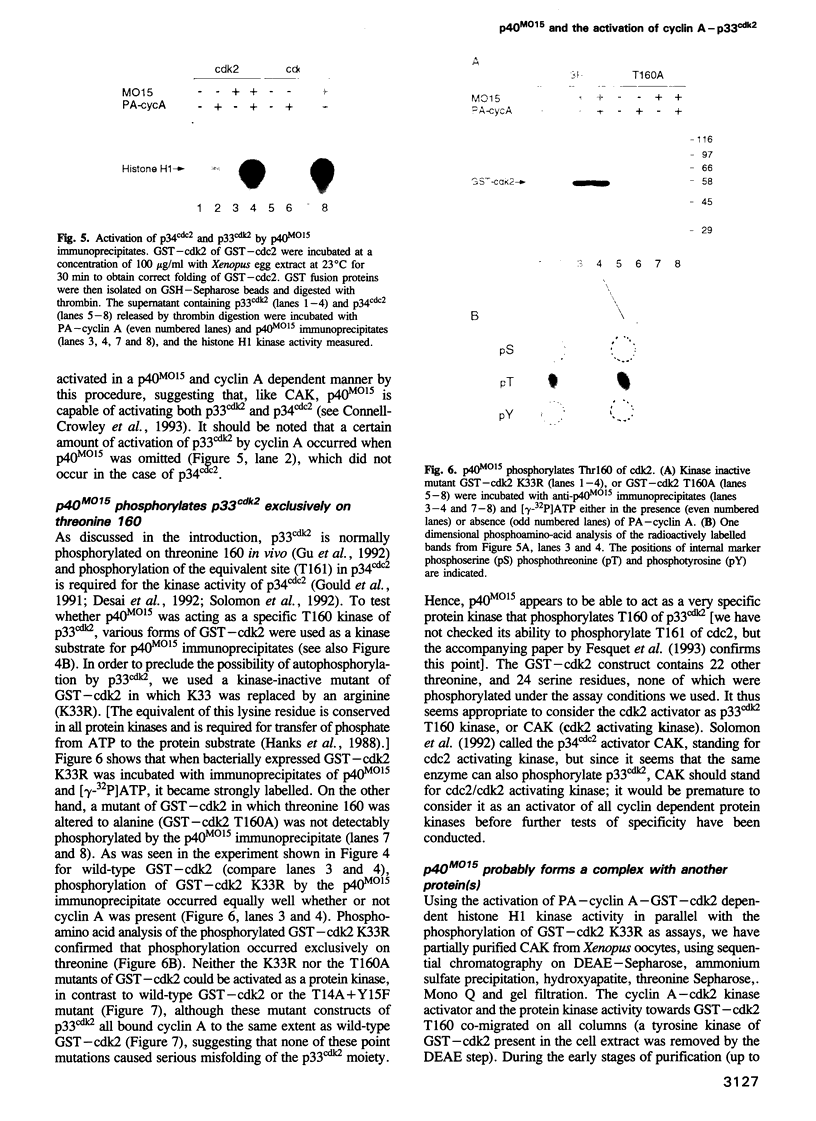
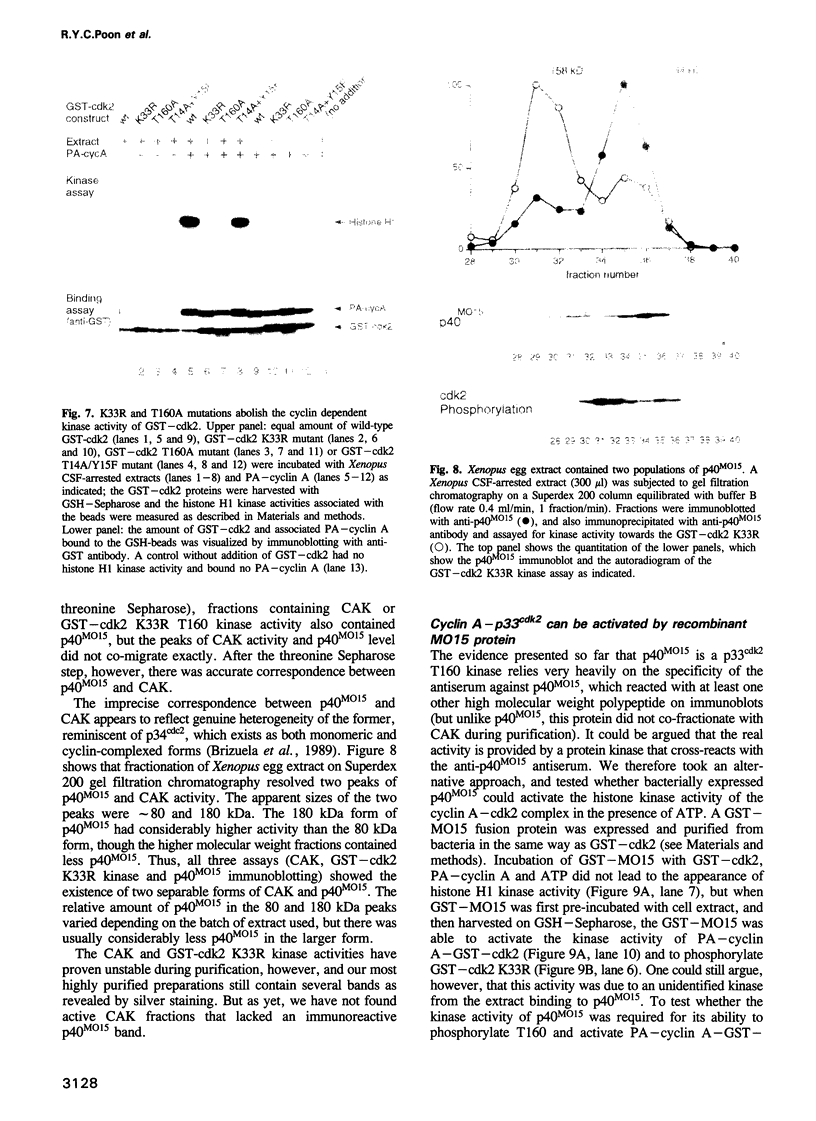




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of human CDC2 protein as a histone H1 kinase is associated with complex formation with the p62 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4362–4366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell-Crowley L., Solomon M. J., Wei N., Harper J. W. Phosphorylation independent activation of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by cyclin A in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):79–92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai D., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Activation of human cyclin-dependent kinases in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 May;3(5):571–582. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.5.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Spottswood M. R. A new human p34 protein kinase, CDK2, identified by complementation of a cdc28 mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a homolog of Xenopus Eg1. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2653–2659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07808.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Biochemical characterization of the p34cdc2 protein kinase component of purified maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus eggs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19577–19582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ershler M., Nagorskaya T. V., Visser J. W., Belyavsky A. V. Novel CDC2-related protein kinases produced in murine hematopoietic stem cells. Gene. 1993 Feb 28;124(2):305–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90411-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Derancourt J., Capony J. P., Galas S., Girard F., Lorca T., Shuttleworth J., Dorée M., Cavadore J. C. The MO15 gene encodes the catalytic subunit of a protein kinase that activates cdc2 and other cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) through phosphorylation of Thr161 and its homologues. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3111–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleig U. N., Gould K. L., Nurse P. A dominant negative allele of p34cdc2 shows altered phosphoamino acid content and sequesters p56cdc13 cyclin. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2295–2301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleig U. N., Gould K. L. Regulation of cdc2 activity in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: the role of phosphorylation. Semin Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;2(4):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Rosenblatt J., Morgan D. O. Cell cycle regulation of CDK2 activity by phosphorylation of Thr160 and Tyr15. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3995–4005. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata S. cDNA cloning of a novel cdc2+/CDC28-related protein kinase from rice. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 11;279(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai T., Yamashita M., Yoshikuni M., Tokumoto T., Kajiura H., Sakai N., Nagahama Y. Isolation and characterization of goldfish cdk2, a cognate variant of the cell cycle regulator cdc2. Dev Biol. 1992 Jul;152(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Purification of his-tagged proteins in non-denaturing conditions suggests a convenient method for protein interaction studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6337–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P. Determination of phosphoamino acid composition by acid hydrolysis of protein blotted to Immobilon. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:21–27. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01005-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Stewart E., Gannon J., Minshull J., Smith R., Hunt T. Cyclins and their partners during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:437–447. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Stewart E., Poon R., Adamczewski J. P., Gannon J., Hunt T. Identification of the domains in cyclin A required for binding to, and activation of, p34cdc2 and p32cdk2 protein kinase subunits. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Nov;3(11):1279–1294. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.11.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Cross F., Fisher A., Schumacher J., Leguellec K., Philippe M., Roberts J. M. Human cyclin E, a new cyclin that interacts with two members of the CDC2 gene family. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90044-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Cell cycle regulation of vertebrate p34cdc2 activity: identification of Thr161 as an essential in vivo phosphorylation site. New Biol. 1992 Apr;4(4):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbé J. C., Capony J. P., Caput D., Cavadore J. C., Derancourt J., Kaghad M., Lelias J. M., Picard A., Dorée M. MPF from starfish oocytes at first meiotic metaphase is a heterodimer containing one molecule of cdc2 and one molecule of cyclin B. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08456.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Ogg S., Xu M., Parker L. L., Donoghue D. J., Maller J. L., Piwnica-Worms H. cdc25+ encodes a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates p34cdc2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew J., Winkfein R. J., Paudel H. K., Wang J. H. Brain proline-directed protein kinase is a neurofilament kinase which displays high sequence homology to p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25922–25926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorca T., Labbé J. C., Devault A., Fesquet D., Capony J. P., Cavadore J. C., Le Bouffant F., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation of cdc2 on threonine 161 is required for cdc2 kinase inactivation and normal anaphase. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2381–2390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Enders G. H., Wu C. L., Su L. K., Gorka C., Nelson C., Harlow E., Tsai L. H. A family of human cdc2-related protein kinases. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2909–2917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Dunphy W. G., Russell P., Gould S. J., Newport J. W. Cloning and characterization of Xenopus cdc2, a component of MPF. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:377–384. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., McGowan C. H., Lenaers G., Jones R., Russell P. p80cdc25 mitotic inducer is the tyrosine phosphatase that activates p34cdc2 kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4301–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166–179. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris J., Le Guellec R., Couturier A., Le Guellec K., Omilli F., Camonis J., MacNeill S., Philippe M. Cloning by differential screening of a Xenopus cDNA coding for a protein highly homologous to cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):1039–1043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Piwnica-Worms H. p107wee1 is a dual-specificity kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2 on tyrosine 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamu C. E., Murray A. W. Sister chromatid separation in frog egg extracts requires DNA topoisomerase II activity during anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):921–934. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Godfrey R., Colman A. p40MO15, a cdc2-related protein kinase involved in negative regulation of meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3233–3240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Seraphin B., Faye G. KIN28, a yeast split gene coding for a putative protein kinase homologous to CDC28. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2697–2701. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., Gonzalez C., Maldonado-Codina G., Glover D. M. The A- and B-type cyclins of Drosophila are accumulated and destroyed in temporally distinct events that define separable phases of the G2-M transition. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2563–2572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Beach D. Population explosion in the cyclin family. Curr Biol. 1991 Dec;1(6):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(91)90193-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]