Abstract
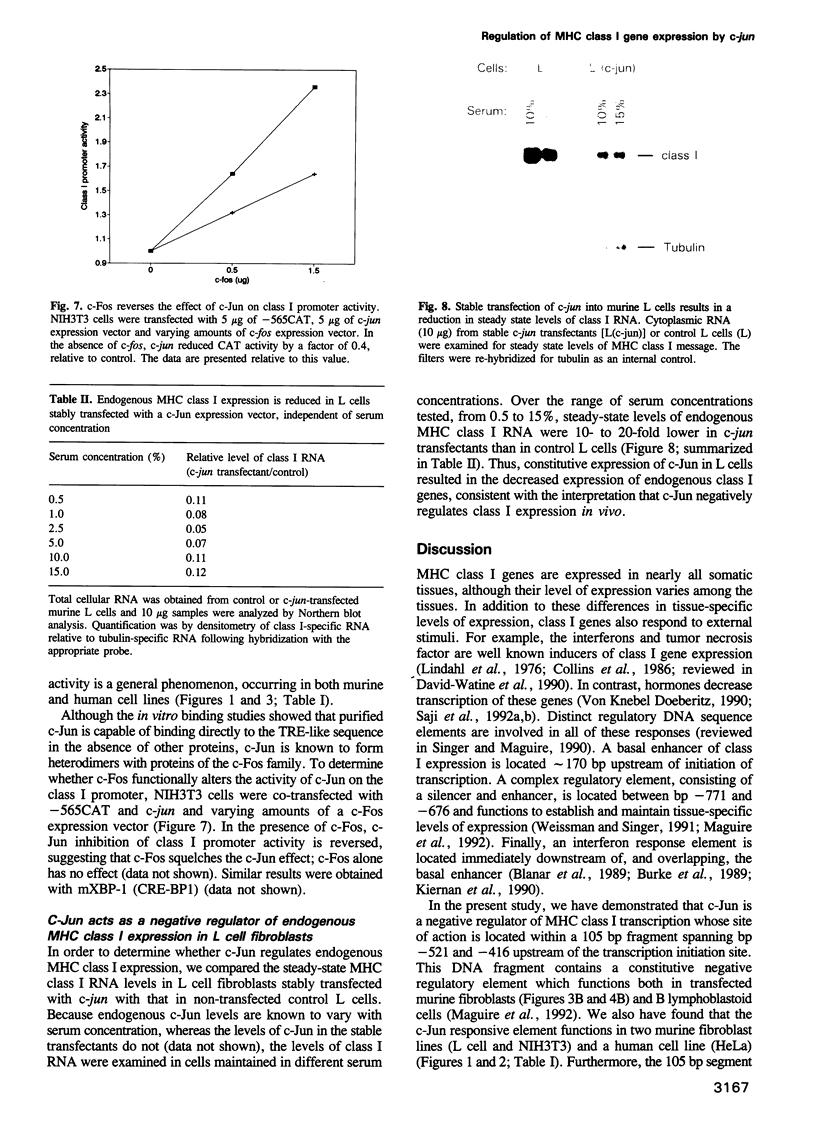
The trans-acting factor AP-1 is a heterodimeric complex composed of c-Jun and c-Fos family proteins which bind and regulate genes containing a TPA responsive enhancer element. Although AP-1 binding sites have been identified within the regulatory region of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I genes in vitro, the role of AP-1 in regulating MHC class I transcription in vivo has not been investigated previously. The present study demonstrates that expression of c-Jun results in decreased MHC class I promoter activity as determined in cotransfection assays of an MHC class I reporter construct with a c-Jun expression construct. The c-Jun responsive element is located between bp -440 and -431 upstream of initiation of transcription as determined both functionally and by direct binding of purified c-Jun. Furthermore, over-expression of c-Jun reduced the steady state levels of endogenous MHC class I RNA in murine L cells by approximately 10-fold. These data indicate that c-Jun/AP-1 acts as a negative trans-acting factor that down-regulates MHC class I gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Hattori K., Smeal T., Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90143-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Monteclaro F. S., Mitsunobu F., Ball A. R., Jr, Chang C. H., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K. Efficient transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by c-Jun requires structural modification in coding and noncoding sequences. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1677–1687. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenowitz M., Senear D. F., Shea M. A., Ackers G. K. Quantitative DNase footprint titration: a method for studying protein-DNA interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:132–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke P. A., Hirschfeld S., Shirayoshi Y., Kasik J. W., Hamada K., Appella E., Ozato K. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of nuclear proteins that bind the regulatory element of the major histocompatibility complex class I gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1309–1321. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Khoury G., Jay G. Three classes of mouse H-2 messenger RNA distinguished by analysis of cDNA clones. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):73–76. doi: 10.1038/295073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Watine B., Israël A., Kourilsky P. The regulation and expression of MHC class I genes. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90114-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., Spies T. New genes in the MHC that encode proteins for antigen processing. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;2(3):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90077-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Lifshitz R., Pescovitz M. D., Rudikoff S., Singer D. S. Tissue-specific expression and structure of a divergent member of a class I MHC gene family. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):593–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki N., Maekawa T., Sudo T., Ishii S., Seino Y., Imura H. c-Jun represses the human insulin promoter activity that depends on multiple cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1045–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamph W. W., Wamsley P., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. Induction of proto-oncogene JUN/AP-1 by serum and TPA. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):629–631. doi: 10.1038/334629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Chambard J. C., Karin M., Olson E. N. Fos and Jun repress transcriptional activation by myogenin and MyoD: the amino terminus of Jun can mediate repression. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):676–689. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Gresser I., Leary P., Tovey M. Interferon treatment of mice: enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Lowag C., Neuberg M., Müller R. trans-repression of the mouse c-fos promoter: a novel mechanism of Fos-mediated trans-regulation. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):999–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90756-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor P. F., Abate C., Curran T. Direct cloning of leucine zipper proteins: Jun binds cooperatively to the CRE with CRE-BP1. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):451–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
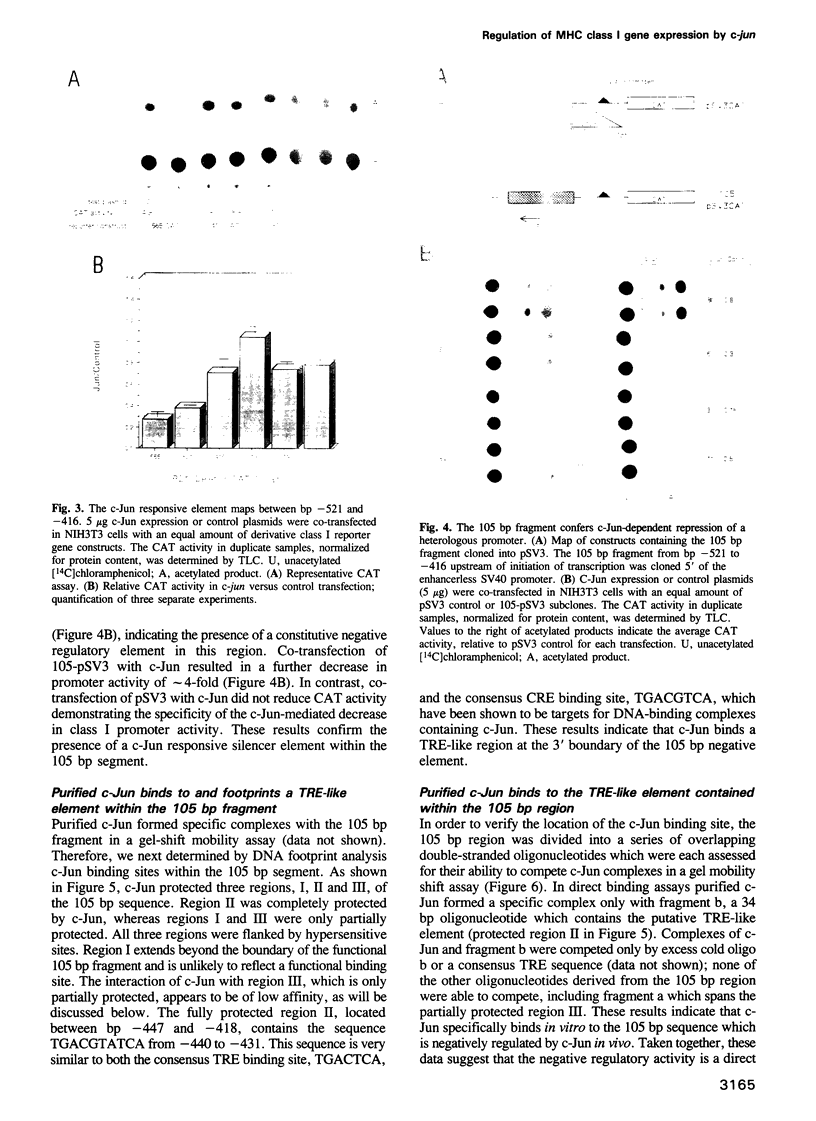
- Maguire J. E., Frels W. I., Richardson J. C., Weissman J. D., Singer D. S. In vivo function of regulatory DNA sequence elements of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3078–3086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley D. J., Pound J. D. Modulation of MHC antigen expression by viruses and oncogenes. Immunol Today. 1991 Dec;12(12):429–431. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90013-J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
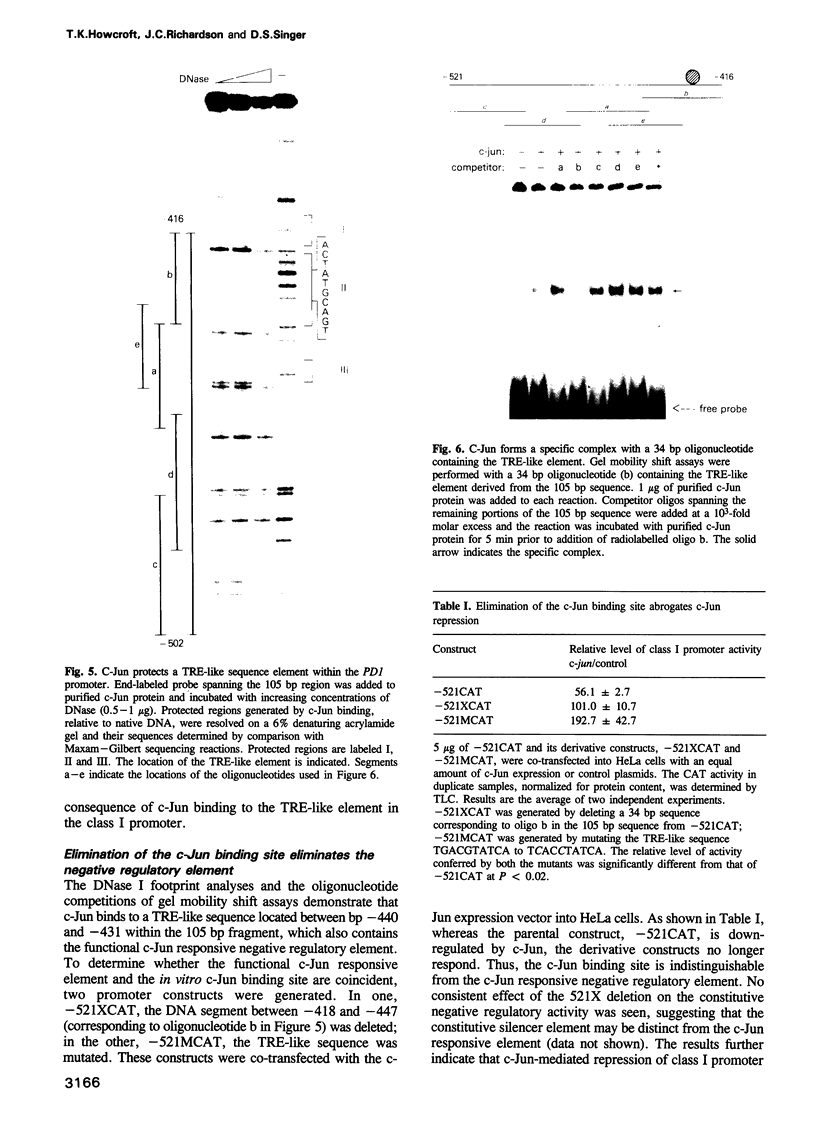
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Nathans D. Induction of protooncogene c-jun by serum growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8464–8467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Hirai S. I., Yaniv M., Bravo R. Transcriptional activation of c-jun during the G0/G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):535–537. doi: 10.1038/334535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saji M., Moriarty J., Ban T., Kohn L. D., Singer D. S. Hormonal regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I genes in rat thyroid FRTL-5 cells: thyroid-stimulating hormone induces a cAMP-mediated decrease in class I expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1944–1948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saji M., Moriarty J., Ban T., Singer D. S., Kohn L. D. Major histocompatibility complex class I gene expression in rat thyroid cells is regulated by hormones, methimazole, and iodide as well as interferon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 Sep;75(3):871–878. doi: 10.1210/jcem.75.3.1381373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Sisson J. C., Verma I. M. Transcriptional autoregulation of the proto-oncogene fos. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):314–319. doi: 10.1038/334314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W., Festenstein H. Resistance to cell-mediated cytotoxicity is correlated with reduction of H-2K gene products in AKR leukemia. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(3):257–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00343314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Büscher M., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H., Hattori K., Chiu R., Karin M., Herrlich P. The Fos and Jun/AP-1 proteins are involved in the downregulation of Fos transcription. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Bolado J., Pike J. W., Evans R. M. Jun-Fos and receptors for vitamins A and D recognize a common response element in the human osteocalcin gene. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90531-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte J., Minna J. D., Birrer M. J. Deregulated expression of human c-jun transforms primary rat embryo cells in cooperation with an activated c-Ha-ras gene and transforms rat-1a cells as a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2257–2261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D. S., Maguire J. E. Regulation of the expression of class I MHC genes. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(3):235–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sistonen L., Hölttä E., Mäkelä T. P., Keski-Oja J., Alitalo K. The cellular response to induction of the p21 c-Ha-ras oncoprotein includes stimulation of jun gene expression. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):815–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03442.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Post-transcriptional control of class I MHC mRNA expression in adenovirus 12-transformed cells. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1486–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.3823900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasavada R., Eager K. B., Barbanti-Brodano G., Caputo A., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus type 12 early region 1A proteins repress class I HLA expression in transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Bos T. J. The oncogene jun and nuclear signalling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 May;14(5):172–175. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Knebel Doeberitz M., Koch S., Drzonek H., Zur Hausen H. Glucocorticoid hormones reduce the expression of major histocompatibility class I antigens on human epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):35–40. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Bulbuc N., Hämmerling G. J., Katzav S., Segal S., Feldman M. Abrogation of metastatic properties of tumour cells by de novo expression of H-2K antigens following H-2 gene transfection. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):301–305. doi: 10.1038/315301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Imler J. L., Wasylyk B. Transforming but not immortalizing oncogenes activate the transcription factor PEA1. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2475–2483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. D., Singer D. S. A complex regulatory DNA element associated with a major histocompatibility complex class I gene consists of both a silencer and an enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4217–4227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R., Foulkes N., Mulder M., Kruijer W., Sassone-Corsi P. Positive regulation of jun/AP-1 by E1A. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):192–201. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]