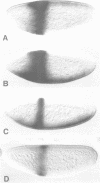
Abstract
The dorsal (dl) protein gradient determines patterns of gene expression along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. dl protein is at peak levels in ventral nuclei of the embryo where it activates some genes (twist and snail) and represses others [zerknullt (zen), decapentaplegic and tolloid]. It is a member of the rel family of transcription factors and interacts with specific DNA sequences in the regulatory regions of its target genes. These sequences (dl binding sites), when taken from the context of either an activated or repressed promoter, mediate transcriptional activation of a heterologous promoter, but not repression. We found that T-rich sequences close to the dl binding sites in the silencer region of the zen promoter are conserved between three Drosophila species. Using this sequence information we defined a minimal element that can mediate repression of a heterologous promoter. This element interacts with at least two factors present in embryonic extracts, one of which is dl protein. The other factor binds to the T-rich site. Point mutations in either site abolish ventral repression in vivo. In addition, mutations in the T-rich site cause ectopic expression in ventral regions indicating that the minimal silencer was converted into an enhancer.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., West R. W., Jr, Johnson S. L., Gans H., Kruger B., Ma J. TSF3, a global regulatory protein that silences transcription of yeast GAL genes, also mediates repression by alpha 2 repressor and is identical to SIN4. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):831–840. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Kraut R., Levine M. Spatial regulation of zerknüllt: a dorsal-ventral patterning gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1518–1533. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faisst S., Meyer S. Compilation of vertebrate-encoded transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 11;20(1):3–26. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann J. F., Laroche T., Brand A. H., Gasser S. M. RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):725–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90788-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Kraut R., Levine M., Rushlow C. A. The dorsal morphogen is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein that interacts with a long-range repression element in Drosophila. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90651-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Park R. E., Kosman D., Bier E., Levine M. The dorsal gradient morphogen regulates stripes of rhomboid expression in the presumptive neuroectoderm of the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1728–1739. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. E. Negative regulation of eukaryotic transcription. J Cell Sci. 1991 Sep;100(Pt 1):1–7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Cai H., Zhou Q., Levine M. Conversion of a dorsal-dependent silencer into an enhancer: evidence for dorsal corepressors. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3201–3209. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Kosman D., Ip Y. T., Levine M. The dorsal morphogen gradient regulates the mesoderm determinant twist in early Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1881–1891. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Rushlow C. A., Zhou Q., Small S., Levine M. Individual dorsal morphogen binding sites mediate activation and repression in the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3147–3154. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y. W., Stillman D. J. Involvement of the SIN4 global transcriptional regulator in the chromatin structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4503–4514. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Passmore S., Johnson A. D. Yeast repressor alpha 2 binds to its operator cooperatively with yeast protein Mcm1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5228–5230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger W., Herskowitz I. A negative regulator of HO transcription, SIN1 (SPT2), is a nonspecific DNA-binding protein related to HMG1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4135–4146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D. J., Huang J. D., Courey A. J. Functional analysis of the Drosophila twist promoter reveals a dorsal-binding ventral activator region. Genes Dev. 1991 Oct;5(10):1892–1901. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.10.1892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan D., Courey A. J. The same dorsal binding site mediates both activation and repression in a context-dependent manner. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1837–1842. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray R. P., Arora K., Nüsslein-Volhard C., Gelbart W. M. The control of cell fate along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):35–54. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Doyle H., Hoey T., Levine M. Molecular characterization of the zerknüllt region of the Antennapedia gene complex in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1268–1279. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Frasch M., Doyle H., Levine M. Maternal regulation of zerknüllt: a homoeobox gene controlling differentiation of dorsal tissues in Drosophila. Nature. 1987 Dec 10;330(6148):583–586. doi: 10.1038/330583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Warrior R. The rel family of proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Feb;14(2):89–95. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimell M. J., Ferguson E. L., Childs S. R., O'Connor M. B. The Drosophila dorsal-ventral patterning gene tolloid is related to human bone morphogenetic protein 1. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90522-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S., Kraut R., Hoey T., Warrior R., Levine M. Transcriptional regulation of a pair-rule stripe in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):827–839. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The origin of pattern and polarity in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90466-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic transcripts are localized along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F., Stoetzel C., Thisse B. Sequence-specific transactivation of the Drosophila twist gene by the dorsal gene product. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1191–1201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90014-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Stillman D. J. In vitro regulation of a SIN3-dependent DNA-binding activity by stimulatory and inhibitory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9761–9765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C. C., Bienz M. Segmental determination in Drosophila conferred by hunchback (hb), a repressor of the homeotic gene Ultrabithorax (Ubx). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7511–7515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]