Abstract
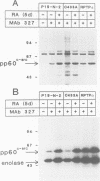
Here we report that protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPases), like their enzymatic counterpart the protein tyrosine kinases, can play an important role in cell differentiation. Expression of the transmembrane PTPase receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (RPTP alpha) is transiently enhanced during neuronal differentiation of embryonal carcinoma (EC) and neuroblastoma cells. Retinoic acid induces wild type P19 cells to differentiate into endoderm- and mesoderm-like cells. By contrast, retinoic acid treatment leads to neuronal differentiation of P19 cells, ectopically expressing functional RPTP alpha, as illustrated by their ability to generate action potentials. Endogenous pp60c-src kinase activity is enhanced in the RPTP alpha-transfected cells, which may be due to direct dephosphorylation of the regulatory Tyr residue at position 527 in pp60c-src by RPTP alpha. Our results demonstrate that RPTP alpha is involved in neuronal differentiation and imply a role for pp60c-src in the differentiation process.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander D. R. The role of phosphatases in signal transduction. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1049–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Sato G. Methods for growth of cultured cells in serum-free medium. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelfman C., Meyerson G., Cartwright C. A., Mellström K., Hammerling U., Påhlman S. Early activation of endogenous pp60src kinase activity during neuronal differentiation of cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):361–370. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Veillette A., Schwartz A. M., Deseau V., Rosen N. Analysis of pp60c-src in human colon carcinoma and normal human colon mucosal cells. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):149–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. Keeping track of neurotrophin receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):915–918. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90540-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter C. A., Wagner E. F. Expression of c-src and c-abl in embryonal carcinoma cells and adult mouse tissues. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Nov;179(1):214–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter C. A., Wagner E. F. The effects of v-src expression on the differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1988 Mar;2(3):207–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown-Shimer S., Johnson K. A., Lawrence J. B., Johnson C., Bruskin A., Green N. R., Hill D. E. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of the human gene encoding protein phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 1B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5148–5152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K., Kumar S., Diltz C. D., Harrylock M., Cool D. E., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Human placenta protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: amino acid sequence and relationship to a family of receptor-like proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernoff J., Schievella A. R., Jost C. A., Erikson R. L., Neel B. G. Cloning of a cDNA for a major human protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Tonks N. K., Charbonneau H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. cDNA isolated from a human T-cell library encodes a member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5257–5261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. E., Maness P. F. Neurite extension and protein tyrosine phosphorylation elicited by inducible expression of the v-src oncogene in a PC12 cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M., Stallcup W. B., Pittman Q. J. Induction of neural differentiation by serum deprivation in cultures of the embryonal carcinoma cell line 1003. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Zander N. F., Morse B., Hurwitz D., Schlessinger J., Fischer E. H. Characterization of a human recombinant receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12211–12215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Broyles S. S., Dixon J. E. A Tyr/Ser protein phosphatase encoded by vaccinia virus. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):359–362. doi: 10.1038/350359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Evidence for protein-tyrosine-phosphatase catalysis proceeding via a cysteine-phosphate intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17026–17030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltmeier H., Rohrer H. Distinct and different effects of the oncogenes v-myc and v-src on avian sympathetic neurons: retroviral transfer of v-myc stimulates neuronal proliferation whereas v-src transfer enhances neuronal differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2087–2098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. K., Sefton B. M., Firtel R. A. Analysis of a spatially regulated phosphotyrosine phosphatase identifies tyrosine phosphorylation as a key regulatory pathway in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90597-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Villeneuve E. M., McBurney M. W., Rogers K. A., Kalnins V. I. Retinoic acid induces embryonal carcinoma cells to differentiate into neurons and glial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):253–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler R., Brûlet P., Schnebelen M. T., Gaillard J., Jacob F. Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies against intermediate filament proteins during embryonic development. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Aug;64:45–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Abraham J. A., Haaparanta T., Palisi T. M., Kirschner M. W. The presence of fibroblast growth factor in the frog egg: its role as a natural mesoderm inducer. Science. 1988 Nov 18;242(4881):1053–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.3194757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Palfrey C., Spector I., Barak Y., Littauer U. Z. Maturation of neuroblastoma cells in the presence of dimethylsulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):462–466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Parada L. F., Coulier F., Barbacid M. trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer N. E., D'Arcangelo G., Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., Brugge J. S., Halegoua S. Signal transduction by nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor in PC12 cells requires a sequence of src and ras actions. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):809–819. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger N. X., Streuli M., Saito H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3241–3252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch S. A., Brugge J. S., Levine J. M. Induction of altered c-src product during neural differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Science. 1986 Nov 14;234(4778):873–876. doi: 10.1126/science.3095923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Oskam R., Mitra G., Copeland T., Barbacid M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of the human trk proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):24–33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Teratocarcinomas and mammalian embryogenesis. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):768–776. doi: 10.1126/science.6250214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. J., Cahir E. D., Thomas M. L. Identification of an additional member of the protein-tyrosine-phosphatase family: evidence for alternative splicing in the tyrosine phosphatase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4444–4448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Jones-Villeneuve E. M., Edwards M. K., Anderson P. J. Control of muscle and neuronal differentiation in a cultured embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):165–167. doi: 10.1038/299165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBurney M. W., Rogers B. J. Isolation of male embryonal carcinoma cells and their chromosome replication patterns. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):503–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90338-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlemas D. S., Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. trkB, a neural receptor protein-tyrosine kinase: evidence for a full-length and two truncated receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):143–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mummery C. L., Feijen A., Moolenaar W. H., van den Brink C. E., de Laat S. W. Establishment of a differentiated mesodermal line from P19 EC cells expressing functional PDGF and EGF receptors. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jul;165(1):229–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90547-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Altman A. Rapid activation of the T-cell tyrosine protein kinase pp56lck by the CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6302–6306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Streuli M. Molecular characterization of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Jan;2(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., D'Eustachio P., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of a widely expressed receptor tyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. W., Brugge J. S., Nelson W. J. pp60src tyrosine kinase modulates P19 embryonal carcinoma cell fate by inhibiting neuronal but not epithelial differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(4):1019–1033. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroo M., Goff L., Biffen M., Shivnan E., Alexander D. CD45 tyrosine phosphatase-activated p59fyn couples the T cell antigen receptor to pathways of diacylglycerol production, protein kinase C activation and calcium influx. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4887–4897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Darlington B. G., Heath J. K., Godsave S. F. Mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos by heparin-binding growth factors. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):197–200. doi: 10.1038/326197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solter D., Knowles B. B. Monoclonal antibody defining a stage-specific mouse embryonic antigen (SSEA-1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Thai T., Tang M., Saito H. Distinct functional roles of the two intracellular phosphatase like domains of the receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases LCA and LAR. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2399–2407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Krueger N. X., Tsai A. Y., Saito H. A family of receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatases in humans and Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8698–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Duband J. L., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in early chicken embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6737–6741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., Hayes M., D'Arcangelo G., Armstrong R. C., Meyer B. E., Zilberstein A., Brugge J. S., Halegoua S. Induction of neurite outgrowth by v-src mimics critical aspects of nerve growth factor-induced differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4739–4750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian S. S., Tsoulfas P., Zinn K. Three receptor-linked protein-tyrosine phosphatases are selectively expressed on central nervous system axons in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):675–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Fryling C., Johnson P. A., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factors (TGFs): properties and possible mechanisms of action. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(3):287–301. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Cicirelli M. F., Diltz C. D., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Effect of microinjection of a low-Mr human placenta protein tyrosine phosphatase on induction of meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Characterization of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6731–6737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Fischer E. H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6722–6730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Pallen C. J. The receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatase HPTP alpha has two active catalytic domains with distinct substrate specificities. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3231–3237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. H., Seow K. T., Bahri S. M., Oon S. H., Chia W. Two Drosophila receptor-like tyrosine phosphatase genes are expressed in a subset of developing axons and pioneer neurons in the embryonic CNS. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Wang Y., Pallen C. J. Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):336–339. doi: 10.1038/359336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog J., Pals C. E., Jonk L. J., Kruijer W. Differential expression of a novel murine non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase during differentiation of P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1241–1249. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog J., de Laat S. W., Schlessinger J., Kruijer W. Neuronal differentiation in response to epidermal growth factor of transfected murine P19 embryonal carcinoma cells expressing human epidermal growth factor receptors. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Mar;2(3):155–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]