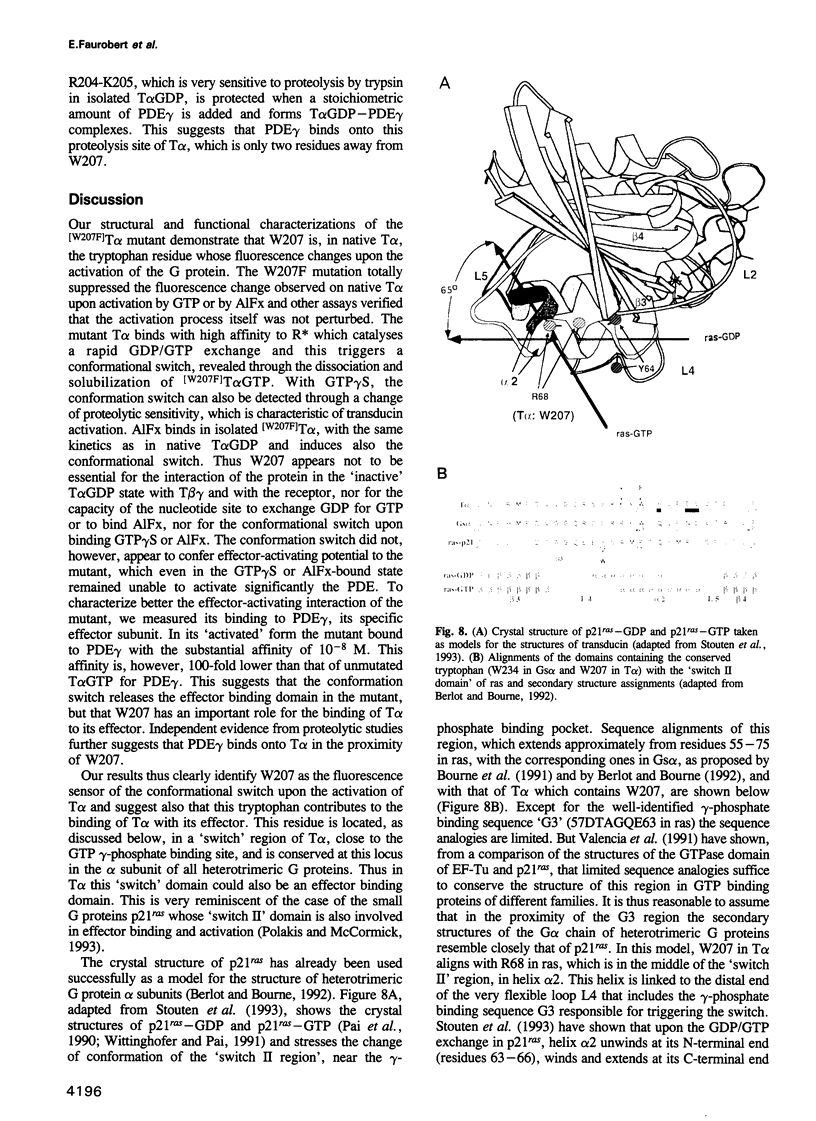
Abstract
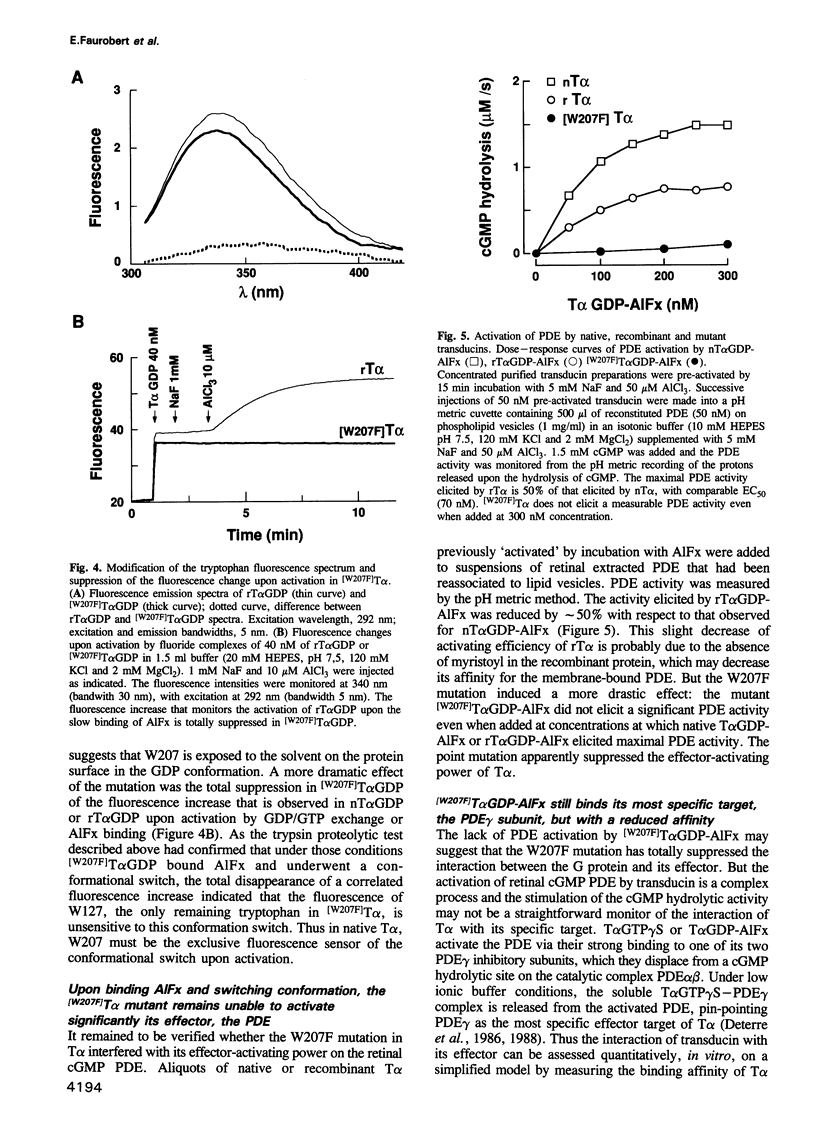
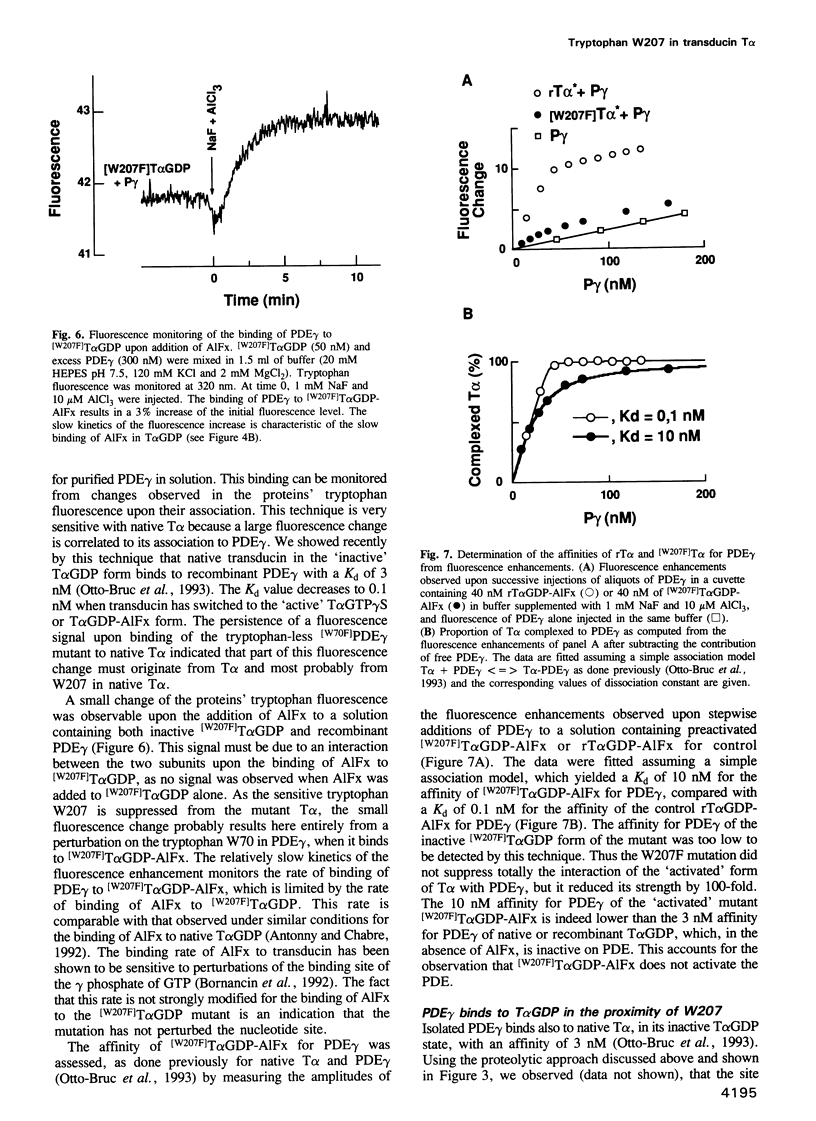
We have produced a recombinant transducin alpha subunit (rT alpha) in sf9 cells, using a baculovirus system. Deletion of the myristoylation site near the N-terminal increased the solubility and allowed the purification of rT alpha. When reconstituted with excess T beta gamma on retinal membrane, rT alpha displayed functional characteristics of wild-type T alpha vis à vis its coupled receptor, rhodopsin and its effector, cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE). We further mutated a tryptophan, W207, which is conserved in all G proteins and is suspected to elicit the fluorescence change correlated to their activation upon GDP/GTP exchange or aluminofluoride (AlFx) binding. [W207F]T alpha mutant displayed high affinity receptor binding and underwent a conformational switch upon receptor-catalysed GTP gamma S binding or upon AlFx binding, but this did not elicit any fluorescence change. Thus W207 is the only fluorescence sensor of the switch. Upon the switch the mutant remained unable to activate the PDE. To characterize better its effector-activating interaction we measured the affinity of [W207F]T alpha GDP-AlFx for PDE gamma, the effector subunit that binds most tightly to T alpha. [W207F]T alpha still bound in an activation-dependent way to PDE gamma, but with a 100-fold lower affinity than rT alpha. This suggests that W207 contributes to the G protein effector binding.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonny B., Chabre M. Characterization of the aluminum and beryllium fluoride species which activate transducin. Analysis of the binding and dissociation kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6710–6718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonny B., Chardin P., Roux M., Chabre M. GTP hydrolysis mechanisms in ras p21 and in the ras-GAP complex studied by fluorescence measurements on tryptophan mutants. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 27;30(34):8287–8295. doi: 10.1021/bi00098a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonny B., Sukumar M., Bigay J., Chabre M., Higashijima T. The mechanism of aluminum-independent G-protein activation by fluoride and magnesium. 31P NMR spectroscopy and fluorescence kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2393–2402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Bourne H. R. Identification of effector-activating residues of Gs alpha. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):911–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90034-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoride complexes of aluminium or beryllium act on G-proteins as reversibly bound analogues of the gamma phosphate of GTP. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2907–2913. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornancin F., Franco M., Bigay J., Chabre M. Functional modifications of transducin induced by cholera or pertussis-toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):33–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M., Deterre P. Molecular mechanism of visual transduction. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 1;179(2):255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Structural elements of G alpha subunits that interact with G beta gamma, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deterre P., Bigay J., Forquet F., Robert M., Chabre M. cGMP phosphodiesterase of retinal rods is regulated by two inhibitory subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deterre P., Bigay J., Robert M., Pfister C., Kühn H., Chabre M. Activation of retinal rod cyclic GMP-phosphodiesterase by transducin: characterization of the complex formed by phosphodiesterase inhibitor and transducin alpha-subunit. Proteins. 1986 Oct;1(2):188–193. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Nash C. R. Characterization of transducin from bovine retinal rod outer segments. II. Evidence for distinct binding sites and conformational changes revealed by limited proteolysis with trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10503–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A., Koenig B., Hofmann K. P. Site of G protein binding to rhodopsin mapped with synthetic peptides from the alpha subunit. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):832–835. doi: 10.1126/science.3136547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Ferguson K. M., Sternweis P. C., Ross E. M., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The effect of activating ligands on the intrinsic fluorescence of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashijima T., Graziano M. P., Suga H., Kainosho M., Gilman A. G. 19F and 31P NMR spectroscopy of G protein alpha subunits. Mechanism of activation by Al3+ and F-. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Simon M. I., Teplow D. B., Robishaw J. D., Gilman A. G. Homologies between signal transducing G proteins and ras gene products. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):860–862. doi: 10.1126/science.6436980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Simonds W. F., Merendino J. J., Jr, Brann M. R., Spiegel A. M. Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein alpha subunit is essential for its membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):568–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journot L., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Audigier Y. Deletion within the amino-terminal region of Gs alpha impairs its ability to interact with beta gamma subunits and to activate adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9009–9015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Ayres M. D., Possee R. D. Linearization of baculovirus DNA enhances the recovery of recombinant virus expression vectors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5667–5672. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light- and GTP-regulated interaction of GTPase and other proteins with bovine photoreceptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):587–589. doi: 10.1038/283587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Pang I. H., Duronio R. J., Gordon J. I., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Lipid modifications of G protein subunits. Myristoylation of Go alpha increases its affinity for beta gamma. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4654–4659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters S. B., Stroud R. M., Bourne H. R. Family of G protein alpha chains: amphipathic analysis and predicted structure of functional domains. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medynski D. C., Sullivan K., Smith D., Van Dop C., Chang F. H., Fung B. K., Seeburg P. H., Bourne H. R. Amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of transducin deduced from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4311–4315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Kim S. H. Molecular switch for signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):939–945. doi: 10.1126/science.2406906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Heukeroth R. O., Gordon J. I., Gilman A. G. G-protein alpha-subunit expression, myristoylation, and membrane association in COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):728–732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. J., Cerione R. A. The intrinsic fluorescence of the alpha subunit of transducin. Measurement of receptor-dependent guanine nucleotide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15498–15505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polakis P., McCormick F. Structural requirements for the interaction of p21ras with GAP, exchange factors, and its biological effector target. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9157–9160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rarick H. M., Artemyev N. O., Hamm H. E. A site on rod G protein alpha subunit that mediates effector activation. Science. 1992 May 15;256(5059):1031–1033. doi: 10.1126/science.1317058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakmar T. P., Khorana H. G. Total synthesis and expression of a gene for the alpha-subunit of bovine rod outer segment guanine nucleotide-binding protein (transducin). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6361–6372. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouten P. F., Sander C., Wittinghofer A., Valencia A. How does the switch II region of G-domains work? FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 29;320(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81644-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Kjeldgaard M., Pai E. F., Sander C. GTPase domains of ras p21 oncogene protein and elongation factor Tu: analysis of three-dimensional structures, sequence families, and functional sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5443–5447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Pai E. F. The structure of Ras protein: a model for a universal molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90156-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]