Abstract
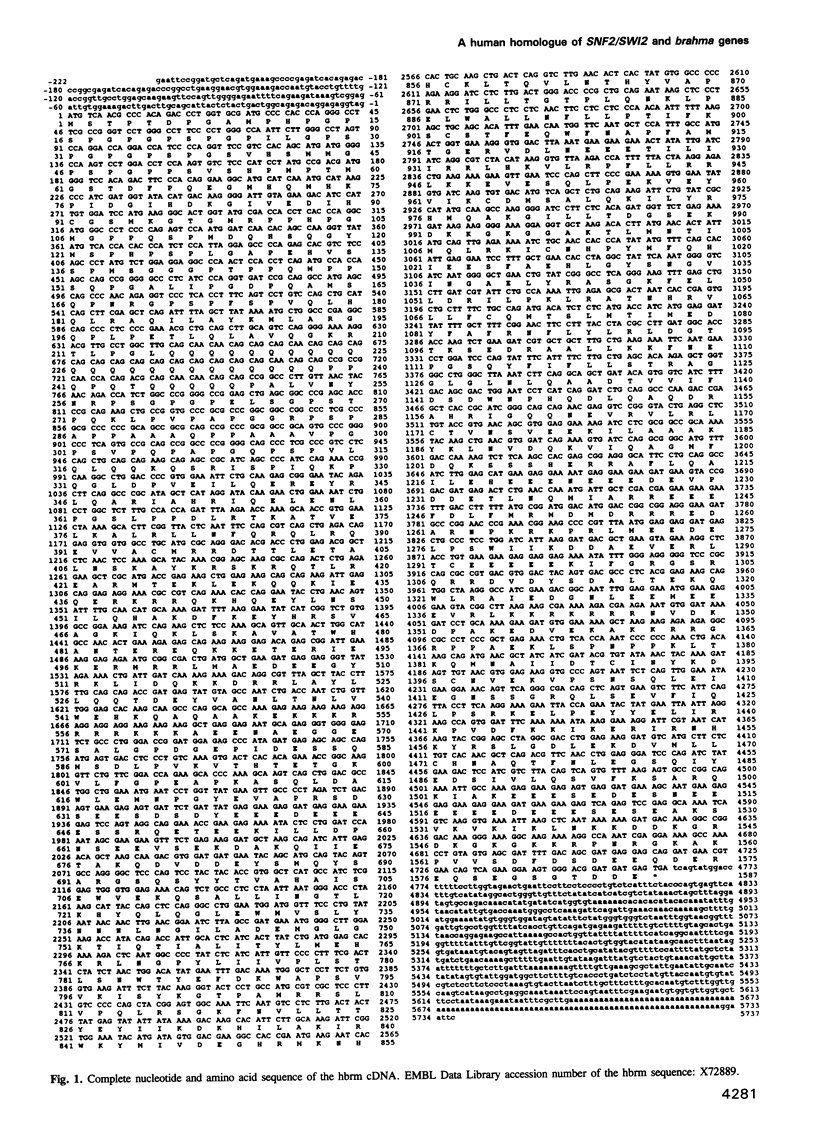
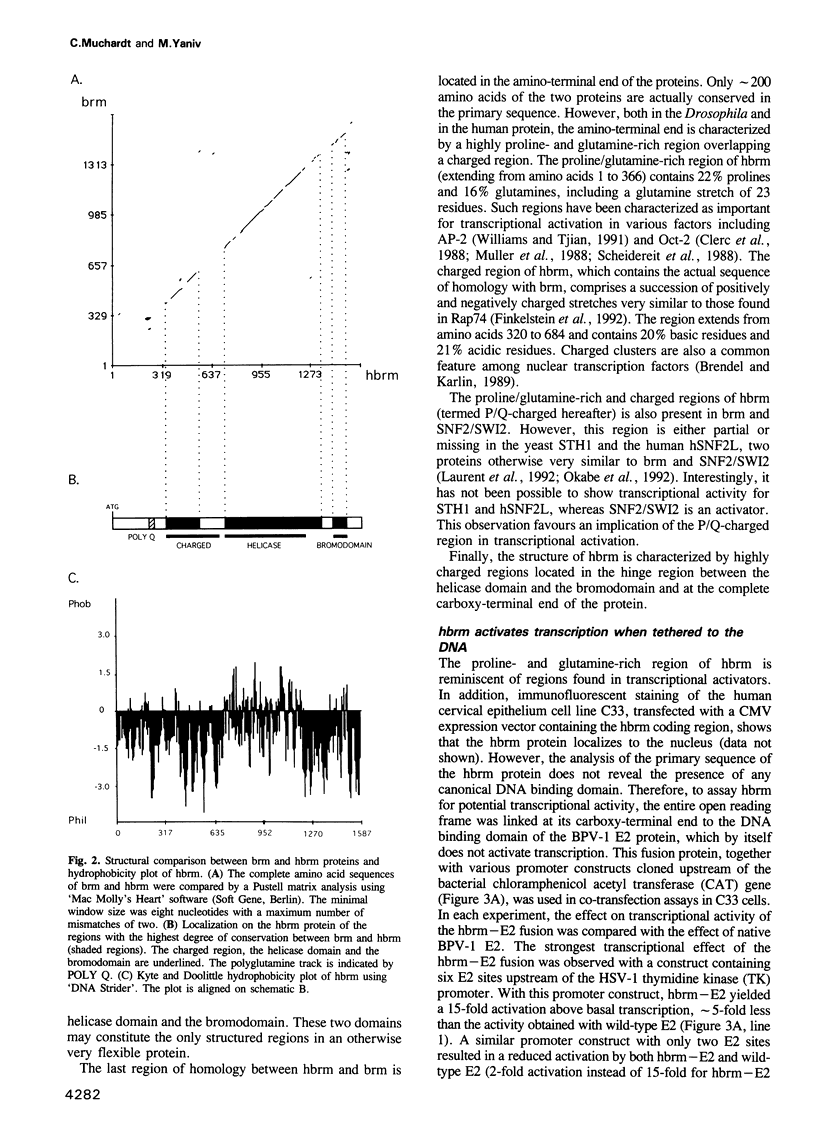
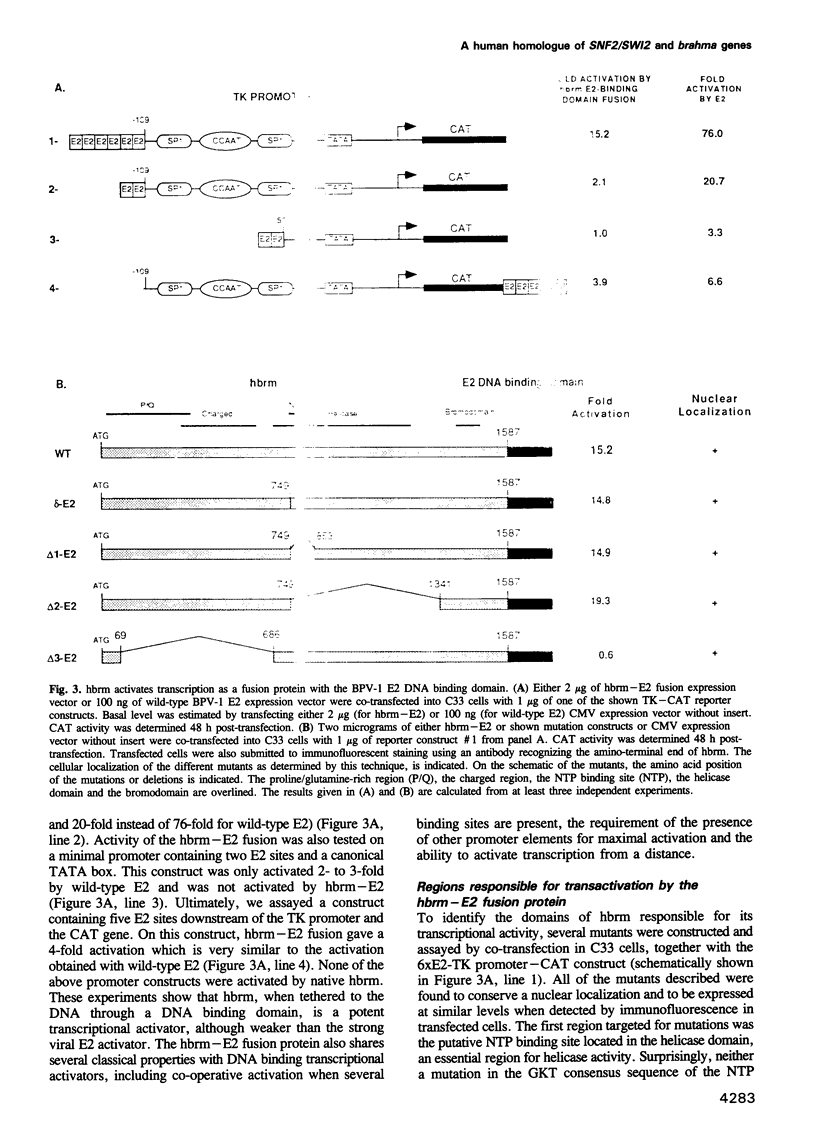
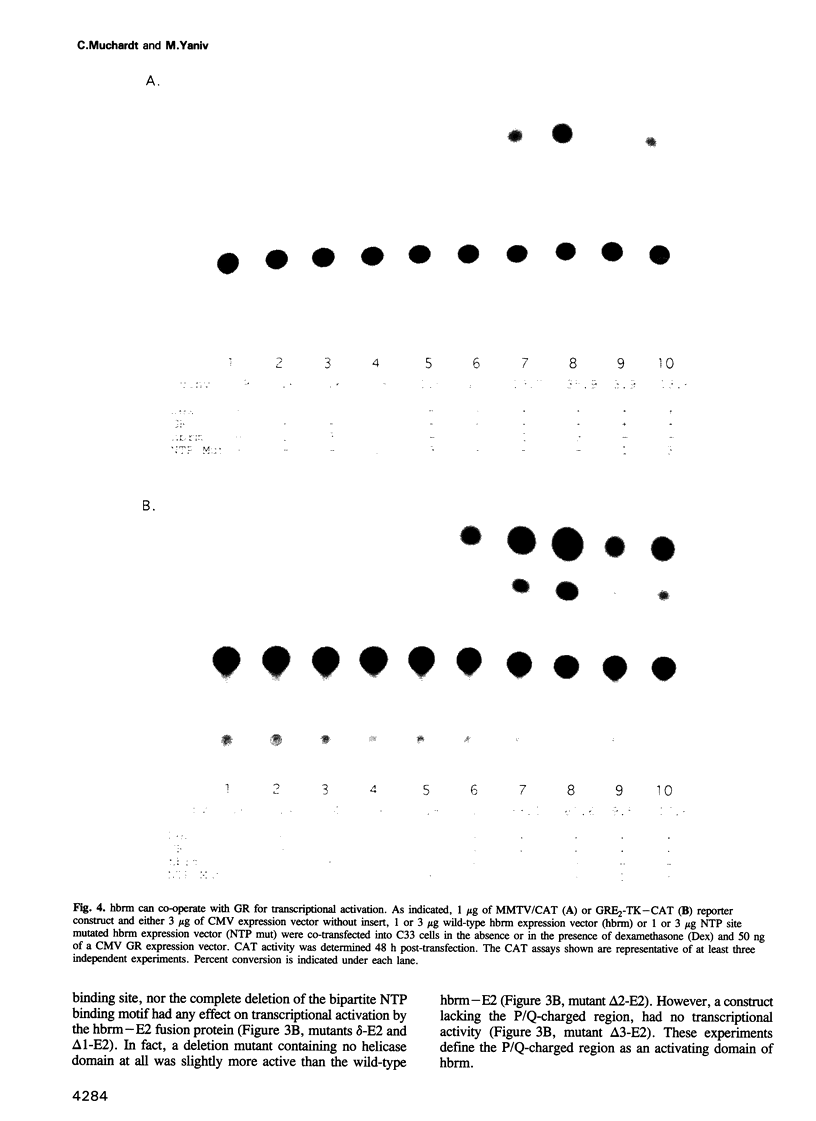
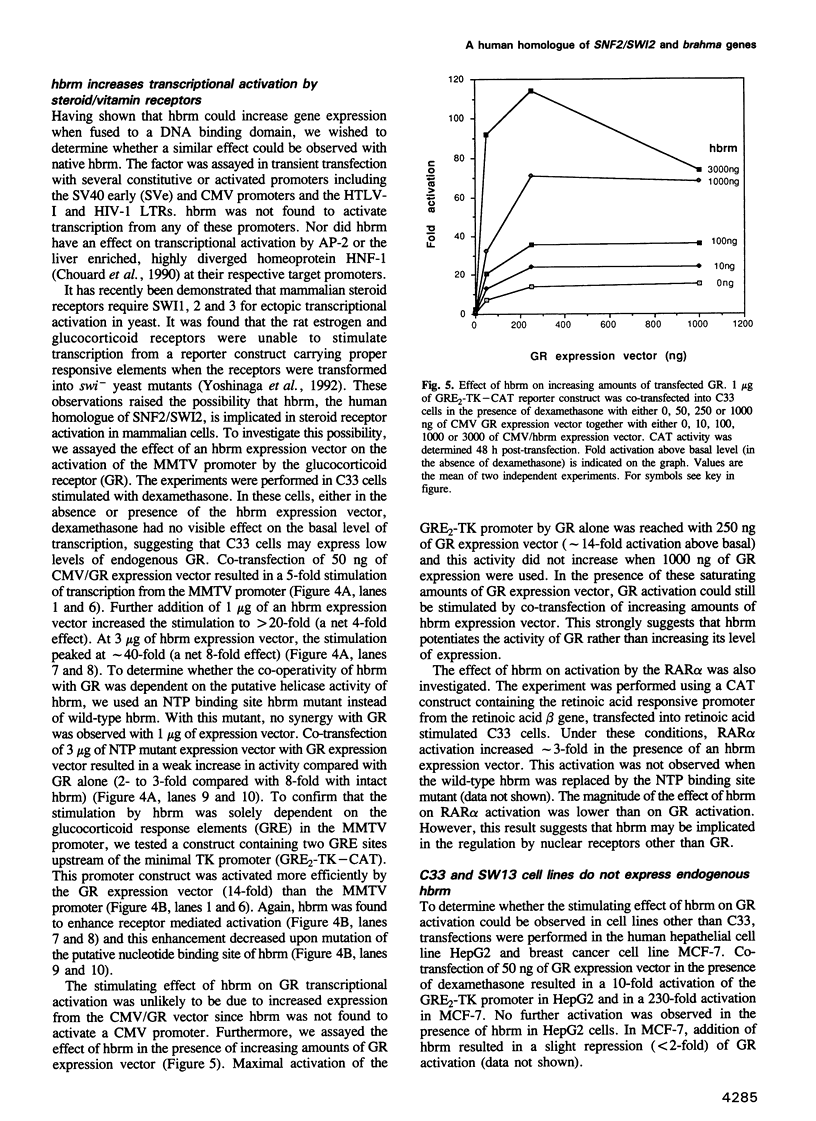
Several of the SNF and SWI genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae code for proteins believed to assist transcriptional activators by relieving nucleosome repression. One of these proteins, SNF2/SWI2, has a homologue in Drosophila, a regulator of homeotic genes known as brahma or brm. In this report, we show that a counterpart of SNF2/SWI2 also exists in mice and humans. The human protein, designated hbrm, is a 180 kDa nuclear factor that can function as a transcriptional activator when fused to a heterologous DNA binding domain. The mouse homologue of hbrm is expressed in all mouse organs tested while hbrm was detected in some but not all investigated human cell lines. In cells failing to express the endogenous gene, transfected hbrm cooperates with the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) in transcriptional activation. However, hbrm had no effect on the activity of several other transcription factors, including the homeoprotein HNF-1. The co-operation between hbrm and GR required the DNA binding domain of GR and two separated regions of the hbrm protein, including a domain with homology to known helicases.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. C., Workman J. L. Nucleosome displacement in transcription. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brendel V., Karlin S. Association of charge clusters with functional domains of cellular transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5698–5702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Bustin M., Marsaud V., Richard-Foy H., Hager G. L. The transcriptionally-active MMTV promoter is depleted of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):273–278. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Skroch P., Weinmann J., Butkeraitis P., Ponta H. DNA sequences outside the receptor-binding sites differently modulate the responsiveness of the mouse mammary tumour virus promoter to various steroid hormones. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1403–1410. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc R. G., Corcoran L. M., LeBowitz J. H., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. The B-cell-specific Oct-2 protein contains POU box- and homeo box-type domains. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1570–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Kerrigan L. A., Lira L. M., Marshak D. R., Kadonaga J. T. Sequence-specific antirepression of histone H1-mediated inhibition of basal RNA polymerase II transcription. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):643–649. doi: 10.1126/science.1899487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas V., Stokes D. G., Perry R. P. A mammalian DNA-binding protein that contains a chromodomain and an SNF2/SWI2-like helicase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2414–2418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estruch F., Carlson M. SNF6 encodes a nuclear protein that is required for expression of many genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2544–2553. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Kostrub C. F., Li J., Chavez D. P., Wang B. Q., Fang S. M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F. A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464–467. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke A., DeCamillis M., Zink D., Cheng N., Brock H. W., Paro R. Polycomb and polyhomeotic are constituents of a multimeric protein complex in chromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2941–2950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg Y., Glineur C., Bosselut R., Ghysdael J. Thyroid hormone action and the erbA oncogene family. Biochimie. 1989 Feb;71(2):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(89)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A conserved NTP-motif in putative helicases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–22. doi: 10.1038/333022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss C., Sogo J. M. Chromatin replication. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Happel A. M., Swanson M. S., Winston F. The SNF2, SNF5 and SNF6 genes are required for Ty transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1991 May;128(1):69–77. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes S. R., Dollard C., Winston F., Beck S., Trowsdale J., Dawid I. B. The bromodomain: a conserved sequence found in human, Drosophila and yeast proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2603–2603. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn J. N., Brown S. A., Clark C. D., Winston F. Evidence that SNF2/SWI2 and SNF5 activate transcription in yeast by altering chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2288–2298. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatake K., Hasegawa S., Takada R., Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. The p250 subunit of native TATA box-binding factor TFIID is the cell-cycle regulatory protein CCG1. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):179–181. doi: 10.1038/362179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Weinzierl R. O., Gill G., Chen J. L., Dynlacht B. D., Tjian R. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of Drosophila TAF110 reveal properties expected of coactivators. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):247–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90664-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Signal transduction from cell surface to nucleus in development and disease. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2581–2590. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1317309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Irresistible force meets immovable object: transcription and the nucleosome. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):833–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90354-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger W., Herskowitz I. A negative regulator of HO transcription, SIN1 (SPT2), is a nonspecific DNA-binding protein related to HMG1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4135–4146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Carlson M. Yeast SNF2/SWI2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins function coordinately with the gene-specific transcriptional activators GAL4 and Bicoid. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1707–1715. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treich I., Carlson M. The yeast SNF2/SWI2 protein has DNA-stimulated ATPase activity required for transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):583–591. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. Functional interdependence of the yeast SNF2, SNF5, and SNF6 proteins in transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Treitel M. A., Carlson M. The SNF5 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a glutamine- and proline-rich transcriptional activator that affects expression of a broad spectrum of genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5616–5625. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent B. C., Yang X., Carlson M. An essential Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene homologous to SNF2 encodes a helicase-related protein in a new family. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1893–1902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Initiation on chromatin templates in a yeast RNA polymerase II transcription system. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2282–2287. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matallana E., Franco L., Pérez-Ortín J. E. Chromatin structure of the yeast SUC2 promoter in regulatory mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Feb;231(3):395–400. doi: 10.1007/BF00292708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe I., Bailey L. C., Attree O., Srinivasan S., Perkel J. M., Laurent B. C., Carlson M., Nelson D. L., Nussbaum R. L. Cloning of human and bovine homologs of SNF2/SWI2: a global activator of transcription in yeast S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 11;20(17):4649–4655. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.17.4649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Kabsch W., Krengel U., Holmes K. C., John J., Wittinghofer A. Structure of the guanine-nucleotide-binding domain of the Ha-ras oncogene product p21 in the triphosphate conformation. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):209–214. doi: 10.1038/341209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. G., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Interaction between an acidic activator and transcription factor TFIIB is required for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):741–744. doi: 10.1038/363741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert S., Wang E. H., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of human TAFII250: a TBP-associated factor implicated in cell-cycle regulation. Nature. 1993 Mar 11;362(6416):175–179. doi: 10.1038/362175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande S., Sharif M., Chen H., Privalsky M. v-erbA acts on retinoic acid receptors in immature avian erythroid cells. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):1067–1074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.1067-1074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid A., Fascher K. D., Hörz W. Nucleosome disruption at the yeast PHO5 promoter upon PHO5 induction occurs in the absence of DNA replication. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):853–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90560-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. TATA-binding protein is a classless factor. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):819–821. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soininen R., Schoor M., Henseling U., Tepe C., Kisters-Woike B., Rossant J., Gossler A. The mouse Enhancer trap locus 1 (Etl-1): a novel mammalian gene related to Drosophila and yeast transcriptional regulator genes. Mech Dev. 1992 Nov;39(1-2):111–123. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90030-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Deuring R., Scott M. P., Kissinger M., Pattatucci A. M., Kaufman T. C., Kennison J. A. brahma: a regulator of Drosophila homeotic genes structurally related to the yeast transcriptional activator SNF2/SWI2. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90191-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Herr W. Differential transcriptional activation by Oct-1 and Oct-2: interdependent activation domains induce Oct-2 phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasset D., Tora L., Fromental C., Scheer E., Chambon P. Distinct classes of transcriptional activating domains function by different mechanisms. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1177–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90394-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Dostatni N., Arnos F., Yaniv M. Cooperative activation of transcription by bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 can occur over a large distance. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4431–4437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. The reprogramming of transcriptional competence. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):573–575. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Roeder R. G., Sawadogo M. Physical analysis of transcription preinitiation complex assembly on a class II gene promoter. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1335–1338. doi: 10.1126/science.3413495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittinghofer A., Pai E. F. The structure of Ras protein: a model for a universal molecular switch. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90156-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Kingston R. E. Nucleosome core displacement in vitro via a metastable transcription factor-nucleosome complex. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1780–1784. doi: 10.1126/science.1465613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto H., Yamashita I. The GAM1/SNF2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a highly charged nuclear protein required for transcription of the STA1 gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):270–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00282476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga S. K., Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I., Yamamoto K. R. Roles of SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 proteins for transcriptional enhancement by steroid receptors. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1598–1604. doi: 10.1126/science.1360703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Lavau C., Marchio A., Chomienne C., Degos L., Dejean A. The PML-RAR alpha fusion mRNA generated by the t(15;17) translocation in acute promyelocytic leukemia encodes a functionally altered RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90113-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]