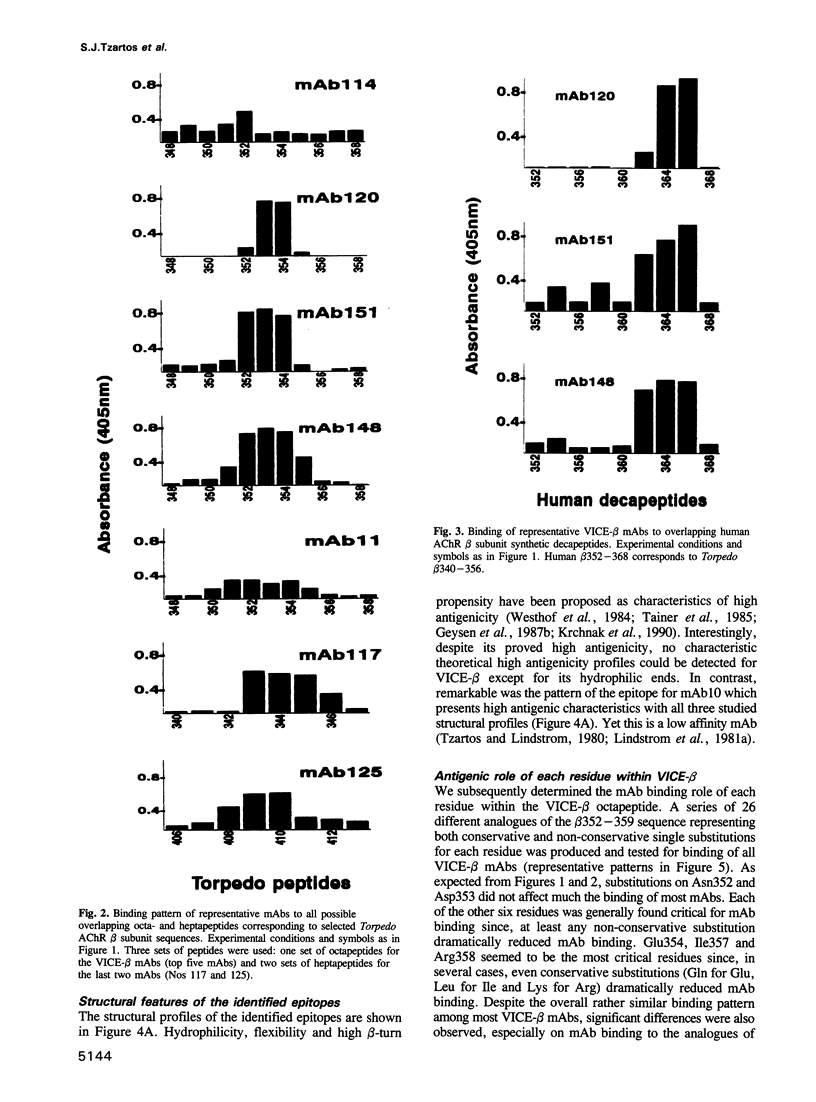
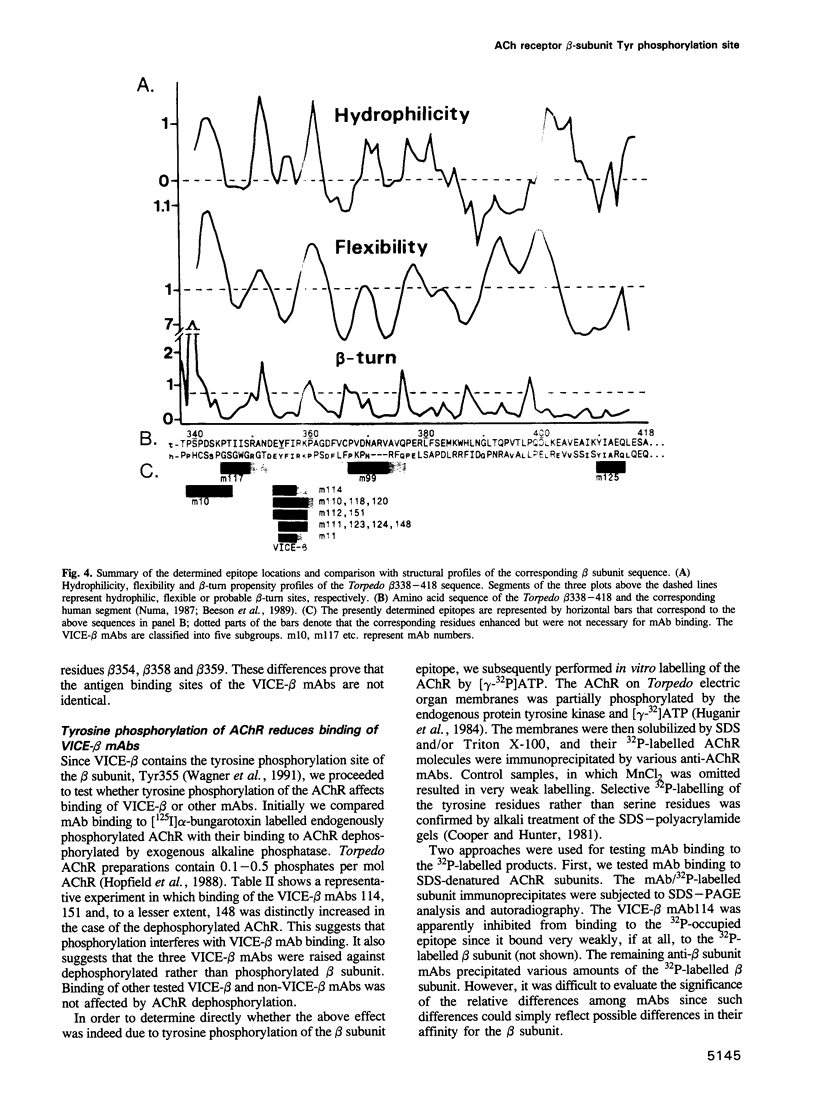
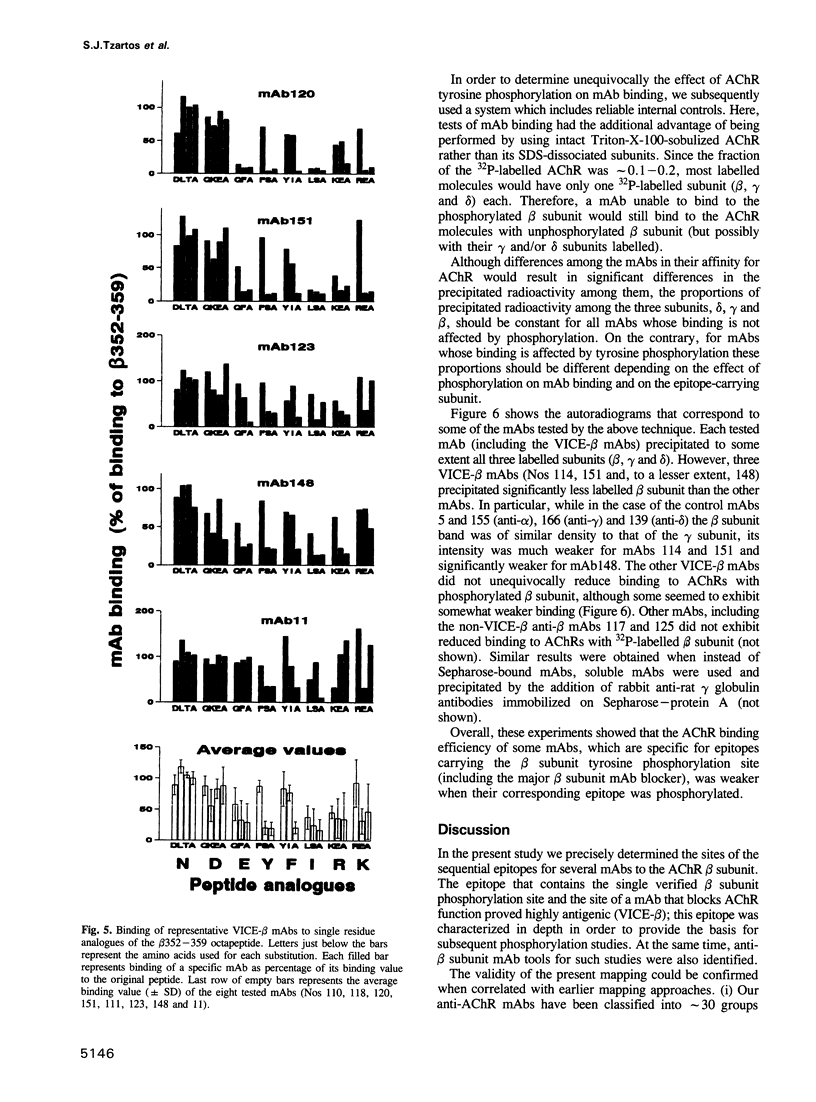
Abstract
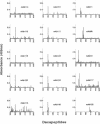
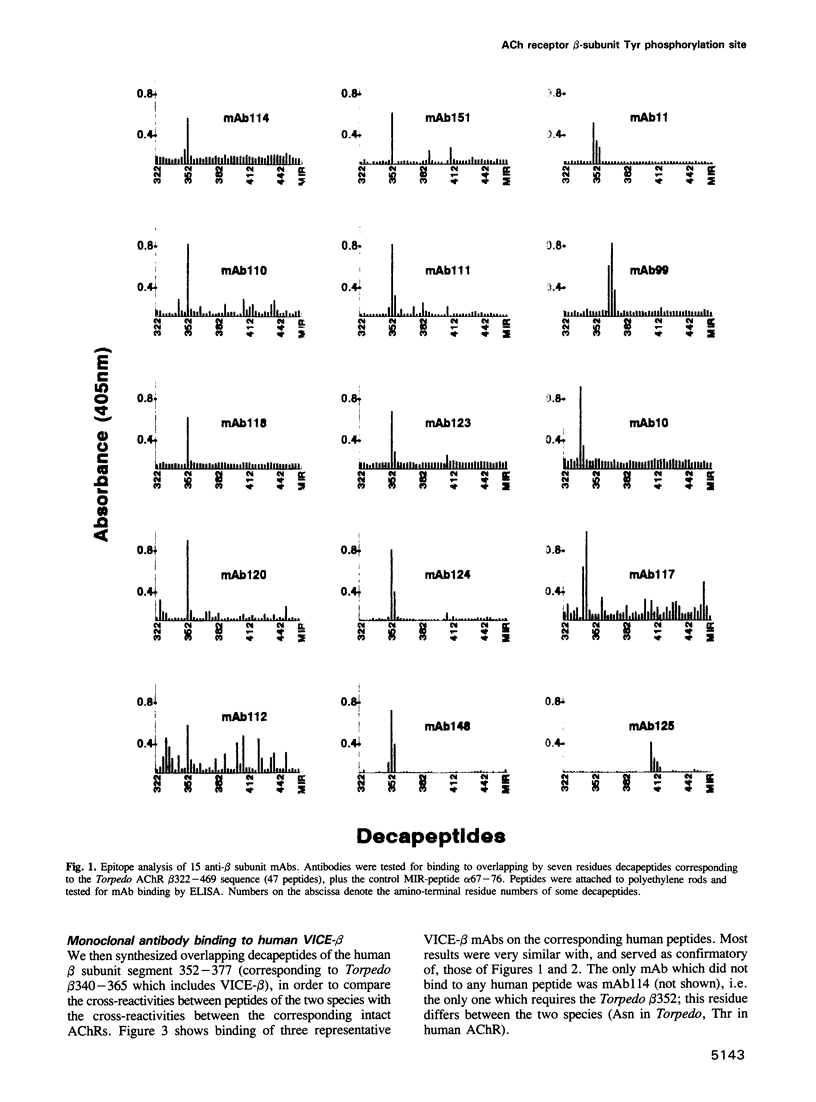
Tyrosine phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) seems to be involved in AChR desensitization and localization on the postsynaptic membrane. This study reveals a probable function of the single known beta subunit phosphorylation site (beta Tyr355) and provides suitable tools for its study. The epitopes for 15 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against the cytoplasmic side of the AChR beta subunit were precisely mapped using > 100 synthetic peptides attached on polyethylene rods. Eleven mAbs bound to a very immunogenic cytoplasmic epitope (VICE-beta) on Torpedo beta 352-359, which contains the beta Tyr355, and to the corresponding sequence of human AChR. The contribution of each VICE-beta residue to mAb binding was then studied by peptide analogues having single residue substitutions. Overall, each of the residues beta 354-359, including beta Tyr355, proved critical for mAb binding. Two of our four mAbs known to block the ion channel were found to bind at (mAb148) or close (mAb10) to VICE-beta. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Torpedo AChR by endogenous kinase(s) selectively reduced binding of some VICE-beta mAbs, including the channel blocking mAb148. We conclude that VICE-beta probably plays a key role in AChR function. Elucidation of this role should be facilitated by the identified mAb tools.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker L. P., Peng H. B. Tyrosine phosphorylation and acetylcholine receptor cluster formation in cultured Xenopus muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):185–195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeson D., Brydson M., Newsom-Davis J. Nucleotide sequence of human muscle acetylcholine receptor beta-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4391–4391. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt Y., Montal M. S., Lindstrom J. M., Montal M. Monoclonal antibodies specific to the beta and gamma subunits of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor inhibit single-channel activity. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):481–486. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00481.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Bertrand D. The functional architecture of the acetylcholine nicotinic receptor explored by affinity labelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Q Rev Biophys. 1992 Nov;25(4):395–432. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of beta-turns. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85259-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cung M. T., Demange P., Marraud M., Tsikaris V., Sakarellos C., Papadouli I., Kokla A., Tzartos S. J. Two-dimensional 1H-NMR study of antigen-antibody interactions: binding of synthetic decapeptides to an anti-acetylcholine receptor monoclonal antibody. Biopolymers. 1991 May;31(6):769–776. doi: 10.1002/bip.360310622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Specificity and localization of the acetylcholine receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer-Montiel A. V., Montal M. S., Díaz-Muñoz M., Montal M. Agonist-independent activation of acetylcholine receptor channels by protein kinase A phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10213–10217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Meloen R. H., Barteling S. J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3998–4002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Tainer J. A., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Alexander H., Getzoff E. D., Lerner R. A. Chemistry of antibody binding to a protein. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.3823878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. N., Ross A. F., Claudio T. Acetylcholine receptor assembly is stimulated by phosphorylation of its gamma subunit. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90378-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping the binding of monoclonal antibodies to the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 5;22(14):3312–3320. doi: 10.1021/bi00283a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W. Recognition domains in assembly of oligomeric membrane proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;2(3):66–68. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90058-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. F., Tank D. W., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Functional modulation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):677–680. doi: 10.1038/336677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Delcour A. H., Greengard P., Hess G. P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates its rate of desensitization. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):774–776. doi: 10.1038/321774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Miles K., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by an endogenous tyrosine-specific protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Miles K. Protein phosphorylation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24(3):183–215. doi: 10.3109/10409238909082553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordossi A. A., Tzartos S. J. Conformation of cytoplasmic segments of acetylcholine receptor alpha- and beta-subunits probed by monoclonal antibodies: sensitivity of the antibody competition approach. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1605–1610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krchnák V., Mach O., Malý A. Computer prediction of B-cell determinants from protein amino acid sequences based on incidence of beta turns. Methods Enzymol. 1989;178:586–611. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)78041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubalek E., Ralston S., Lindstrom J., Unwin N. Location of subunits within the acetylcholine receptor by electron image analysis of tubular crystals from Torpedo marmorata. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Einarson B., Tzartos S. Production and assay of antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):432–460. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Shelton D., Fujii Y. Myasthenia gravis. Adv Immunol. 1988;42:233–284. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60847-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J., Tzartos S., Gullick W. Structure and function of the acetylcholine receptor molecule studied using monoclonal antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;377:1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb33721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., O'Connor R., Geuder K. I., Hoppe F., Schalke B., Tzartos S., Kalies I., Kirchner T., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Characterization of a protein with an acetylcholine receptor epitope from myasthenia gravis-associated thymomas. Lab Invest. 1990 Mar;62(3):279–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Benoit P., Pinset C., Roa M., Changeux J. P. Calcitonin gene-related peptide enhances the rate of desensitization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in cultured mouse muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5728–5732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S., Shelton G. D., Lei S., Lindstrom J. M., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies to Torpedo acetylcholine receptor gamma subunits, which specifically recognize the epsilon subunit of mammalian muscle acetylcholine receptor. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Jan;36(1):13–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90027-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Neuronal phosphoproteins: physiological and clinical implications. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1357–1364. doi: 10.1126/science.6474180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadouli I., Potamianos S., Hadjidakis I., Bairaktari E., Tsikaris V., Sakarellos C., Cung M. T., Marraud M., Tzartos S. J. Antigenic role of single residues within the main immunogenic region of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):239–245. doi: 10.1042/bj2690239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadouli I., Sakarellos C., Tzartos S. J. High-resolution epitope mapping and fine antigenic characterization of the main immunogenic region of the acetylcholine receptor. Improving the binding activity of synthetic analogues of the region. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb19890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu Z. C., Moritz E., Huganir R. L. Regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor at the rat neuromuscular junction. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90049-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Sargent P. B., Lindstrom J. Transmembrane topography of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: immunochemical tests contradict theoretical predictions based on hydrophobicity profiles. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2633–2643. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Sargent P. B., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Criado M., Lindstrom J. Location of antigenic determinants on primary sequences of subunits of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2621–2632. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedi M. S., Anand R., Conroy W. G., Lindstrom J. Determination of amino acids critical to the main immunogenic region of intact acetylcholine receptors by in vitro mutagenesis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 2;267(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80286-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safran A., Sagi-Eisenberg R., Neumann D., Fuchs S. Phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor by protein kinase C and identification of the phosphorylation site within the receptor delta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10506–10510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh T., Oswald R., Wennogle L. P., Changeux J. P. Conditions for the selective labelling of the 66 000 dalton chain of the acetylcholine receptor by the covalent non-competitive blocker 5-azido-[3H]trimethisoquin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80522-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B., Hedges B. E., Tsavaler L., Clemmons L., Tzartos S., Lindstrom J. M. Structure and transmembrane nature of the acetylcholine receptor in amphibian skeletal muscle as revealed by cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):609–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W., Meyer H. E., Buchner K., Bayer H., Hucho F. Phosphorylation sites of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A novel site detected in position delta S362. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3583–3588. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., McCarthy M. P., Shuster M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11009–11023. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tainer J. A., Getzoff E. D., Paterson Y., Olson A. J., Lerner R. A. The atomic mobility component of protein antigenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:501–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Cung M. T., Demange P., Loutrari H., Mamalaki A., Marraud M., Papadouli I., Sakarellos C., Tsikaris V. The main immunogenic region (MIR) of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and the anti-MIR antibodies. Mol Neurobiol. 1991 Spring;5(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02935610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Kokla A., Walgrave S. L., Conti-Tronconi B. M. Localization of the main immunogenic region of human muscle acetylcholine receptor to residues 67-76 of the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2899–2903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Lindstrom J. M. Monoclonal antibodies used to probe acetylcholine receptor structure: localization of the main immunogenic region and detection of similarities between subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Remoundos M. S. Fine localization of the major alpha-bungarotoxin binding site to residues alpha 189-195 of the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor. Residues 189, 190, and 195 are indispensable for binding. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21462–21467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Remoundos M. S. Precise epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies to the cytoplasmic side of the acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit. Dissecting a potentially myasthenogenic epitope. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 1;207(3):915–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S., Langeberg L., Hochschwender S., Swanson L. W., Lindstrom J. Characteristics of monoclonal antibodies to denatured Torpedo and to native calf acetylcholine receptors: species, subunit and region specificity. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Jan;10(3):235–253. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90105-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N. Neurotransmitter action: opening of ligand-gated ion channels. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):31–41. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner K., Edson K., Heginbotham L., Post M., Huganir R. L., Czernik A. J. Determination of the tyrosine phosphorylation sites of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23784–23789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G., Qu Z., Huganir R. L. Agrin induces phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):869–878. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90227-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan K. K., Lindstrom J. M. Effects of monoclonal antibodies on the function of acetylcholine receptors purified from Torpedo californica and reconstituted into vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1212–1221. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]