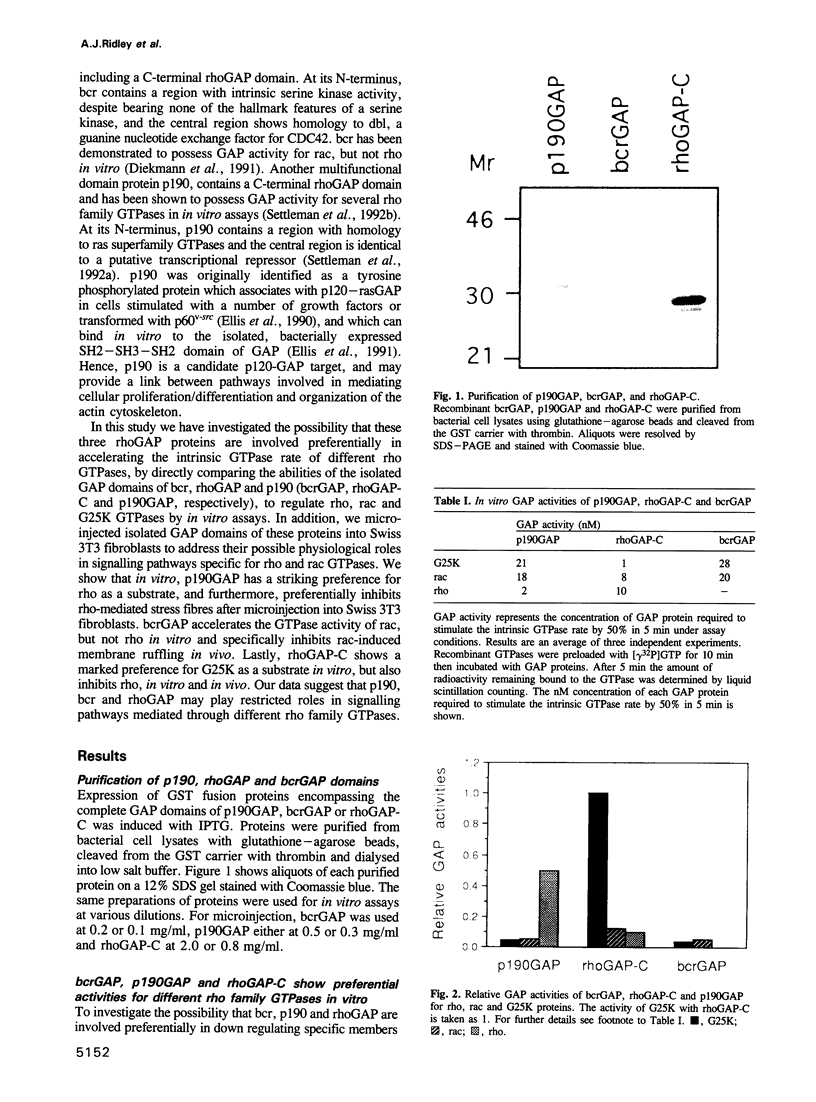
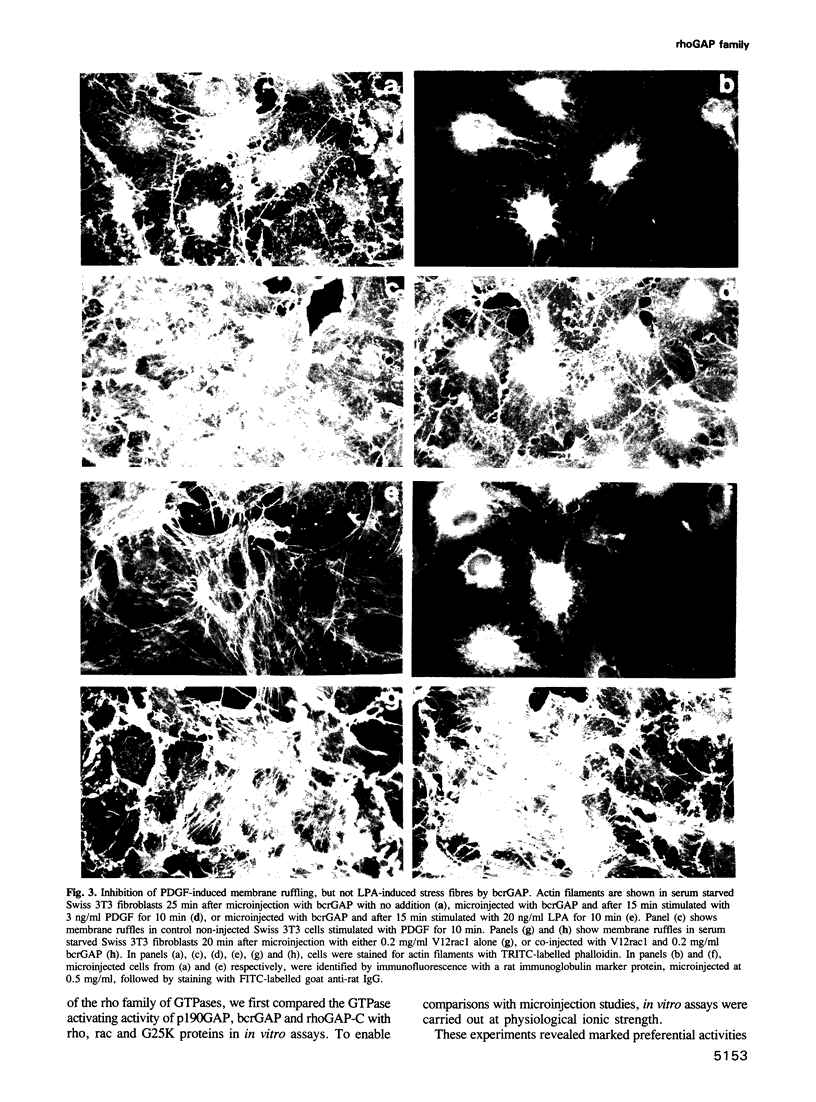
Abstract
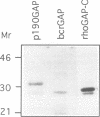
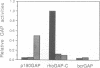
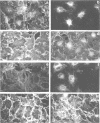
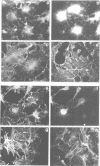
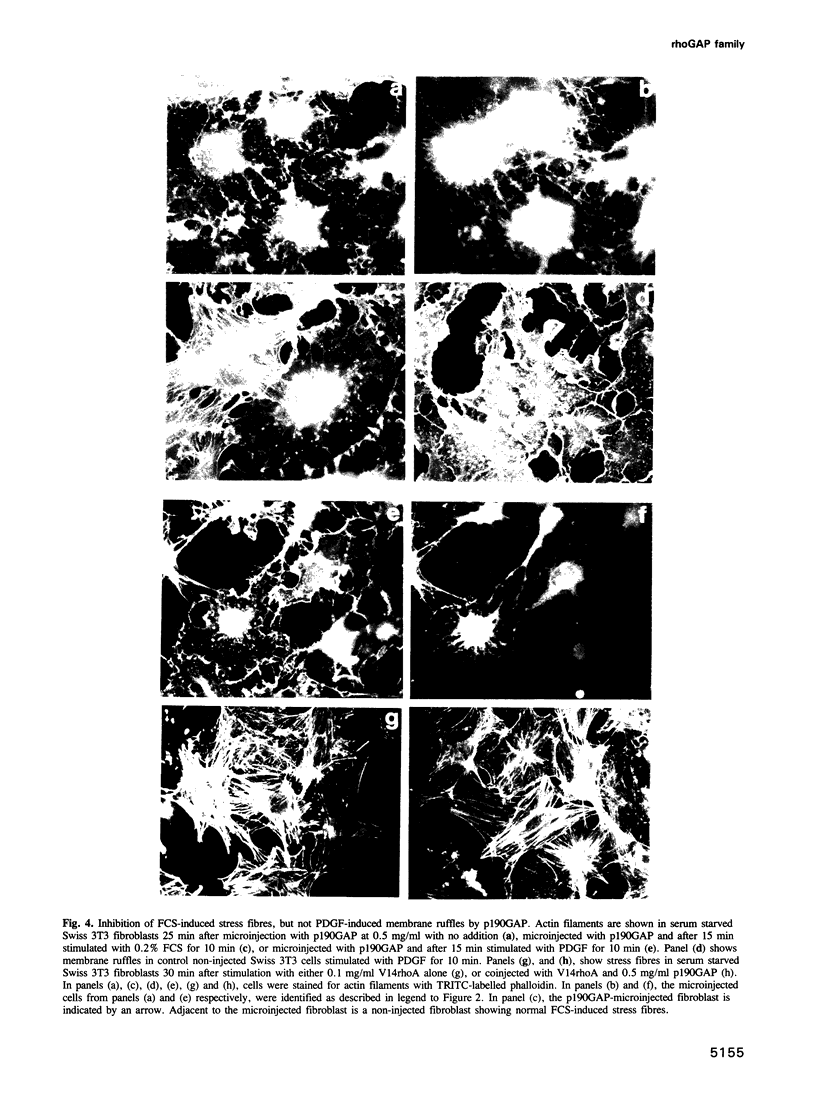
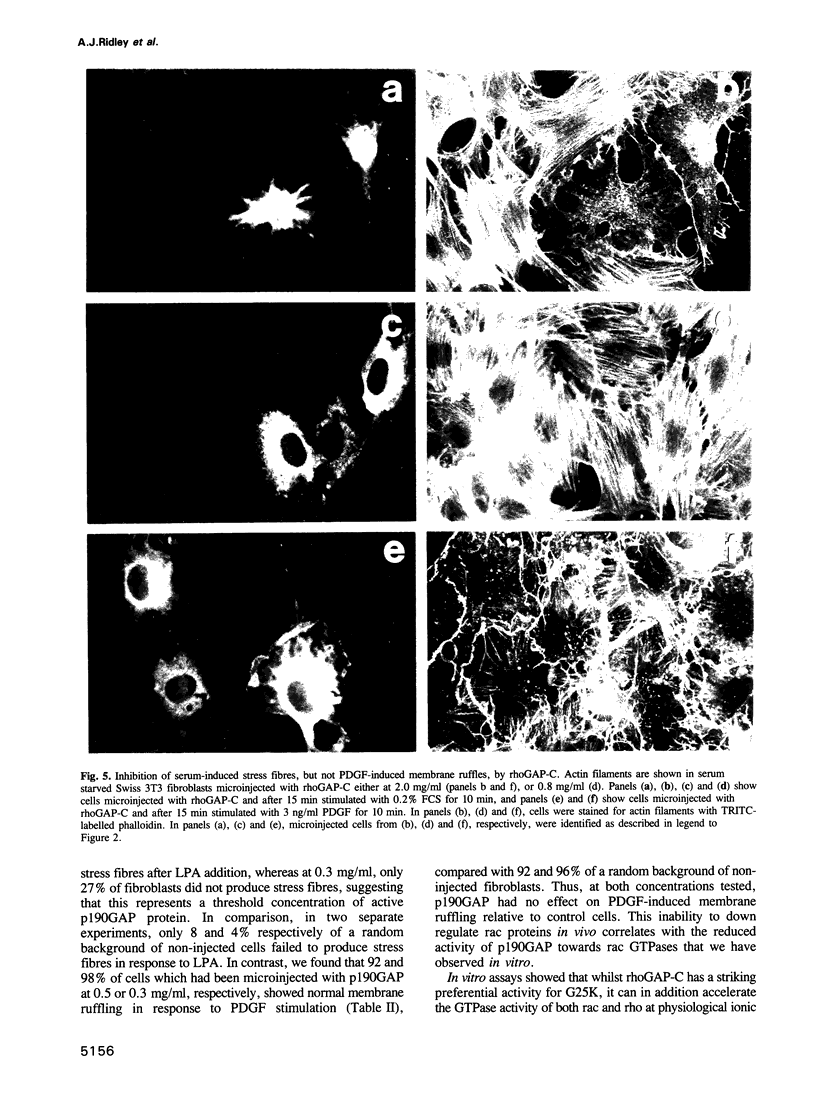
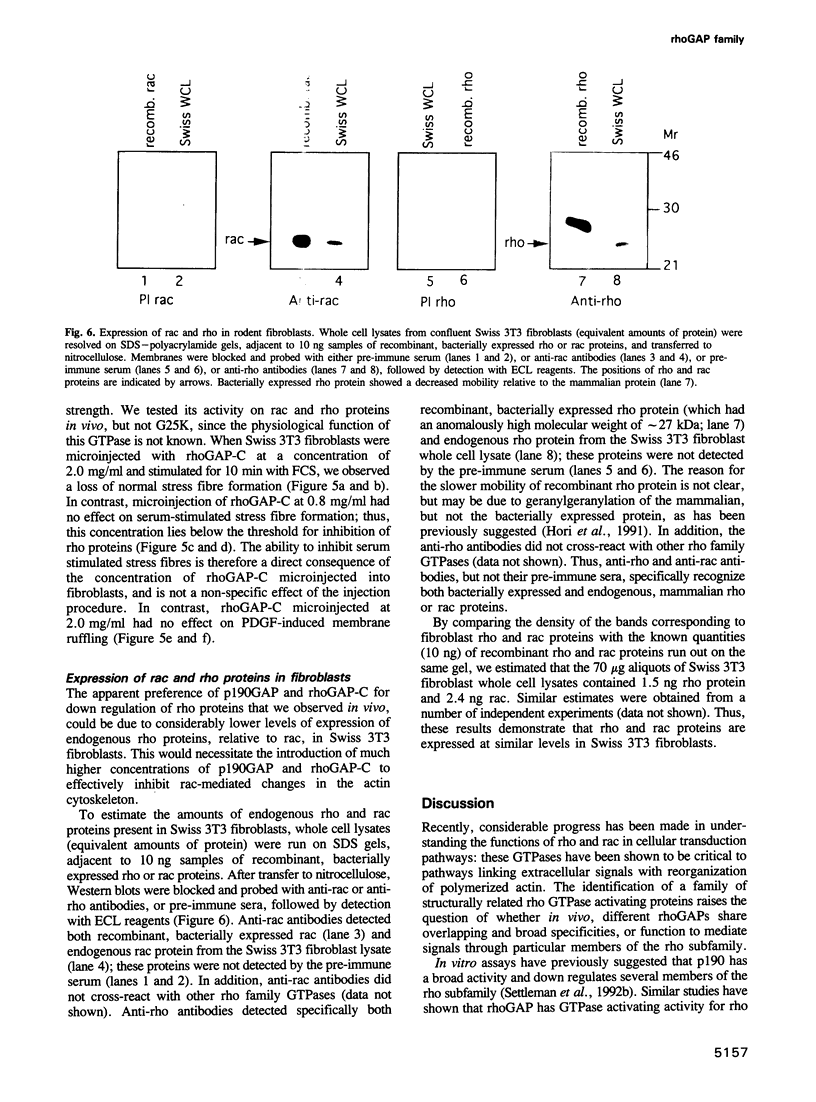
rho family GTPases link extracellular signals to changes in the organization of cytoskeletal actin. Serum stimulation of quiescent Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts leads to rho-dependent actin stress fibre formation and focal adhesions, whilst several growth factors initiate signalling pathways leading to rac-dependent actin polymerization at the plasma membrane, and membrane ruffling. The product of the breakpoint cluster region gene bcr, rho GTPase accelerating protein (rhoGAP) and rasGAP-associated p190 share structurally related rho GAP domains, and possess GAP activity for rho family members in vitro. We have directly compared the activities of the isolated GAP domains of these three proteins in regulating different rho family GTPases, both by in vitro assays and by microinjection, to address their possible physiologic functions. We show that bcr accelerates the GTPase activity of rac, but not rho in vitro, and inhibits rac-mediated membrane ruffling, but not rho-mediated stress fibre formation, after microinjection into Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. In vitro, rhoGAP has a striking preference for G25K as a substrate, whilst p190GAP has marked preferential activity for rho. Furthermore, p190 preferentially inhibits rho-mediated stress fibre formation in vivo. Our data suggest that p190, rhoGAP and bcr play distinct roles in signalling pathways mediated through different rho family GTPases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adari H., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M., Der C. J., McCormick F. Guanosine triphosphatase activating protein (GAP) interacts with the p21 ras effector binding domain. Science. 1988 Apr 22;240(4851):518–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2833817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calés C., Hancock J. F., Marshall C. J., Hall A. The cytoplasmic protein GAP is implicated as the target for regulation by the ras gene product. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):548–551. doi: 10.1038/332548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Didsbury J., Weber R. F., Bokoch G. M., Evans T., Snyderman R. rac, a novel ras-related family of proteins that are botulinum toxin substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16378–16382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann D., Brill S., Garrett M. D., Totty N., Hsuan J., Monfries C., Hall C., Lim L., Hall A. Bcr encodes a GTPase-activating protein for p21rac. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):400–402. doi: 10.1038/351400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivas G. T., Shih A., Coutavas E., Rush M. G., D'Eustachio P. Characterization of four novel ras-like genes expressed in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1793–1798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne M., Schweighoffer F., Parker F., Clerc F., Frobert Y., Thang M. N., Tocqué B. Identification of the SH3 domain of GAP as an essential sequence for Ras-GAP-mediated signaling. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):525–528. doi: 10.1126/science.7678707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Liu X. Q., Anderson D., Abraham N., Veillette A., Pawson T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins in lymphoid and fibroblast cells expressing lck. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):895–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. Signal transduction through small GTPases--a tale of two GAPs. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90441-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):635–640. doi: 10.1126/science.2116664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori Y., Kikuchi A., Isomura M., Katayama M., Miura Y., Fujioka H., Kaibuchi K., Takai Y. Post-translational modifications of the C-terminal region of the rho protein are important for its interaction with membranes and the stimulatory and inhibitory GDP/GTP exchange proteins. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. C., Marshall C. J., Hancock J. F. Plasma membrane-targeted ras GTPase-activating protein is a potent suppressor of p21ras function. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2420–2431. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R. A novel ras-related gene family. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. A., Yatani A., Clark R., Conroy L., Polakis P., Brown A. M., McCormick F. GAP domains responsible for ras p21-dependent inhibition of muscarinic atrial K+ channel currents. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1553544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maru Y., Witte O. N. The BCR gene encodes a novel serine/threonine kinase activity within a single exon. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90521-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Polakis P., McCormick F., Pawson T., Ellis C. Protein-tyrosine kinases regulate the phosphorylation, protein interactions, subcellular distribution, and activity of p21ras GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1804–1812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A. J., Pendergast A. M., Havlik M. H., Puil L., Pawson T., Witte O. N. A limited set of SH2 domains binds BCR through a high-affinity phosphotyrosine-independent interaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5087–5093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergast A. M., Muller A. J., Havlik M. H., Maru Y., Witte O. N. BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Albright C. F., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Association between GTPase activators for Rho and Ras families. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):153–154. doi: 10.1038/359153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., Narasimhan V., Foster L. C., Weinberg R. A. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the GAP-associated protein p190: implications for a signaling pathway from ras to the nucleus. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90454-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinjo K., Koland J. G., Hart M. J., Narasimhan V., Johnson D. I., Evans T., Cerione R. A. Molecular cloning of the gene for the human placental GTP-binding protein Gp (G25K): identification of this GTP-binding protein as the human homolog of the yeast cell-division-cycle protein CDC42. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9853–9857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trahey M., McCormick F. A cytoplasmic protein stimulates normal N-ras p21 GTPase, but does not affect oncogenic mutants. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):542–545. doi: 10.1126/science.2821624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S., Jeanteur P., Fort P. Growth-regulated expression of rhoG, a new member of the ras homolog gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3138–3148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel U. S., Dixon R. A., Schaber M. D., Diehl R. E., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. Cloning of bovine GAP and its interaction with oncogenic ras p21. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):90–93. doi: 10.1038/335090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G. F., O'Connell P., Viskochil D., Cawthon R., Robertson M., Culver M., Dunn D., Stevens J., Gesteland R., White R. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]