Abstract
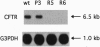
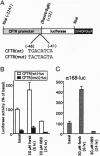
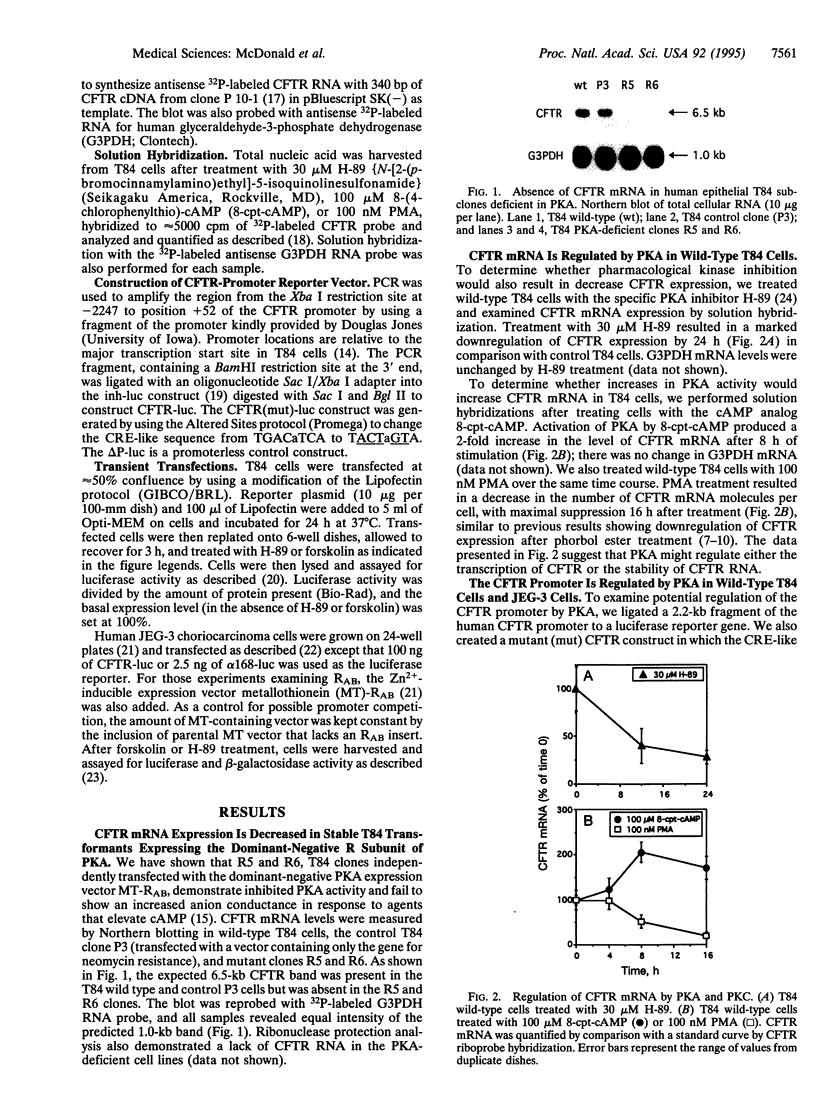
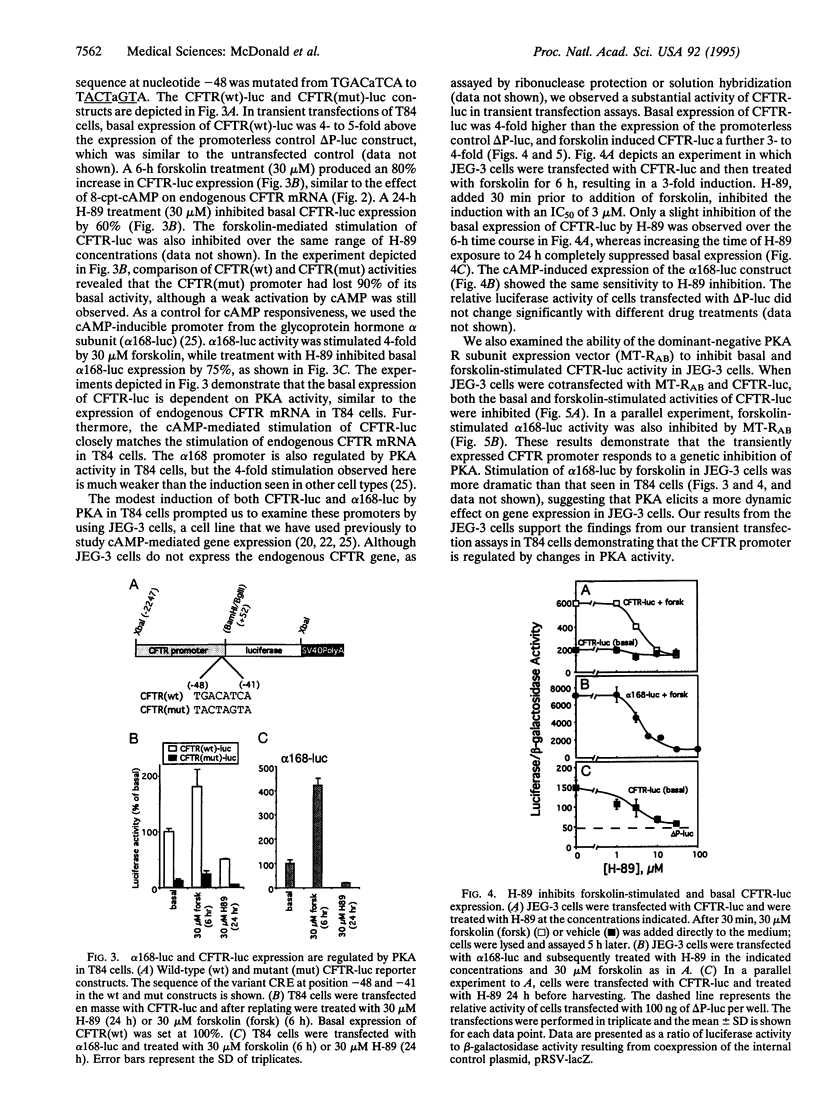
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) functions as a Cl- channel that becomes activated after phosphorylation by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). We demonstrate that PKA also plays a crucial role in maintaining basal expression of the CFTR gene in the human colon carcinoma cell line T84. Inhibition of PKA activity by expression of a dominant-negative regulatory subunit or treatment with the PKA-selective inhibitor N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89) caused a complete suppression of CFTR gene expression without affecting other constitutively active genes. Basal expression of a 2.2-kb region of the CFTR promoter linked to a luciferase reporter gene (CFTR-luc) exhibited the same dependence on PKA. The ability of cAMP to induce CFTR over basal levels is cell-type specific. In T84 cells, both the endogenous CFTR gene and CFTR-luc exhibited only a modest inducibility (approximately 2-fold), whereas in the human choriocarcinoma cell line JEG-3, CFTR-luc could be induced at least 4-fold. A variant cAMP-response element is present at position -48 to -41 in the CFTR promoter, and mutation of this sequence blocks basal expression. We conclude that cAMP, acting through PKA, is an essential regulator of basal CFTR gene expression and may mediate an induction of CFTR in responsive cell types.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsen M. S., Li R. S., Dietrich-Goetz W., Morris D. R. Multiple DNA elements responsible for transcriptional regulation of the ornithine decarboxylase gene by protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18866–18873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. P., Welsh M. J. Calcium and cAMP activate different chloride channels in the apical membrane of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6003–6007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargon J., Trapnell B. C., Chu C. S., Rosenthal E. R., Yoshimura K., Guggino W. B., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Down-regulation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene expression by agents that modulate intracellular divalent cations. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1872–1878. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H. A., Travis S. M., Welsh M. J. Regulation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- channel by specific protein kinases and protein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2037–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokar J. A., Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Kaetzel D. M., Hanson R. W., Nilson J. H. Characterization of the cAMP responsive elements from the genes for the alpha-subunit of glycoprotein hormones and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Conserved features of nuclear protein binding between tissues and species. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19740–19747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuer W., Kartner N., Riordan J. R., Cabantchik Z. I. Induction of expression of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10465–10469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Rich D. P., Marshall J., Gregory R. J., Welsh M. J., Smith A. E. Phosphorylation of the R domain by cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulates the CFTR chloride channel. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90446-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa T., Mishima A., Hagiwara M., Sano M., Hayashi K., Inoue T., Naito K., Toshioka T., Hidaka H. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5267–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. L., Rozmahel R., Tsui L. C. Characterization of the promoter region of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24471–24476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L. L., Grubb B. R., Yankaskas J. R., Cotton C. U., McKenzie A., Boucher R. C. Relationship of a non-cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-mediated chloride conductance to organ-level disease in Cftr(-/-) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):479–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Abrahamsen M. S., Degen J. L., Morris D. R., McKnight G. S. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase controls basal gene activity and steroidogenesis in Y1 adrenal tumor cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 14;31(14):3720–3726. doi: 10.1021/bi00129a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll L. A., Woodford T. A., Corbin J. D., Mellon P. L., McKnight G. S. Functional characterization of cAMP-binding mutations in type I protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16672–16678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. N., Walder J. A., Maurer R. A. A protein kinase inhibitor gene reduces both basal and multihormone-stimulated prolactin gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):431–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechecchi M. C., Rolfini R., Tamanini A., Gamberi C., Berton G., Cabrini G. Effect of modulation of protein kinase C on the cAMP-dependent chloride conductance in T84 cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 12;311(1):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81358-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Troccoli N. M., Jameson J. L. Binding specificity of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-responsive element (CRE)-binding proteins and activating transcription factors to naturally occurring CRE sequence variants. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1541–1551. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. E., Brigman K. N., Koller B. H., Boucher R. C., Stutts M. J. Cystic fibrosis heterozygote resistance to cholera toxin in the cystic fibrosis mouse model. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):107–109. doi: 10.1126/science.7524148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Deutsch P. J., Price D. J., Habener J. F., Avruch J. Plasmids encoding PKI(1-31), a specific inhibitor of cAMP-stimulated gene expression, inhibit the basal transcriptional activity of some but not all cAMP-regulated DNA response elements in JEG-3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19506–19513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro H., Kim K. T., Joh T. H., Kim K. S. Neuron-specific expression of the human dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene requires both the cAMP-response element and a silencer region. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17987–17994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Lee M. K., Carroll J., Joh T. H. Both the basal and inducible transcription of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene are dependent upon a cAMP response element. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15689–15695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J., Sferra T. J., Collins F. S. Characterization of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator promoter region. Chromatin context and tissue-specificity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15912–15921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. P., Guthrie C. R., Wailes L. M., Zhao X., Means A. R., McKnight G. S. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase types II and IV differentially regulate CREB-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6107–6116. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medcalf R. L., Rüegg M., Schleuning W. D. A DNA motif related to the cAMP-responsive element and an exon-located activator protein-2 binding site in the human tissue-type plasminogen activator gene promoter cooperate in basal expression and convey activation by phorbol ester and cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14618–14626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Amieux P. S., Zhao X., McKnight G. S. Mutations in the catalytic subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase interfere with holoenzyme formation without disrupting inhibition by protein kinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):6843–6846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., McKnight G. S. Mutations in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase result in unregulated biological activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4726–4730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei L., Dodson R., Schoderbek W. E., Maurer R. A., Mayo K. E. Regulation of the alpha inhibin gene by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate after transfection into rat granulosa cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;5(4):521–534. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-4-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. P., Gregory R. J., Anderson M. P., Manavalan P., Smith A. E., Welsh M. J. Effect of deleting the R domain on CFTR-generated chloride channels. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.1712985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. V., Goldman P. S., Frizzell R. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of Cl- transport in T84 cell clones expressing a mutant regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8975–8979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B. Q., Barthelson R. A., Skach W., Gruenert D. C., Sigal E., Mrsny R. J., Widdicombe J. H. Mechanism of inhibition of cAMP-dependent epithelial chloride secretion by phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19070–19075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell B. C., Zeitlin P. L., Chu C. S., Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Guggino W. B., Bargon J., Banks T. C., Dalemans W., Pavirani A. Down-regulation of cystic fibrosis gene mRNA transcript levels and induction of the cystic fibrosis chloride secretory phenotype in epithelial cells by phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10319–10323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis S. M., Carson M. R., Ries D. R., Welsh M. J. Interaction of nucleotides with membrane-associated cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15336–15339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura K., Nakamura H., Trapnell B. C., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Crystal R. G. The cystic fibrosis gene has a "housekeeping"-type promoter and is expressed at low levels in cells of epithelial origin. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9140–9144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge H. R., van den Berghe N., Tilly B. C., Kansen M., Bijman J. (Dys)regulation of epithelial chloride channels. Biochem Soc Trans. 1989 Oct;17(5):816–818. doi: 10.1042/bst0170816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]