Abstract
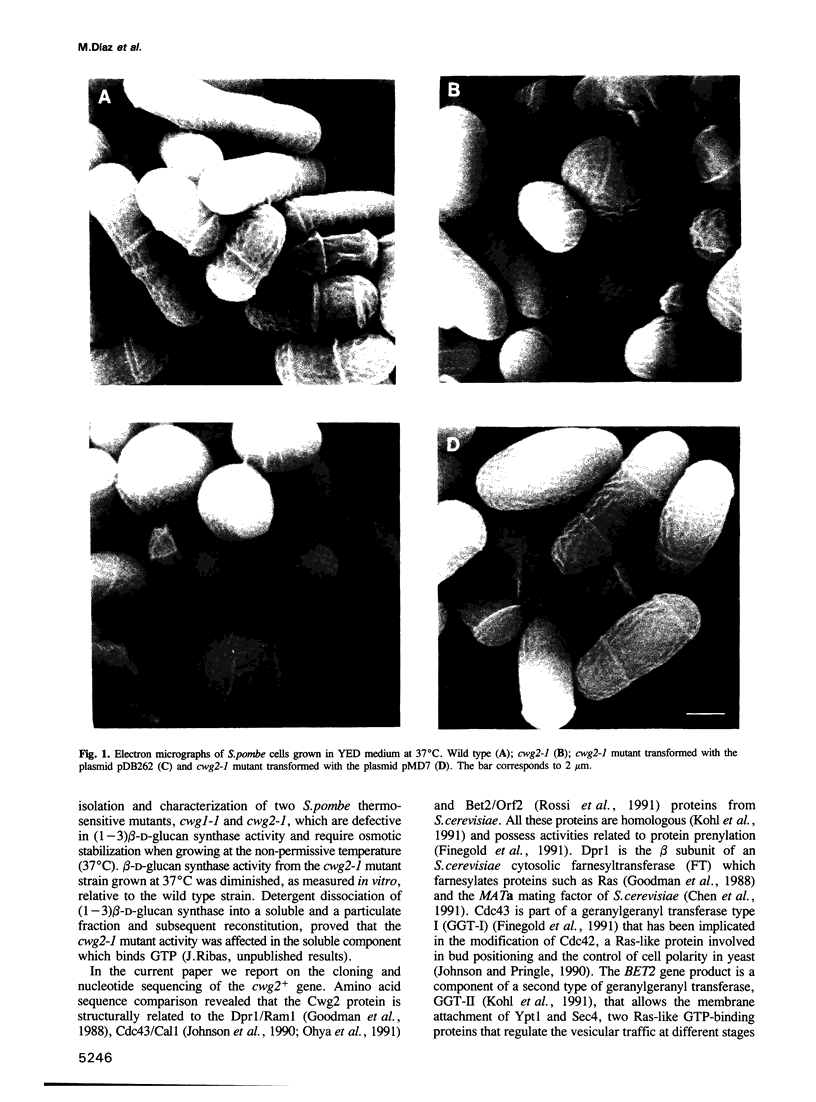
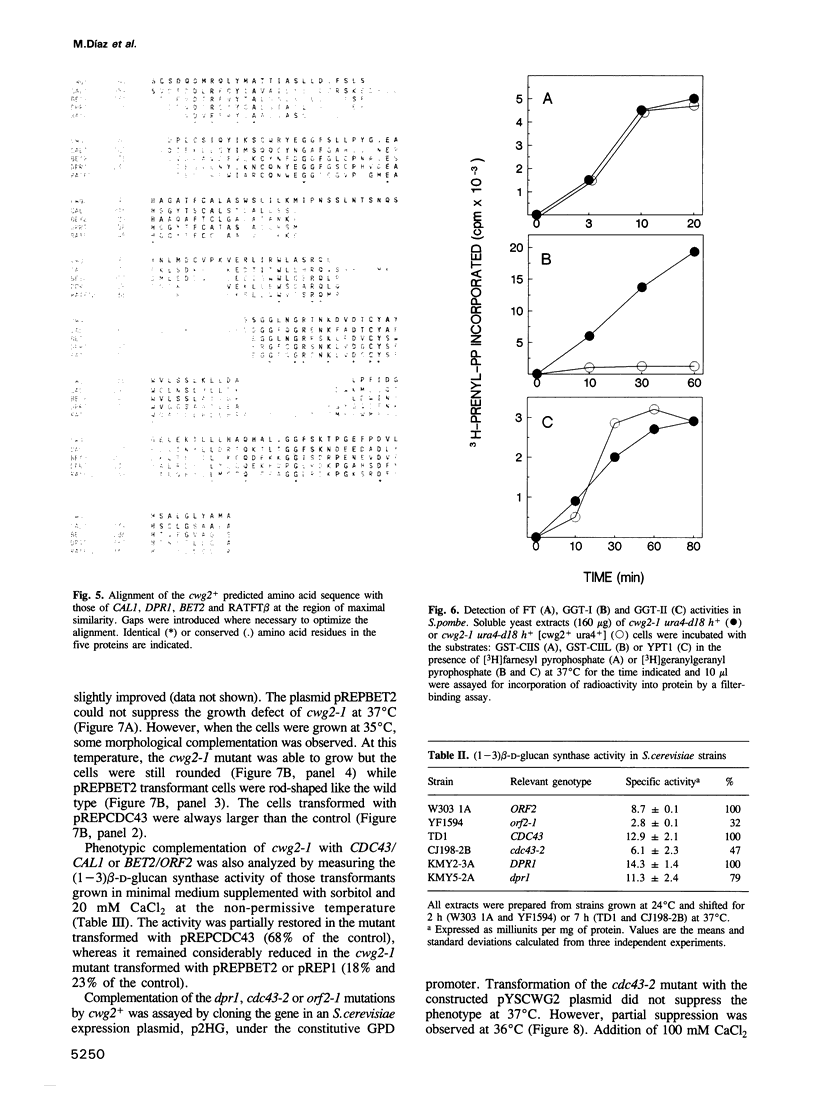
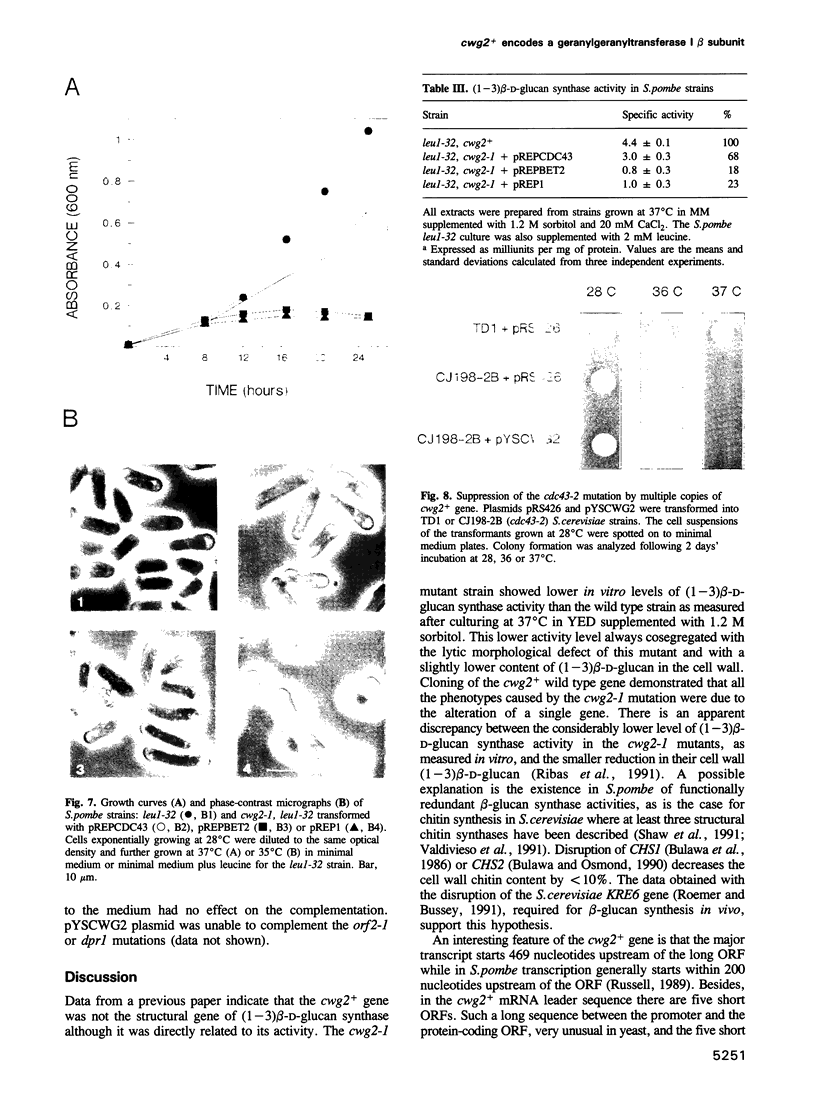
The product of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe cwg2+ gene is involved in the biosynthesis of beta-D-glucan. When grown at the non-permissive temperature, cwg2-1 mutant cells lyse in the absence of an osmotic stabilizer and display a reduced (1-3) beta-D-glucan content and (1-3) beta-D-glucan synthase activity. The cwg2+ gene was cloned by the rescue of the cwg2-1 mutant phenotype using an S. pombe genomic library and subsequently verified by integration of the appropriate insert into the S. pombe genome. Determination of the nucleotide sequence of this gene revealed a putative open reading frame of 1065 bp encoding a polypeptide of 355 amino acids with a calculated M(r) of 40,019. The cwg2+ DNA hybridizes to a main transcript, the 5' end of which maps to a position 469 bp upstream of the predicted start of translation. The sequence between the transcription and the translation start sites is unusually long and has several short open reading frames which suggest a translational control of the gene expression. Comparative analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence shows that it possesses significant similarity to three Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins, encoded by the DPR1/RAM1, CDC43/CAL1 and ORF2/BET2 genes respectively, which are beta subunits of different prenyltransferases. When grown at 37 degrees C, cwg2-1 mutant extracts were specifically deficient in geranylgeranyltransferase type I activity, as measured in vitro. Multiple copies of the CDC43 gene can partially suppress the growth and (1-3) beta-D-glucan synthase defect of the cwg2-1 mutant at the restrictive temperature. In a similar manner, the cwg2+ gene can partially suppress the cdc43-2 growth defect. These results indicate that cwg2+ is the structural gene for the beta subunit of geranylgeranyltransferase type I in S. pombe and that this enzyme is required for (1-3) beta-D-glucan synthase activity. The functional homology of Cwg2 with Cdc43, which has been implicated in the control of cell polarity, suggests a link between two morphogenetic events such as establishment of cell polarity and cell wall biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Johnson D. I., Longnecker R. M., Sloat B. F., Pringle J. R. CDC42 and CDC43, two additional genes involved in budding and the establishment of cell polarity in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):131–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G., Schmid E., Maundrell K. TATA box mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe nmt1 promoter affect transcription efficiency but not the transcription start point or thiamine repressibility. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90552-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone C., Sommer S. S., Hensel A., Bussey H. Yeast KRE genes provide evidence for a pathway of cell wall beta-glucan assembly. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1833–1843. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Osmond B. C. Chitin synthase I and chitin synthase II are not required for chitin synthesis in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7424–7428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulawa C. E., Slater M., Cabib E., Au-Young J., Sburlati A., Adair W. L., Jr, Robbins P. W. The S. cerevisiae structural gene for chitin synthase is not required for chitin synthesis in vivo. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):213–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90738-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabib E., Silverman S. J., Shaw J. A. Chitinase and chitin synthase 1: counterbalancing activities in cell separation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Andres D. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. cDNA cloning and expression of the peptide-binding beta subunit of rat p21ras farnesyltransferase, the counterpart of yeast DPR1/RAM1. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90622-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Sikorski R. S., Dante M., Shero J. H., Hieter P. Multifunctional yeast high-copy-number shuttle vectors. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. Protein isoprenylation and methylation at carboxyl-terminal cysteine residues. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:355–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell E., Bowden S., Armstrong J. A homologue of the ras-related CDC42 gene from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Gene. 1992 May 1;114(1):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90724-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Johnson D. I., Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Judd S. R., Glomset J. A., Tamanoi F. Protein geranylgeranyltransferase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is specific for Cys-Xaa-Xaa-Leu motif proteins and requires the CDC43 gene product but not the DPR1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Font de Mora J., Gil R., Sentandreu R., Herrero E. Isolation and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants resistant to aculeacin A. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2596–2601. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannakouros T., Armstrong J., Magee A. I. Protein prenylation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 3;297(1-2):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80337-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman L. E., Perou C. M., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. Structure and expression of yeast DPR1, a gene essential for the processing and intracellular localization of ras proteins. Yeast. 1988 Dec;4(4):271–281. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm C., Kohli J., Murray J., Maundrell K. Genetic engineering of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a system for gene disruption and replacement using the ura4 gene as a selectable marker. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00331307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., O'Brien J. M., Jacobs C. W. Isolation and sequence analysis of CDC43, a gene involved in the control of cell polarity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1990 May 31;90(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90443-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. I., Pringle J. R. Molecular characterization of CDC42, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in the development of cell polarity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;111(1):143–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang M. S., Cabib E. Regulation of fungal cell wall growth: a guanine nucleotide-binding, proteinaceous component required for activity of (1----3)-beta-D-glucan synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5808–5812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Diehl R. E., Schaber M. D., Rands E., Soderman D. D., He B., Moores S. L., Pompliano D. L., Ferro-Novick S., Powers S. Structural homology among mammalian and Saccharomyces cerevisiae isoprenyl-protein transferases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18884–18888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Hottinger H., Munz P., Strauss A., Thuriaux P. Genetic Mapping in SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE by Mitotic and Meiotic Analysis and Induced Haploidization. Genetics. 1977 Nov;87(3):471–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Levin D. E. Dominant mutations in a gene encoding a putative protein kinase (BCK1) bypass the requirement for a Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein kinase C homolog. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bartlett-Heubusch E. Mutants in the S. cerevisiae PKC1 gene display a cell cycle-specific osmotic stability defect. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1221–1229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Bishop J. M. A putative protein kinase gene (kin1+) is important for growth polarity in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8272–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden K., Costigan C., Snyder M. Cell polarity and morphogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;2(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90140-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Hill W. S., Ng A. S., Vogel U. S., Schaber M. D., Scolnick E. M., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B. A C-terminal domain of GAP is sufficient to stimulate ras p21 GTPase activity. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03480.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey M., Johnson J. S., Goud B., Myers A. M., Rossier J., Popoff M. R., Madaule P., Boquet P. The small GTP-binding protein Rho1p is localized on the Golgi apparatus and post-Golgi vesicles in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):309–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S., Yamamoto M. Identification of ras-related, YPT family genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1417–1422. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman C. M., Giannakouros T., Hancock J. F., Fawell E. H., Armstrong J., Magee A. I. Post-translational processing of Schizosaccharomyces pombe YPT proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11329–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Goebl M., Goodman L. E., Petersen-Bjørn S., Friesen J. D., Tamanoi F., Anraku Y. Yeast CAL1 is a structural and functional homologue to the DPR1 (RAM) gene involved in ras processing. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12356–12360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Genetic study of the role of calcium ions in the cell division cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a calcium-dependent mutant and its trifluoperazine-dependent pseudorevertants. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00382073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen-Bjørn S., Harrington T. R., Friesen J. D. An essential gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae shares an upstream regulatory element with PRP4. Yeast. 1990 Jul-Aug;6(4):345–352. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribas J. C., Diaz M., Duran A., Perez P. Isolation and characterization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe mutants defective in cell wall (1-3)beta-D-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3456–3462. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3456-3462.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roemer T., Bussey H. Yeast beta-glucan synthesis: KRE6 encodes a predicted type II membrane protein required for glucan synthesis in vivo and for glucan synthase activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11295–11299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G., Yu J. A., Newman A. P., Ferro-Novick S. Dependence of Ypt1 and Sec4 membrane attachment on Bet2. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):158–161. doi: 10.1038/351158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Rine J. Protein prenylation: genes, enzymes, targets, and functions. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:209–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Vectors for constitutive and inducible gene expression in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:389–398. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94029-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. A., Mol P. C., Bowers B., Silverman S. J., Valdivieso M. H., Durán A., Cabib E. The function of chitin synthases 2 and 3 in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):111–123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shematek E. M., Braatz J. A., Cabib E. Biosynthesis of the yeast cell wall. I. Preparation and properties of beta-(1 leads to 3)glucan synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):888–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szaniszlo P. J., Kang M. S., Cabib E. Stimulation of beta(1----3)glucan synthetase of various fungi by nucleoside triphosphates: generalized regulatory mechanism for cell wall biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1188–1194. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1188-1194.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres L., Martín H., García-Saez M. I., Arroyo J., Molina M., Sánchez M., Nombela C. A protein kinase gene complements the lytic phenotype of Saccharomyces cerevisiae lyt2 mutants. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2845–2854. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivieso M. H., Mol P. C., Shaw J. A., Cabib E., Durán A. CAL1, a gene required for activity of chitin synthase 3 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):101–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt I., Straub N., Käufer N. F., Gross T. The CAGTCACA box in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe functions like a TATA element and binds a novel factor. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1201–1208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Maundrell K., Heyer W. D., Beach D., Nurse P. Vectors for the construction of gene banks and the integration of cloned genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plasmid. 1986 Mar;15(2):156–158. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]