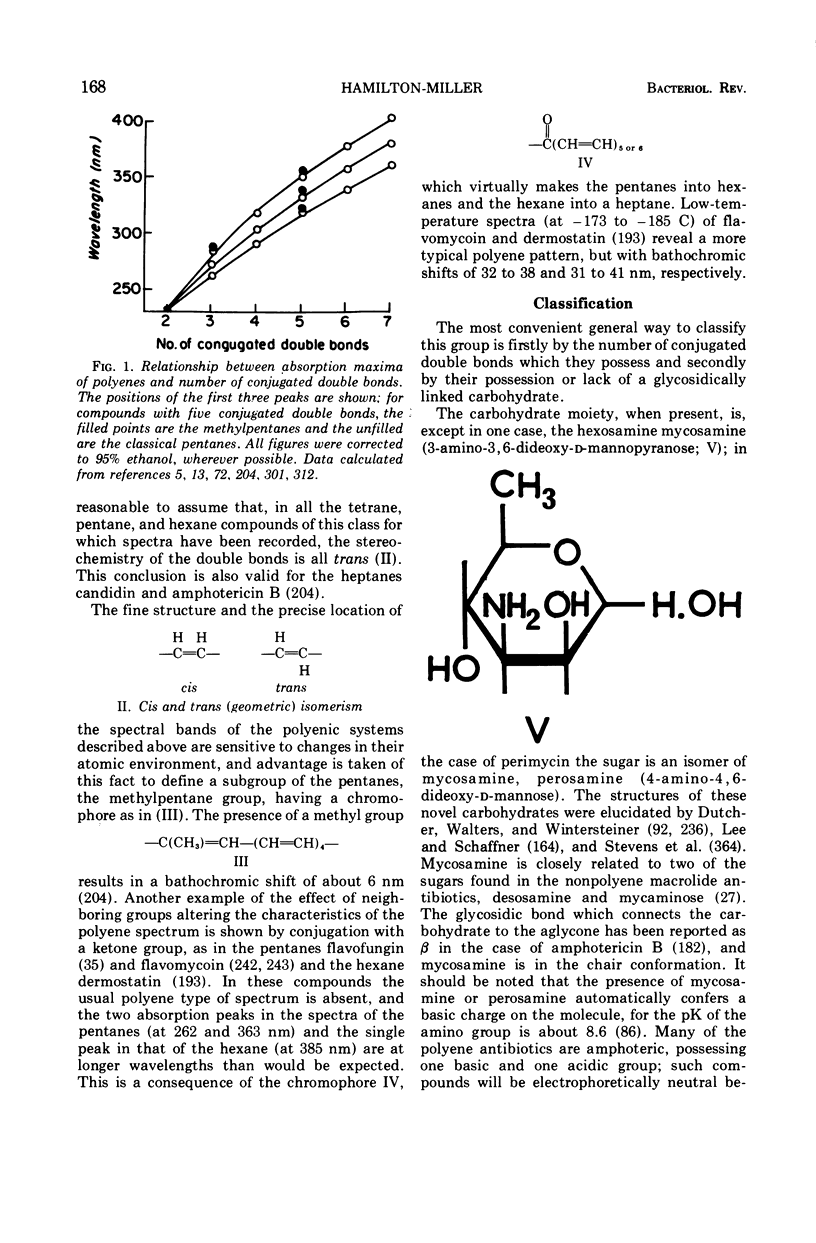
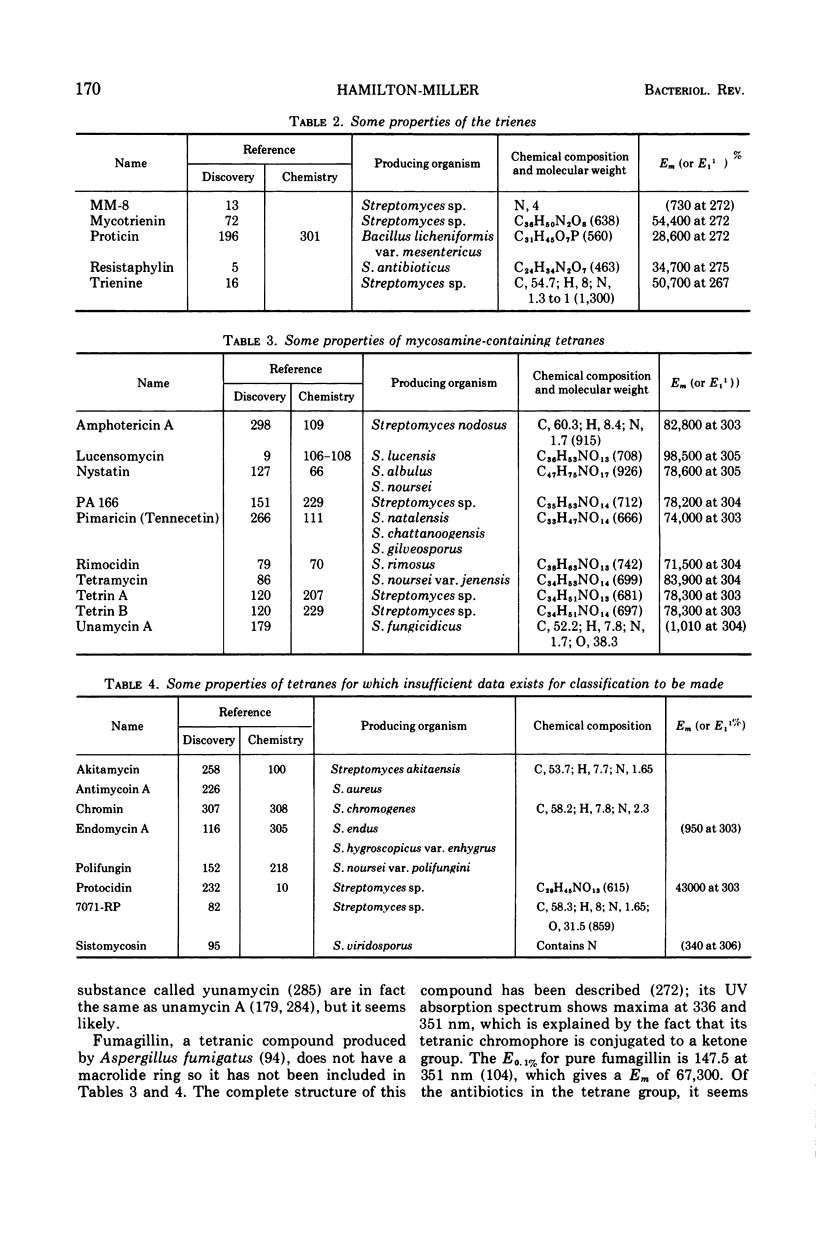
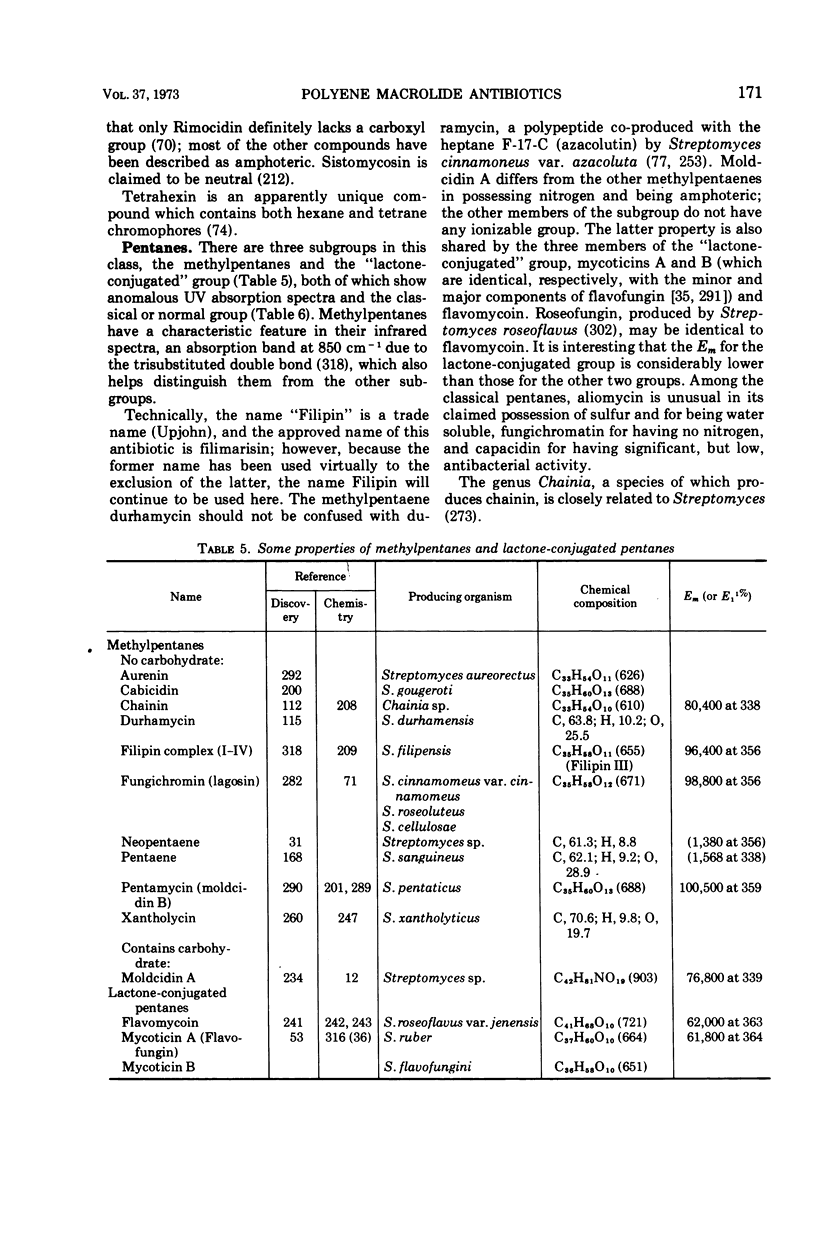
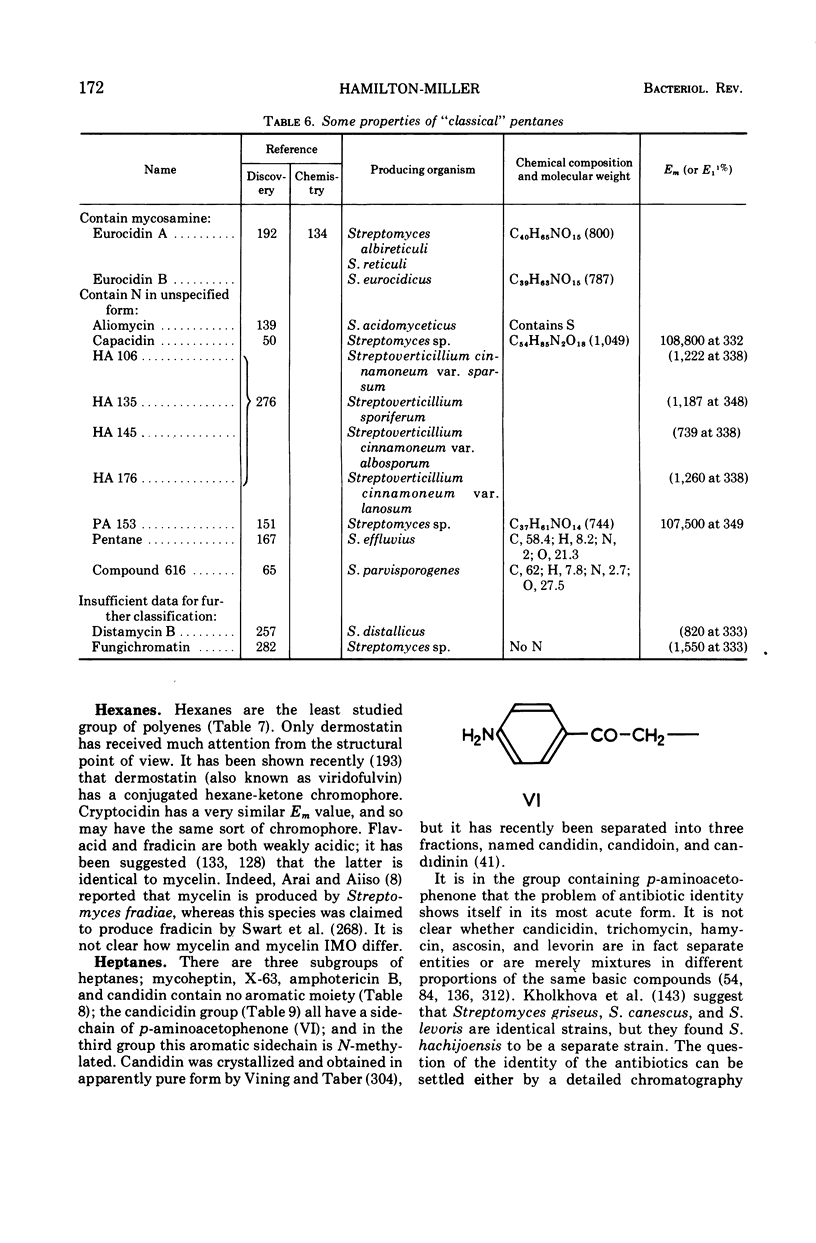
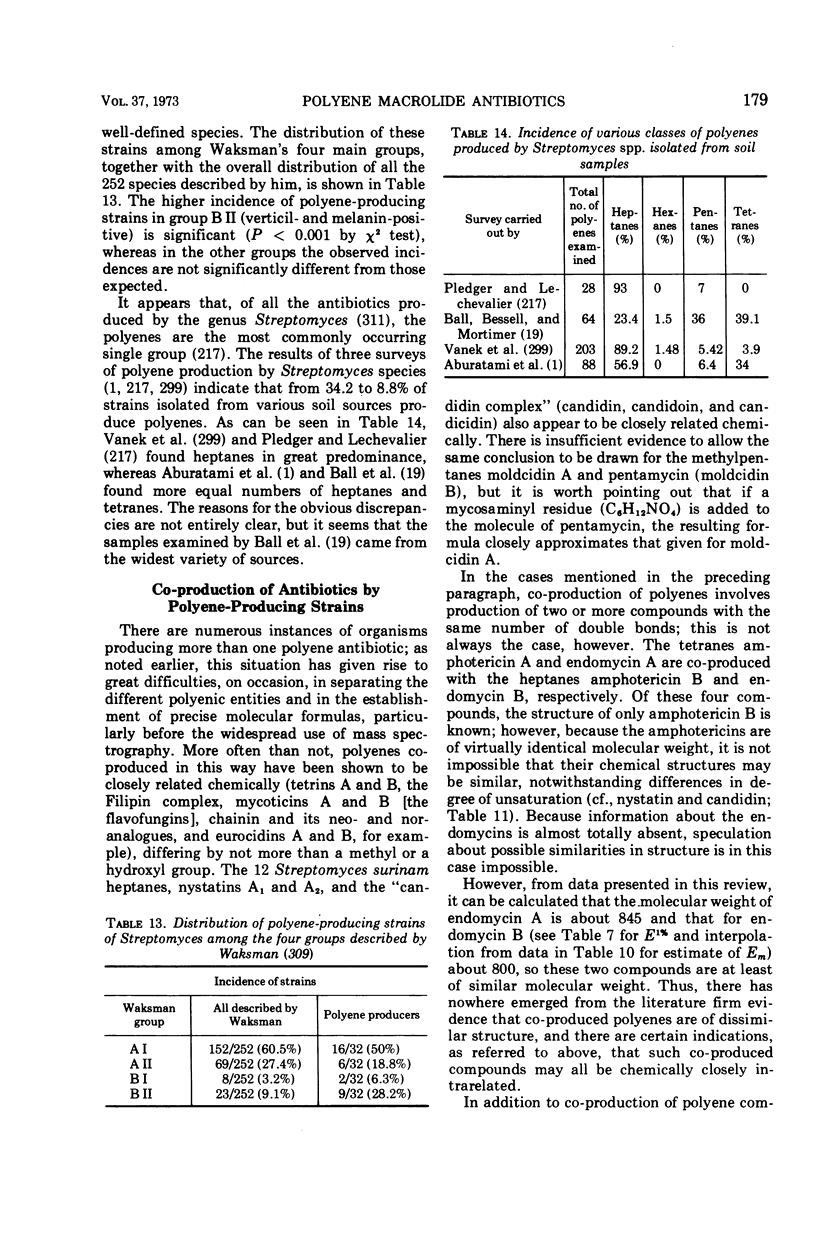
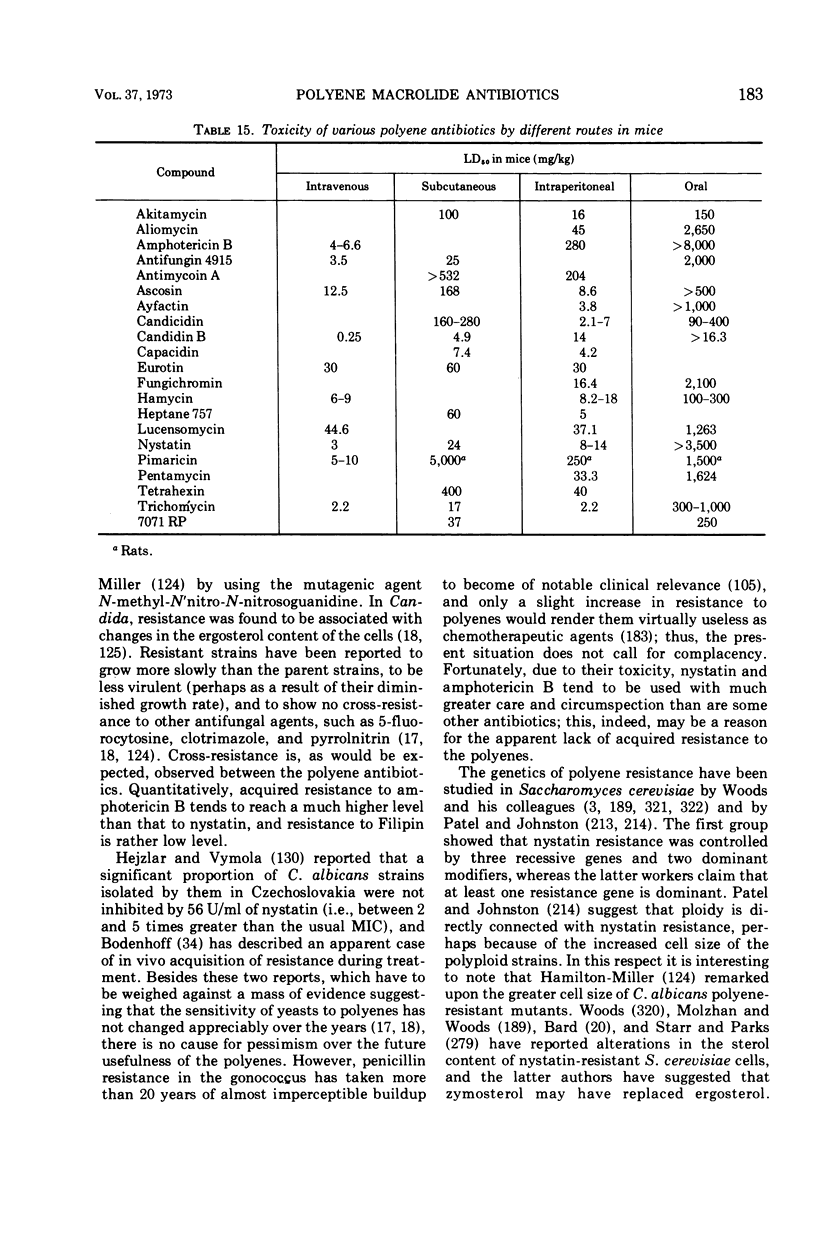
Full text
PDF




















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRIOLE V. T., KRAVETZ H. M. The use of amphotericin B in man. JAMA. 1962 Apr 28;180:269–272. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050170001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams T. H., Wong R. G., Norman A. W. Studies on the mechanism of action of calciferol. II. Effects of the polyene antibiotic, filipin, on vitamin D-mediated calcium transport. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4432–4442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed K. A., Woods R. A. A genetic analysis of resistance to nystatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genet Res. 1967 Apr;9(2):179–193. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aizawa S., Shibuya M., Shirato S. Resistaphylin, a new antibiotic. I. Production, isolation and properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jun;24(6):393–396. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli T. E., Monahan M. The interaction of polyene antibiotics with thin lipid membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):300–325. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. J., Grove J. F., Turner W. B., Ward G. AN ANTIGUNGAL TRIENE FROM A Streptomyces sp. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):399–400. doi: 10.1038/206399b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora H. R., Arora V. A study on the cardiac actions of some polyene antibiotics. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1970 Jun;185(2):234–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arret B., Johnson D. P., Kirshbaum A. Outline of details for microbiological assays of antibiotics: second revision. J Pharm Sci. 1971 Nov;60(11):1689–1694. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600601122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aszalos A., Robison R. S., Lemanski P., Berk B. Trienine, an antitumor triene antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Oct;21(10):611–615. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Athar M. A., Winner H. I. The development of resistance by candida species to polyene antibiotics in vitro. J Med Microbiol. 1971 Nov;4(4):505–517. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALL S., BESSELL C. J., MORTIMER A. The production of polyenic antibiotics by soil streptomycetes. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Aug;17(1):96–103. doi: 10.1099/00221287-17-1-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT J. E. AMPHOTERICIN B TOXICITY; REVIEW OF SELECTED ASPECTS OF PHARMACOLOGY. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Aug;61:335–340. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT J. E., WILLIAMS T. W., PIGGOTT W., EMMONS C. W. IN VIVO ACTIVITY OF COLLOIDAL HAMYCIN, AN ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBOTIC. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:166–170. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDRISS M. W., WOLFF S. M., MOORES R., STOHLMAN F., Jr ANEMIA INDUCED BY AMPHOTERICIN B. JAMA. 1964 Aug 31;189:663–666. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070090013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. The effect of oils and fatty acids on the production of filipin. Appl Microbiol. 1956 May;4(3):131–133. doi: 10.1128/am.4.3.131-133.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURKE R. C., SWARTZ J. H., CHAPMAN S. S., HUANG W. Y. Mycoticin, a new antifungal antibiotic. J Invest Dermatol. 1954 Sep;23(3):163–168. doi: 10.1038/jid.1954.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER W. T., ALLING D. W., COTLOVE E. POTASSIUM LOSS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES EXPOSED TO AMPHOTERICIN B. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:297–300. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER W. T. AMPHOTERICIN B TOXICITY; CHANGES IN RENAL FUNCTION. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Aug;61:344–349. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-2-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard M. Biochemical and genetic aspects of nystatin resistance in saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):649–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.649-657.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Action of amphotericin B on the toad bladder: evidence for sodium transport along two pathways. J Physiol. 1968 Jun;196(3):703–711. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergy M. E., Eble T. E. The filipin complex. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):653–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergy M. E., Hoeksema H. Scopafungin, a crystalline endomycin component. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jan;25(1):39–43. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betina V., Baráthová H., Baráth Z., Nemec P. Effects of polyene antibiotics on plant, fungal and animal cell membranes. Biologia (Bratisl) 1969;24(6):450–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodenhoff J. Resistance studies of Candida albicans, with special reference to two patients subjected to prolonged antimycotic treatment. Odontol Tidskr. 1968 Jun 28;76(3):279–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bognár R., Brown B. O., Lockley W. J., Makleit S., Toube T. P., Weedon B. C., Zsupán K. The structure of flavofungin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Feb;(7):471–474. doi: 10.1016/0040-4039(70)89002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bognár R., Zsupán K., Makleit S., Brown B. O., Lockley W. J., Toube T. P., Weedon B. C. Flavofungin: a mixture of 13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27-octahydroxy-31-isopropyl-14-methyl- and 13,15,17,19,21,23,25,27-octahydroxy-14-methyl-31-s-butyl-hentriaconta-2,4,6,8,10,28-hexaen-31-olide. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1972;14:1848–1856. doi: 10.1039/p19720001848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlmann F., Dehmlow E. V., Neuhahn H. J., Brandt R., Bethke H. Neue Heptaen-Makrolide. II. Grundskelett, stellung der funktionellen Gruppen und struktur der aglykone. Tetrahedron. 1970 May;26(9):2199–2207. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)92799-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlmann F., Dehmlow E. V., Neuhahn H. J., Brandt R., Reinicke B. Neue Heptaen-Makrolide. I. Charakterisierung und abbau. Tetrahedron. 1970 May;26(9):2191–2198. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)92798-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. 3. Biological properties of polyene macrolide ester salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):261–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Malyshkina M., Kotienko T., Soloviev S. Mycoheptin, a new member of non-aromatic group of heptaene macrolide antifungal antibiotics. Chemotherapy. 1964;9(6):359–369. doi: 10.1159/000220385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Malyshkina M., Soloviev S., Zimiński T. Isolation and characterization of levorin A and B, the heptaene macrolide antifungal antibiotics of "aromatic" subgroup. Chemotherapy. 1965;10(3):176–194. doi: 10.1159/000220406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Zieliński J., Ziminski T., Falkowski L., Kolodziejczyk P., Golik J., Jereczek E. Chemical studies with amphotericin B. 3. The complete structure of the antibiotic. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Sep;(45):3909–3914. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)98622-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudru I. De la résistance des Candida albicans à la nystatine. J Pharm Belg. 1969 Mar-Apr;24(3):162–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulder C. J. Anaerobic growth, ergosterol content and sensitivity to a polyene antibiotic, of the yeast Schizosaccharomyces japonicus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(3):353–358. doi: 10.1007/BF02218505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows H. J., Calam D. H. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography of polyene antifungal antibiotics: The nature of candicidin, levorin and trichomycin. J Chromatogr. 1971 Dec 23;53(3):566–571. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)98514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. T., Cotlove E. Increased permeability of human erythrocytes induced by amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1971 Apr;123(4):341–350. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIRILLO V. P., HARSCH M., LAMPEN J. O. ACTION OF THE POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS FILIPIN, NYSTATIN AND N-ACETYLCANDIDIN ON THE YEAST CELL MEMBRANE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCCHI P., BARTOLOZZI G. WATER-SOLUBLE DERIVATIVE OF NYSTATIN. PRELIMINARY CLINICAL EXPERIENCES. Chemotherapy. 1964;27:175–187. doi: 10.1159/000220308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCCHI P., RAPI G. BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE, WATER-SOLUBLE DERIVATIVES OF NYSTATIN-MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES. Chemotherapy. 1963;5358:319–325. doi: 10.1159/000220092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAVERI R., SHOTWELL O. L., DWORSCHACK R. G., PRIDHAM T. G., JACKSON R. W. Antibiotics against plant disease. VII. The antifungal hepataene component (F-17-C) produced by Streptomyces cinnamomeus f. azacoluta. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1960 Jul;10:430–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capek A., Simek A. Antimicrobial agents. XI. Microbiol degradation of fungicidin. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(5):364–366. doi: 10.1007/BF02875755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capek A., Simek A. Antimicrobial agents. XII. Relationship between biochemical resistance and microbial degradation, of antimycotics. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1971;16(6):472–475. doi: 10.1007/BF02872721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capek A., Simek A. Antimicrobial agents. XIV. Content of ergosterol and the problem of transient resistance of dermatophytes. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1972;17(3):239–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02875820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capek A., Simek A., Leiner J., Weichet J. Antimicrobial agents. VI. Antimycotic activity and problems of resistance. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1970;15(4):314–317. doi: 10.1007/BF02869060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra P., Götz A., Wacker A., Verini M. A., Casazza A. M., Fioretti A., Arcamone F., Ghione M. Some structural requirements for the antibiotic action of distamycins. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong C. N., Rickards R. W. Macrolide antibiotic studies. XVI. The structure of nystatin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Dec;(59):5145–5148. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)96962-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coronelli C., Pasqualucci R. C., Thiemann J. E., Tamoni G. Mycotrienin, a new polyene antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Nov;20(6):329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crifò Carlo, Strom Roberto, Santoro Antonio Scioscia, Mondovì Bruno. Fluorescence of lucensomycin upon binding to erythrocyte ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 15;17(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOVICK R., GOLD W., PAGANO J. F., STOUT H. A. Amphotericins A and B, antifungal antibiotics produced by a streptomycete. I. In vitro studies. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:579–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande G. R., Kerur D. R., Narasimhachari N. Chemical studies on hamycin. I. Purification, counter-current distribution and chemical degradation. Hindustan Antibiot Bull. 1966 May;8(4):185–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divekar P. V., Vora V. C., Khan A. W. Comparison of hamycin with trichomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1966 Mar;19(2):63–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornberger K., Fügner R., Bradler G., Thrum H. Tetramycin, a new polyene antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Mar;24(3):172–177. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EBLE T. E., GARRETT E. R. Studies on the stability of fumagillin. II. Photolytic degradation of crystalline fumagillin. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1954 Sep;43(9):536–538. doi: 10.1002/jps.3030430906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINGOLD D. S. THE ACTION OF AMPHOTERICIN B ON MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Apr 9;19:261–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. T., Jr, Bates J. H., Abernathy R. S. Amphotericin B serum concentrations during therapy. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):955–959. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.955-959.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. T., Jr, Bates J. H., Abernathy R. S. Effect of rapid intravenous infusion on serum concentrations of amphotericin B. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):615–617. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.615-617.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE G. R. The effects of amphotericin B on yeast metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Jul;129:257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARRETT E. R., EBLE T. E. Studies on the stability of fumagillin. I. Photolytic degradation in alcohol solution. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1954 Jul;43(7):385–390. doi: 10.1002/jps.3030430702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARRETT E. R. Studies on the stability of fumagillin. III. Thermal degradation in the presence and absence of air. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1954 Sep;43(9):539–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTLIEB D., CARTER H. E., SLONEKER J. H., AMMANN A. Protection of fungi against polyene antibiotics by sterols. Science. 1958 Aug 15;128(3320):361–361. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3320.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUPTA K. C. MONICAMYCIN, A NEW POLYENE ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBIOTIC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1964;10:65–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganis P., Avitabile G., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide antibiotic amphotericin B. Crystal structure of the N-iodoacetyl derivative. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Sep 8;93(18):4560–4564. doi: 10.1021/ja00747a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudiano G., Bravo P., Quilico A., Golding B. T., Rickards R. W. The structure of lucensomycin. II. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Jul;30:3567–3571. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)82829-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudiano G., Bravo P., Quilico A. The structure of lucensomycin. I. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Jul;30:3559–3565. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)82828-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding B. T., Rickards R. W. The structure of the macrolide antibiotic pimaricin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Jul;30:3551–3557. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)82827-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalkrishnan K. S., Narasimhachari N., Joshi V. B., Thirumalachar M. J. Chainin: a new methylpentaene antibiotic from a species of Chainia. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):597–598. doi: 10.1038/218597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordee R. S., Butler T. F., Narasimhachari N. The antifungal activity of dermostatin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Aug;24(8):561–565. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H. W., Schaffner C. P. The effect of polyene macrolides on the prostate gland and canine prostatic hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1201–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. A., Lapa E. W. Durhamycin, a Pentaene Antifungal Antibiotic from Streptomyces durhamensis sp. n. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):754–760. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.754-760.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouge T. H., Andriole V. T. An experimental model of amphotericin B nephrotoxicity with renal tubular acidosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Nov;78(5):713–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATTORI K. [Studies on trichomycin. 8. On the chemical structure of trichomycin A]. J Antibiot B. 1962 Apr;15:39–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAZEN E. L., BROWN R. Two antifungal agents produced by a soil actinomycete. Science. 1950 Oct 13;112(2911):423–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBEKA E. K., SOLOTOROVSKY M. DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE TO POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS IN CANDIDA ALBICANS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1533–1539. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1533-1539.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEBEKA E. K., SOLOTOROVSKY M. Development of strains of Candida albicans resistant to candidin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:237–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.237-241.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL G. J., 2nd AMPHOTERICIN B TOXICITY; CHANGES IN RENAL MORPHOLOGY. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Aug;61:349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORVATH I., KOCZKA I. INCREASE OF EFFECTIVENESSOF POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS , WITH UNIVALENT CATIONS. Nature. 1964 Sep 19;203:1305–1306. doi: 10.1038/2031305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Physiological properties of mutagen-induced variants of Candida albicans resistant to polyene antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Nov;5(4):425–440. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-4-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Sterols from polyene-resistant mutants of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):201–203. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. The effect of pH and of temperature on the stability and bioactivity of nystatin and amphotericin B. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 May;25(5):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejzlar M., Výmola F. Preliminary report. Comparative study of pimaricin and fungicidin activity in vitro. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1970;14(2):211–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeprich P. D., Finn P. D. Obfuscation of the activity of antifungal antimicrobics by culture media. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):353–361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii S., Shima T., Ouchida A. Partial structure of the eurocidin complex. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Feb;23(2):102–104. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. E., Dietz A. Scopafungin, a crystalline antibiotic produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. enhygrus var. nova. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):303–308. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.303-308.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C. COMPARATIVE RESPONSES OF MAMMALIAN ERYTHROCYTES AND MICROBIAL PROTOPLASTS TO POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS AND VITAMIN A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Aug;102:180–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C. Effect of polyene antibiotics on protoplasts of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.351-358.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOE B. K., TANNER F. W., Jr, RAO K. V., SOBIN B. A., CELMER W. D. Pa 150, PA 153, and PA 166: new polyene antifungal antibiotics. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:897–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan V. L., Khan A. W., Kutty M. R., Vora V. C. A new heptaene antibiotic (X-63) from a streptomyces species. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Sep;20(5):293–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibiotic interaction with model membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. Further studies on the hemolytic action of filipin and derivatives. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Luse S. A., Zopf D., van Deenen L. L., Haxby J. Interaction of filipin and derivatives with erythrocyte membranes and lipid dispersions: electron microscopic observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):844–861. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Luse S. A., van Deenen L. L. Interaction of polyene antibiotics with natural and artificial membrane systems. Fed Proc. 1966 Sep-Oct;25(5):1503–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotiuszko D., Wituch K., Morawska H., Siejko D. Polifungin, a new antifungal antibiotic. I. Morphological, cultural, and physiological properties of Streptomyces sp. strain producing a new complex of tetraene antibiotics. Acta Microbiol Pol A. 1971;4(1):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., ARNOW P. M., BOROWSKA Z., LASKIN A. I. Location and role of sterol at nystatin-binding sites. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1152–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1152-1160.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., ARNOW P. M., SAFFERMAN R. S. Mechanism of protection by sterols against polyene antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:200–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.200-206.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., GILL J. W., ARNOW P. M., MAGANA-PLAZA I. INHIBITION OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM BY CERTAIN POLYENE ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBIOTICS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Nov;86:945–949. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.5.945-949.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., MORGAN E. R., SLOCUM A., ARNOW P. Absorption of nystatin by microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1959 Aug;78:282–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.2.282-289.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHEVALIER H., BOROWSKI E., LAMPEN J. O., SCHAFFNER C. P. Water-soluble N-acetyl derivatives of heptaene macrolide antifungal antibiotics: microbiological studies. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Oct;11:640–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECHEVALIER H., PLEDGER R. A. Survey of the production of polyenic substances by soil streptomycetes. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHTBOWN J. W., KOGUT M., UEMURA K. THE INTERNATIONAL STANDARD FOR NYSTATIN. Bull World Health Organ. 1963;29:87–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTMAN M. L., PISANO M. A., LANCASTER R. M. Induced resistance of Candida species to nystatin and amphotericin B. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:981–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONES G. W., PEACOCK C. L. Alterations in Candida albicans during growth in the presence of amphotericin B. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1959 Sep;9:535–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampen J. O. Amphotericin B and other polyenic antifungal antibiotics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Aug;52(2):138–146. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier H. A., Lechevalier M. P., Gerber N. N. Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of actinomycetes. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1971;14:47–72. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70539-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Schaffner C. P. Perimycin. The structure of some degradation products. Tetrahedron. 1969 May;25(10):2229–2232. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)82770-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. H., Schaffner C. P. Perimycin: chemistry of perosamine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Nov;47:5837–5840. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)76093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. M., McDaniel L. E., Schaffner C. P. Fungimycin, biogenesis of its aromatic moiety. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Mar;25(3):187–188. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. M., McDaniel L. E., Schaffner C. P. Studies on candicidin biogenesis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Feb;25(2):116–121. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINI F., ARNOW P., LAMPEN J. O. The effect of monovalent cations on the inhibition of yeast metabolism by nystatin. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jan;24:51–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUOKA M., UMEZAWA H. Unamycin, an antifungal substance produced by Streptomyces fungicidicus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1960 Mar;13:114–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHALSKA E. MICROBIOLOGICAL STUDIES ON N-SUCCINYL-PERIMYCIN: THE DETERMINATION OF SENSITIVITY OF CLINICAL STRAINS OF CANDIDA. Chemotherapy. 1964;9(1):52–60. doi: 10.1159/000220341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOAT A. G., PETERS N., Jr, SRB A. M. Selection and isolation of auxotrophic yeast mutants with the aid of antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jun;77(6):673–677. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.6.673-677.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHAN R. R., PIANOTTI R. S., MARTIN J. F., RINGEL S. M., SCHWARTZ B. S., BAILEY E. G., MCDANIEL L. E., SCHAFFNER C. P. FUNGIMYCIN PRODUCTION, ISOLATION, BIOSYNTHESIS, AND IN VITRO ANTIFUNGAL ACTIVITY. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:462–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniar A. C., Mavdikar S. Biological activities of hamycin. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Apr;12(2):377–384. doi: 10.1139/m66-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manwaring D. G., Rickards R. W., Gaudiano G., Nicolella V. The biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic lucensomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Nov;22(11):545–550. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. I. N-acylation and esterification reactions with amphotericin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S., Kwan C. N., Schlessinger D., Venkov P. Potentiation of rifampicin and 5-fluorocytosine as antifungal antibiotics by amphotericin B (yeast-membrane permeability-ribosomal RNA-eukaryotic cell-synergism). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):196–199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalska-Trenkner E. Induced resistance of C. albicans strains to sodium salt of N-succinyl perimycin. Chemotherapy. 1970;15(1):19–25. doi: 10.1159/000220661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molzahn S. W., Woods R. A. Polyene resistance and the isolation of sterol mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):339–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondovì B., Strom R., Finazzi Agrò A., Caiafa P., De Sole P., Bozzi A., Rotilio G., Rossi Fanelli A. Effect of polyenic antibiotics on Ehrlich ascites and Novikoff hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 1971 May;31(5):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasimhachari N., Swami M. B. Dermostatin: a revised hexaene structure. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Nov;23(11):566–566. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesemann G., Präve P., Sukatsch D., Vértesy L. Ein Polyen-Antibiotikum aus Bakterien. Naturwissenschaften. 1972 Feb;59(2):81–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00593477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Demel R. A., de Kruyff B., van Deenen L. L. Studies on the biological properties of polyene antibiotics. Evidence for the direct interaction of filipin with cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1918–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMI Y., UTAHARA R., NAKAMURA S., UMEZAWA H. Studies on antibiotic actinomycetes. IX. On Streptomyces producing a new antifungal substance mediocidin and antifungal substances of fungicidin-rimocidin-chromin group, eurocidin group and trichomycin-ascosin-candicidin group. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1954 May;7(3):98–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OROSHNIK W., MEBANE A. D. THE POLYENE ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBIOTICS. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1963;21:17–79. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-7149-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OROSHNIK W., VINING L. C., MEBANE A. D., TABER W. A. Polyene antibiotics. Science. 1955 Feb 4;121(3136):147–149. doi: 10.1126/science.121.3136.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSWALD E. J., RANDALL W. A., REEDY R. J. An antifungal agent, 1968, produced by a new Streptomyces species. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:236–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGANO J. F., STOUT H. A. Resistance studies with nystatin. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:704–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY H. O., ULRICH J. A. Laboratory studies on endomycin, with special reference to its antifungal effect against Candida albicans. J Invest Dermatol. 1955 Jun;24(6):623–631. doi: 10.1038/jid.1955.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., German V. F., Nishikawa Y., Rinehart K. L., Jr Polyene antibiotics. II. The strucutre of tetrin A. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jul 28;93(15):3738–3747. doi: 10.1021/ja00744a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Narasimhachari N., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Millington D. S. Polyene antibiotics. IV. Structure of chainin. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 14;94(12):4306–4310. doi: 10.1021/ja00767a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Polyene antibiotics. V. Characterization of components of the filipin complex by mass spectrometry. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Aug;23(8):414–417. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansy F. E., Basch H., Jambor W. P., Maestrone G., Semar R., Donovick R. Hamycin: in vitro and in vivo studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1966;6:399–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pansy F. E., Jambor W. P., Wilber-Murphy J., Gadebusch H. H. Comparative chemotherapeutic activities of heptaene macrolide antifungal antibiotics in experimental candidiasis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jul;25(7):405–408. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. V., Johnston J. R. Dominant mutation for nystatin resistance in yeast. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Jan;16(1):164–165. doi: 10.1128/am.16.1.164-165.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. V., Johnston J. R. Kinetics of action of nystatin on yeast. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):449–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAGNI G., SZYBALSKI W., BOROWSKI E., SCHAFFNER C. P. N-Acetylcandidin, a water-soluble polyene antibiotic for fungal prophylaxis and decontamination of tissue cultures. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Dec;11:797–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPI G., COCCHI P., BELGODERE E. BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE, WATER-SOLUBLE DERIVATIVES OF NYSTATIN-CHEMICAL STUDIES. Chemotherapy. 1963;5358:326–343. doi: 10.1159/000220093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. BINDING OF NYSTATIN BY MYCOPLASMA (PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 13;78:771–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafalski A., Raczyñska-Bojanowska K. Synthesis of malonate and methylmalonate and the formation of polyene antibiotics. Acta Biochim Pol. 1972;19(1):71–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. N. Cutaneous and venereal diseases seen at a drug-orientated youth clinic. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Oct;104(4):438–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickards R. W., Smith R. M., Golding B. T. Macrolide antibiotic studies. XV. The autoxidation of the polyenes of the filipin complex and lagosin. Jpn J Antibiot. 1970 Dec;23(6):603–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart K. L., Jr, Tucker W. P., Pandey R. C. Polyene antibiotics. 3. The structure of tetrin B. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jul 28;93(15):3747–3751. doi: 10.1021/ja00744a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison R. S., Aszalos A., Kraemer N., Giannini S. M. Production of fungichromin by streptoverticillium cinnamomeum subsp. cinnamomeum NRRL B-1285. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):273–273. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszkowski J., Kotiuszko D., Rafalski A., Morawska H., Raczyńska-Bojanowska K. Characteristics of mutants of Streptomyces noursei var. polifungini producing antibiotics. Acta Microbiol Pol B. 1972;4(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAMOTO J. M. Etude sur antibiotique antifongique. I. La protocidine, un nouvel antibiotique produit par les Streptomycete. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1957 May;10(3):128–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAMOTO J. M. Etude sur antibiotique antifongique. II. La cryptocidine, un nouvel antibiotique produit par les streptomycete. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Jan;12(1):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAMOTO J. M. [Study on an antifugal antibiotic. III. Moldcidine A, a new antibiotic produced by a streptomycete]. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Jul;12:169–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTARELLI C. G. IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC STUDIES OF SENSITIVE AND NYSTATIN-RESISTANT STRAINS OF CANDIDA ALBICANS AND CANDIDA STELLATOIDEA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1964;10:364–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER C. P., BOROWSKI E. Biologically active N-acyl derivatives of polyene macrolide antifungal antibiotics. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Nov;11:724–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER C. P., STEINMAN I. D., SAFFERMAN R. S., LECHEVALIER H. Role of inorganic salts and mevalonic acid in the production of a tetraenic antifungal antibiotic. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:869–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., LAMPEN J. O. Inhibition by antibiotics of the growth of bacterial and yeast protoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:508–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.508-512.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOVEV S. N., SEVERINETS L. Ia. VYDELENIE, SVO ISTVA, REZDELENIE NA KOMPONENTY ANTIBIOTIKA 1130-12. Antibiotiki. 1965 Jan;10:9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SORENSEN L. J., McNALL E. G., STERNBERG T. H. The development of strains of Candida albicans and Coccidioides immitis, which are resistant to amphotericin B. Antibiot Annu. 1958;6:920–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STILLER E. T., VANDEPUTTE J., WACHTEL J. L. Amphotericins A and B, antifungal antibiotics produced by a streptomycete. II. The isolation and properties of the crystalline amphotericins. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRUYK A. P., HOETTE I., DROST G., WAISVISZ J. M., VAN EEK T., HOOGERHEIDE J. C. Pimaricin, a new antifungal antibiotic. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:878–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTTON D. D., ARNOW P. M., LAMPEN J. O. Effect of high concentrations of nystatin upon glycolysis and cellular permeability in yeast. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Oct;108:170–175. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Gordon H. W. The hypocholesterolemic activity of orally administered polyene macrolides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):36–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Mechlinski W. Polyene macrolide derivatives. II. Physical-chemical properties of polyene macrolide esters and their water soluble salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):259–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Thrum H. A new polyene antibiotic, flavomycoin. Structural investigations. I. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jun;24(6):360–367. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Thrum H. A new polyene antibiotic, flavomycoin. Structural investigations. II. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Jun;24(6):368–374. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Thrum H. Flavomycoin, ein neues antifungales Polyenantibiotikum. Experientia. 1968 Jan 15;24(1):11–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02136760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder F., Holland J. F., Bieber L. L. Fluorometric evidence for the binding of cholesterol to the filipin complex. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Dec;24(12):846–849. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Weissmann G. Effects of four components of the polyene antibiotic, filipin, on phospholipid spherules (liposomes) and erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4364–4371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy S., McCay J. A., Schwartz S. I. Bioassay for hamycin and amphotericin B in serum and other biological fluids. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):497–503. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.497-503.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Coggins C. H., Lichtenstein N. S., Leaf A. Evidence for a mucosal effect of aldosterone on sodium transport in the toad bladder. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1640–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI105471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert G., Kieslich K. Preparation and ultraviolet light-induced transformation of an antifungal mixture of heptaene antibiotics of Streptomyces surinam. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jun;21(6):1007–1010. doi: 10.1128/am.21.6.1007-1010.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. An enrichment method for auxotrophic yeast mutants using the antibiotic 'nystatin'. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):206–207. doi: 10.1038/211206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava O. P., Kannan L. V., Kutty M. R., Vora V. C. Effect of serum on the growth of Candida albicans and on the activity of some antifungal antibiotics in vitro. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1965 Jul;18(4):158–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI I. A new antifungal substance flavacid; studies on the antibiotic substances from Actinomyces, XXVII. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1953 Jul;6(3):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIRUMALACHAR M. J. Chainia, a new genus of the Actinomycetales. Nature. 1955 Nov 12;176(4489):934–935. doi: 10.1038/176934b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TINGSTAD J. E., GARRETT E. R. Studies on the stability of filipon. I. Thermal degradation in the presence of air. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1960 Jun;49:352–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi S., Yonehara H. Stereochemical characteristics of variotin as deduced from the nuclear Overhauser effect in the NMR spectra. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Apr;22(4):179–180. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. D., Starr P. R., Parks L. W. Sterol accumulation in a mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in ergosterol production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 18;43(6):1304–1309. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouvenot D. R., Bourgeois C. M. Optimisation de la sélection de mutants de Saccharomyces cerevisiae par la nystatine. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1971 May;120(5):617–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treatment of fungal diseases. A statement by the committee on therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Dec;100(6):908–910. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UEDA M., UMEZAWA H. Observation on the simultaneous production of actinoleukin and trichomycin group antibiotic by a Streptomyces. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1956 Mar;9(2):86–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UMEZAWA S., TANAKA Y., OOKA M., SHIOTSU S. A new antifungal antibiotic, pentamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1958 Jan;11(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URI J., BEKESI I. Flavofungin, a new crystalline antifungal antibiotic: origin and biological properties. Nature. 1958 Mar 29;181(4613):908–908. doi: 10.1038/181908a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UTAHARA R., OKAMI Y., NAKAMURA S., UMEZAWA H. On a new antifungal substance, mediocidin, and other antifungal substances of Streptomyces with three characteristic absorption maxima. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1954 Aug;7(4):120–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UTAHARA R., YAMAZAKI H., OKAMI Y., UMEZAWA H. A new source of fradicinmycelin like antifungal antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Mar;12(2):73–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UTZ J. P. AMPHOTERICIN B TOXICITY; GENERAL SIDE EFFECTS. Ann Intern Med. 1964 Aug;61:340–343. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-61-2-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utz J. P., Shadomy H. J., Shadomy S. Clinical and laboratory studies of a new micronized preparation of hamycin in systemic mycoses in man. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1967;7:113–117. doi: 10.1128/AAC.7.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANEK Z., DOLEZILOVA L., REHACEK Z. Formation of a mixture of antibiotic substances including antibiotics of a polyene character, by strains of actinomycetes freshly isolated from soil samples. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Jun;18(3):649–657. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-3-649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINING L. C. The polyene antifungal antibiotics. Hindustan Antibiot Bull. 1960 Nov;3:37–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetlugina L. A. Antibiotik rozeofungin, vydelenie i fiziko-khimicheskie svoistva. Antibiotiki. 1968 Nov;13(11):992–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vértesy L. Proticin, a new phosphorus-containing antibiotic. II. Characterization and chemical studies. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jan;25(1):4–10. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN S. A. THE ACTINOMYCETES AND THEIR ANTIBIOTICS. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1963;5:235–315. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER M. M., KINSKY S. C. EFFECT OF CHOLESTEROL ON THE SENSITIVITY OF MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII TO THE POLYENE ANTIBIOTIC FILIPIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:306–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.306-312.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman S. A., Lechevalier H. A., Schaffner C. P. Candicidin and other polyenic antifungal antibiotics. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(2):219–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewski C., Jr Allergic contact dermatitis from nystatin. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Aug;102(2):216–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasilewski C., Jr Allergic contact dermatitis from nystatin. Arch Dermatol. 1971 Oct;104(4):437–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman H. H., Van Verth J. E., McCaustland D. J., Borowitz I. J., Kamber B. The mycoticins, polyene macrolides from Streptomyces ruber. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Mar 15;89(6):1535–1536. doi: 10.1021/ja00982a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. G., Adams T. H., Roberts P. A., Norman A. W. Studies on the mechanism of action of calciferol. IV. Interaction of the polyene antibiotic, filipin, with intestinal mucosal membranes from vitamin D-treated and vitamin D-deficient chicks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;219(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods R. A., Ahmed K. A. Genetically controlled cross resistance to polyene antibiotics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):369–370. doi: 10.1038/218369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods R. A. Nystatin-resistant mutants of yeast: alterations in sterol content. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):69–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.69-73.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONEHARA H., TAKEUCHI S., UMEZAWA H., SUMIKI Y. Variotin, a new antifungal antibiotic, produced by Paecilomyces varioti Bainier var. antibioticus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 May;12(3):109–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt W. A. Intracellular Loss of Potassium in Candida albicans After Exposure to Polyene Antifungal Antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Nov;14(6):953–956. doi: 10.1128/am.14.6.953-956.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt W. A., Tavormina P. A. Steroid interference with antifungal activity of polyene antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Nov;14(6):865–869. doi: 10.1128/am.14.6.865-869.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zutphen H., Demel R. A., Norman A. W., van Deenen L. L. The action of polyene antibiotics on lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of several cations and anions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):310–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


