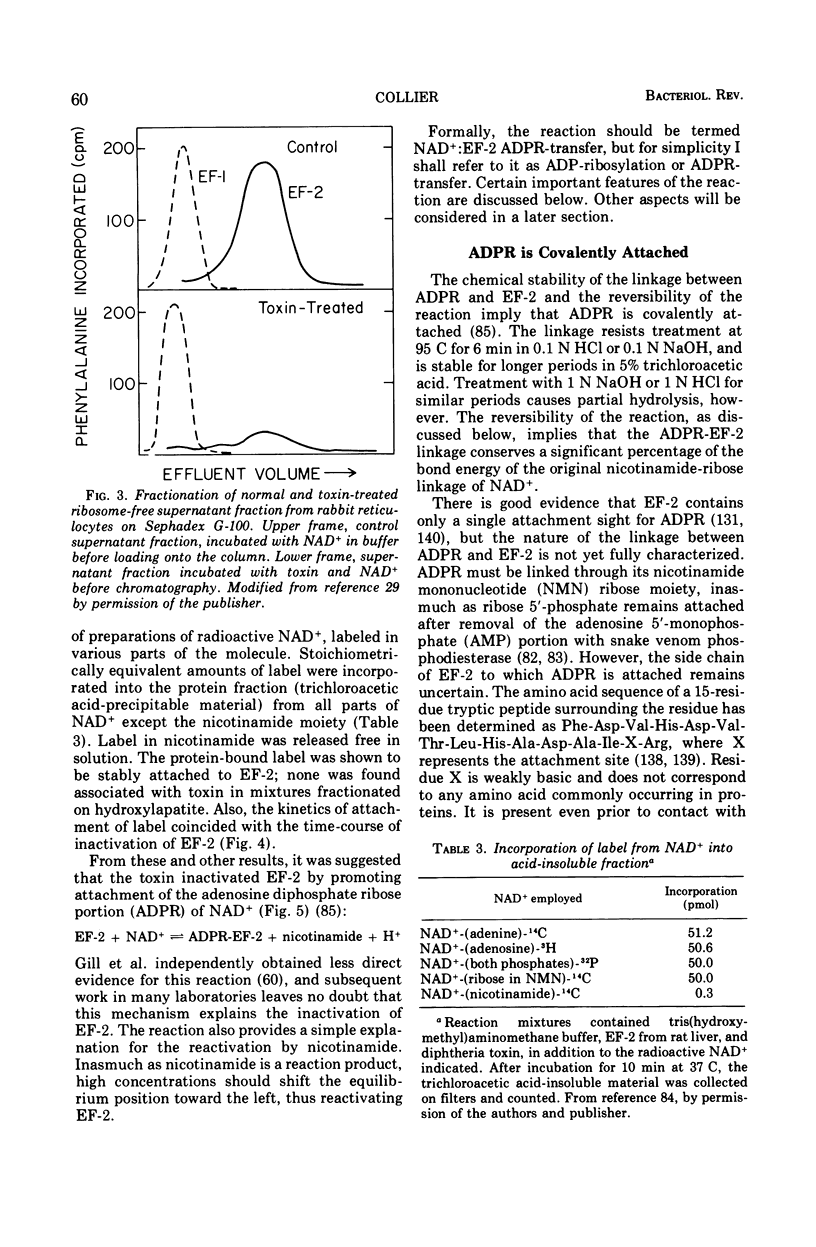
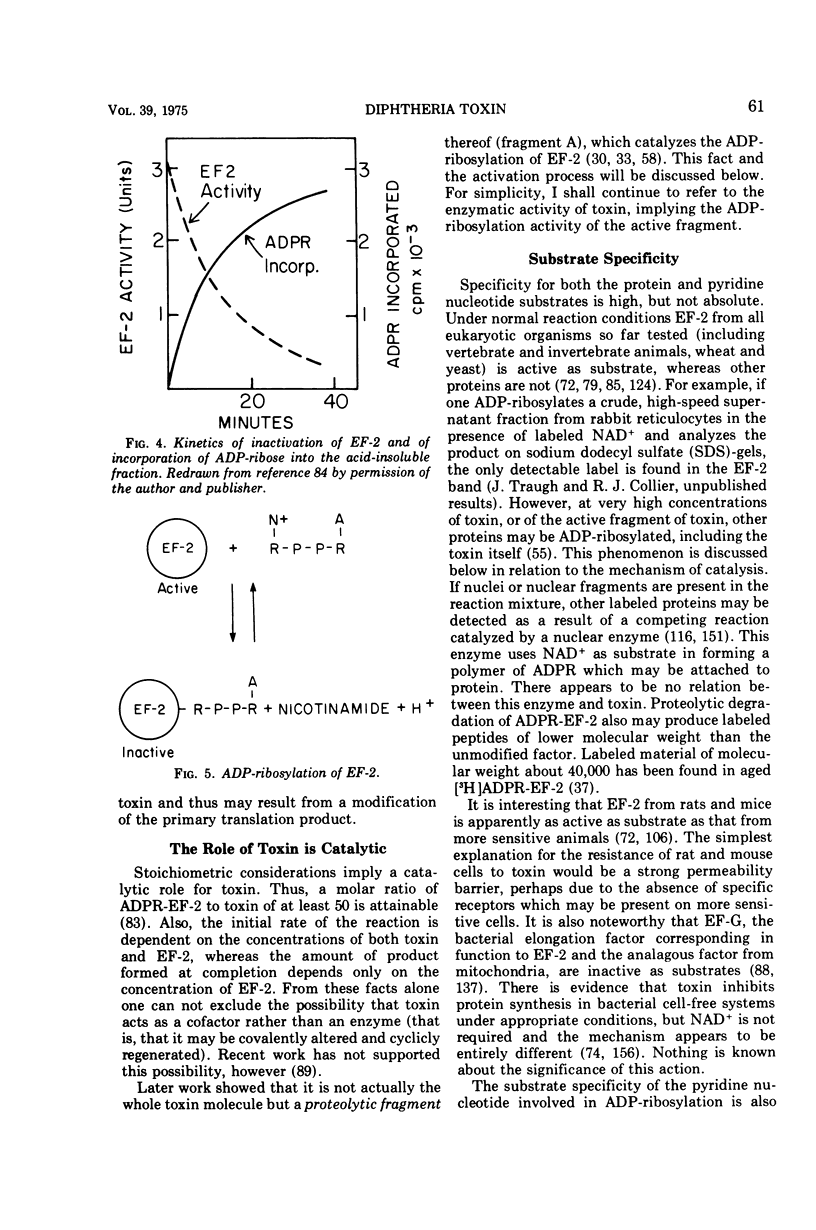
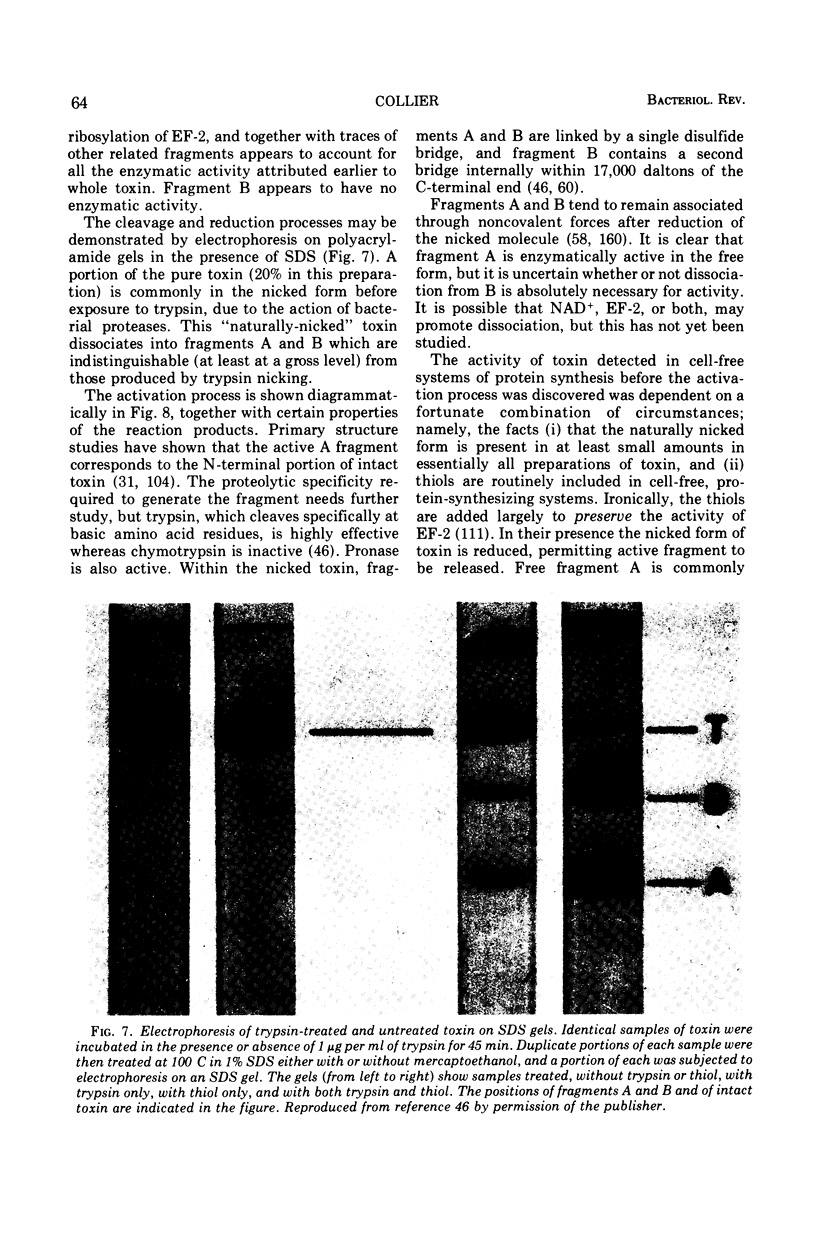
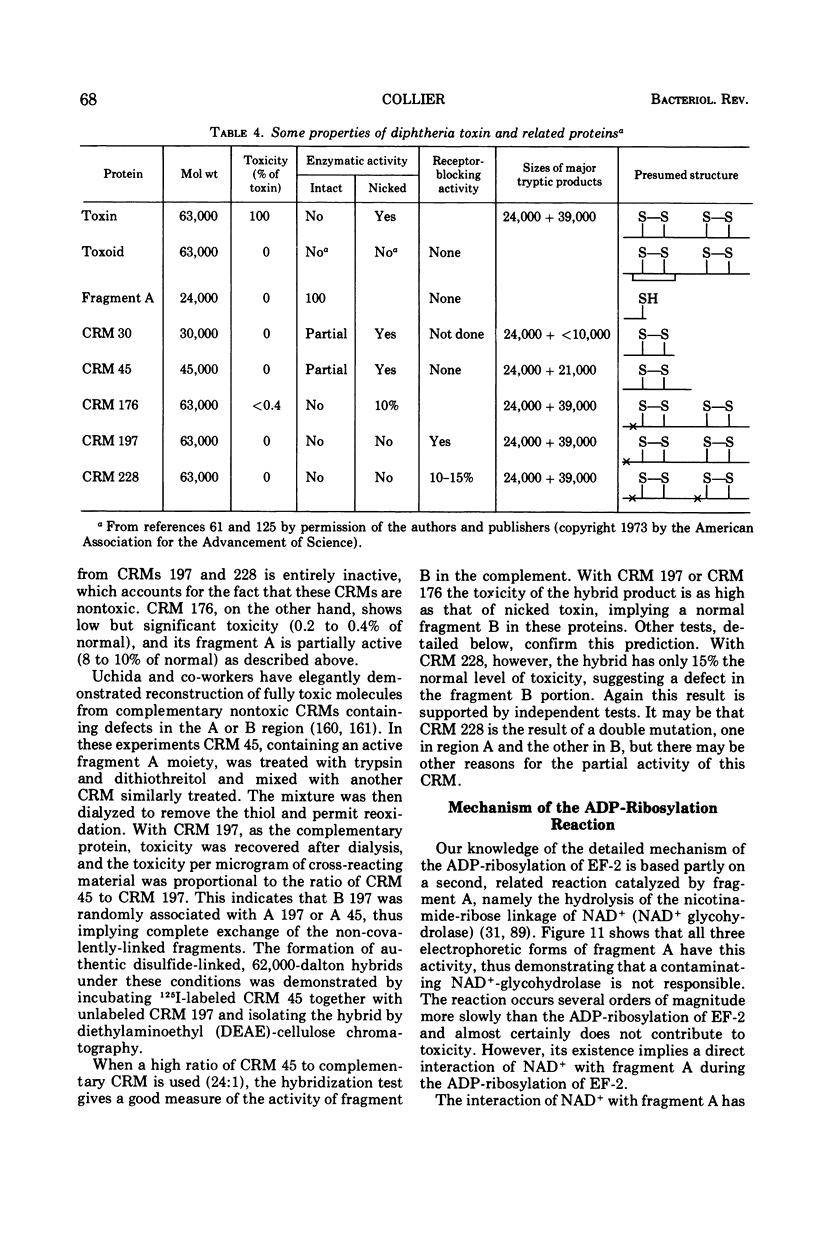
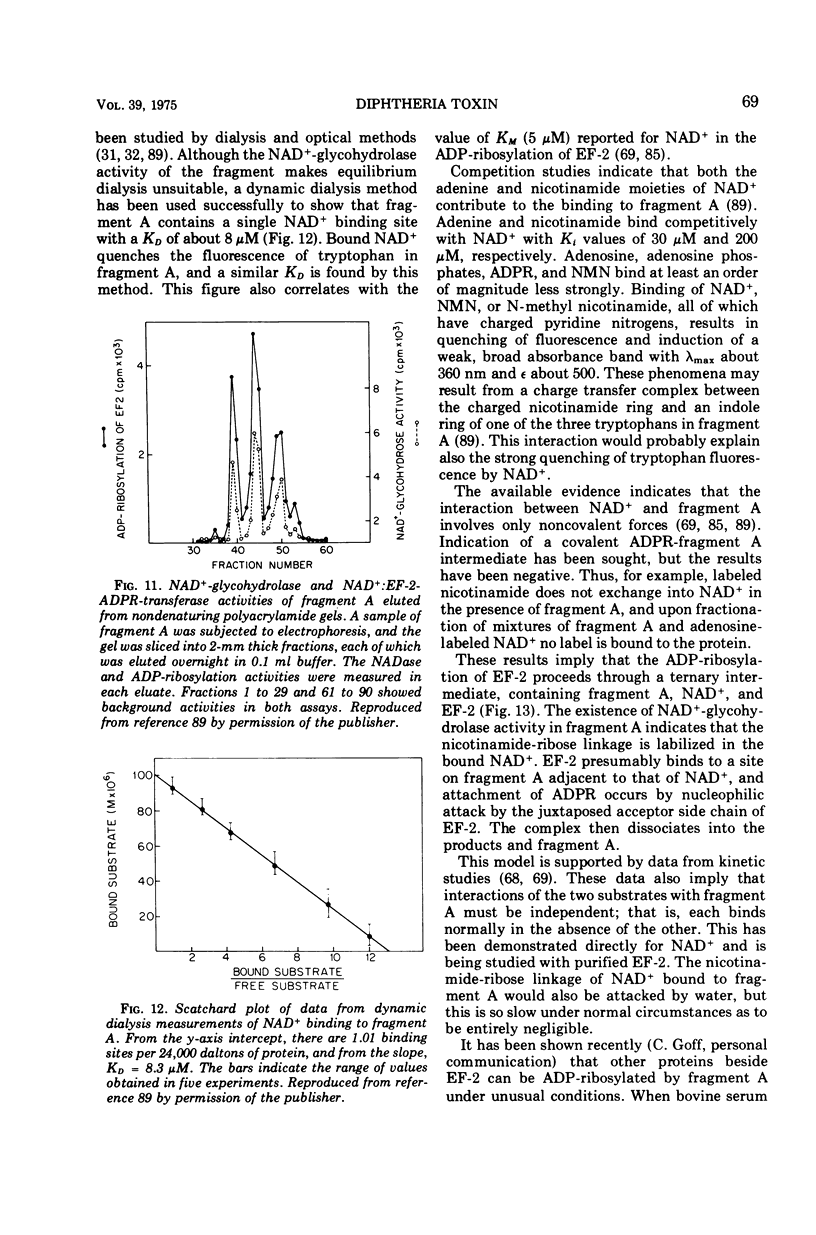
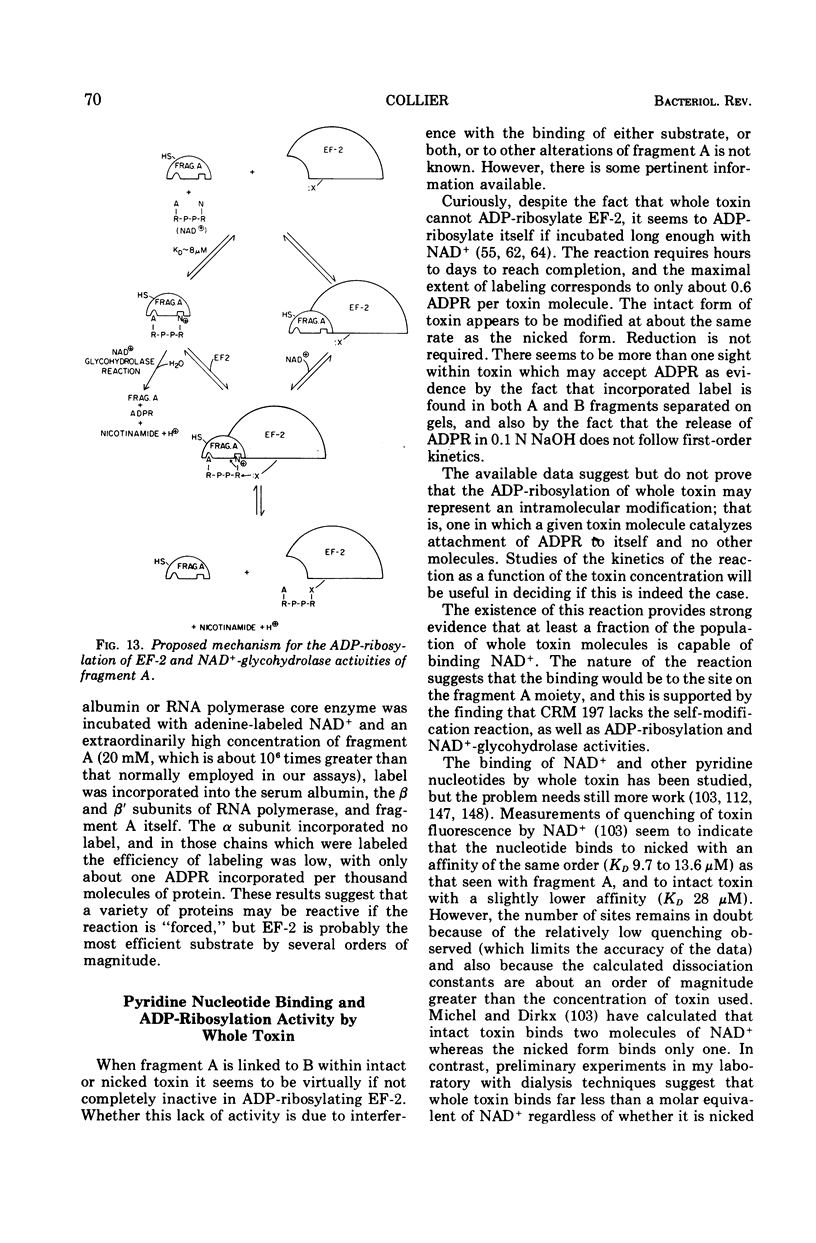
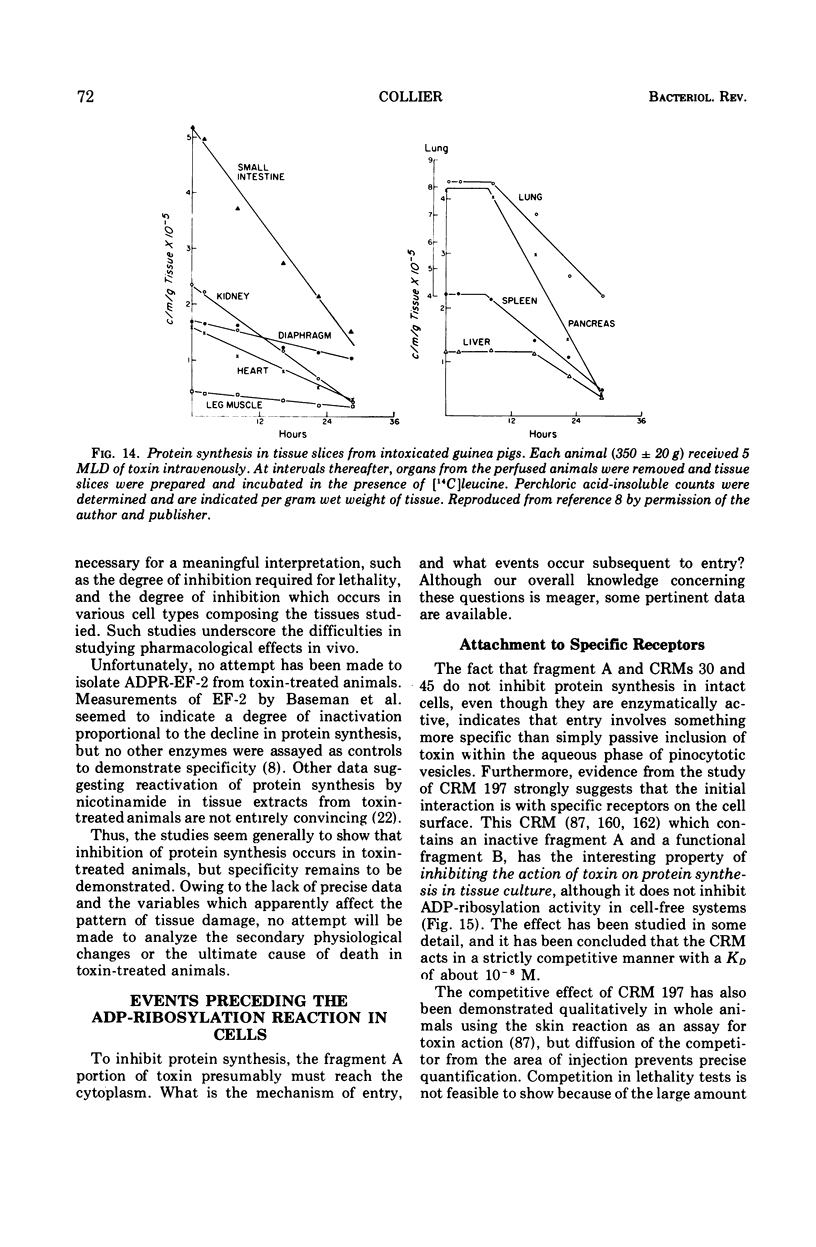
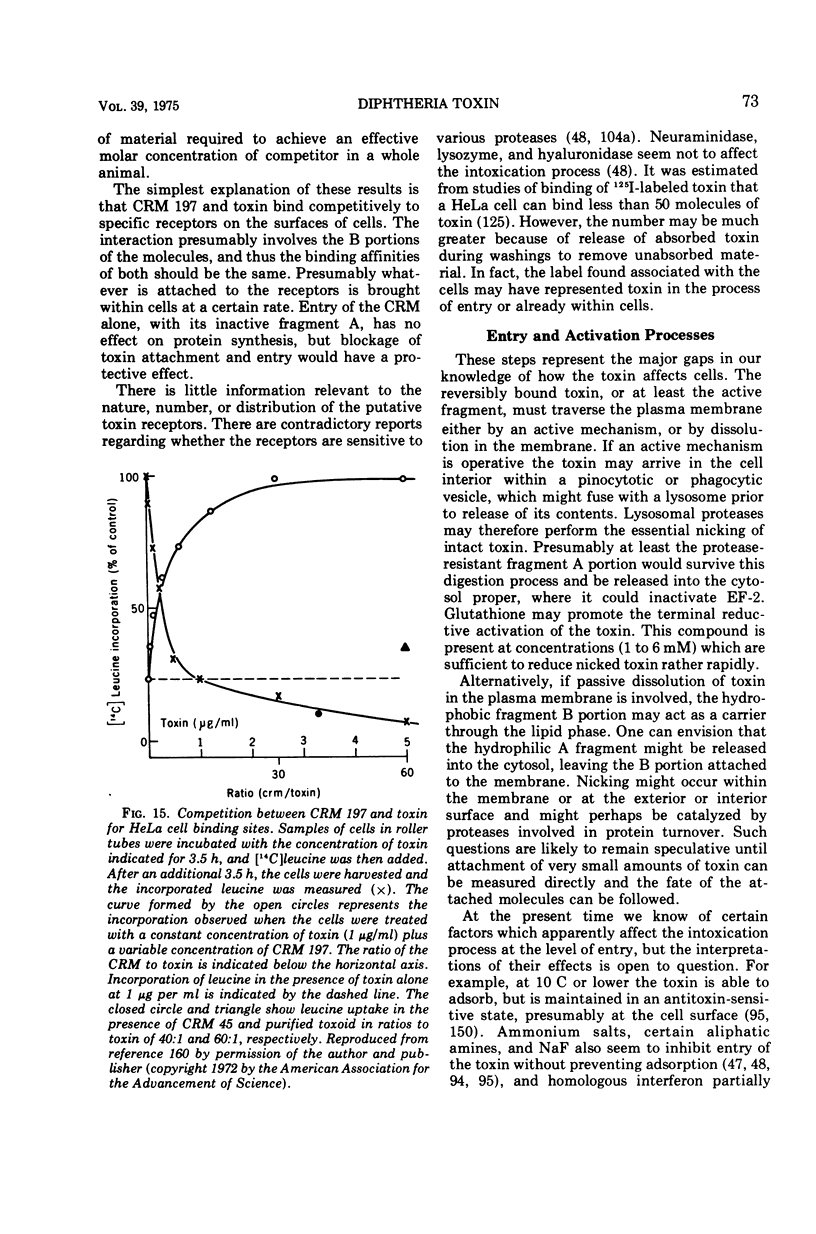
Full text
PDF





















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akama K., Kameyama S., Otani S., Sadahiro S., Murata R. Reversion of toxicity of diphtheria toxoid. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1971 Jun;24(3):183–187. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.24.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARDSDALE W. L., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Phage-host relationships in nontoxigenic and toxigenic diphtheria bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):220–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.220-232.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKSDALE L., GARMISE L., HORIBATA K. Virulence, toxinogeny, and lysogeny in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1093–1108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKSDALE L., GARMISE L., RIVERA R. Toxinogeny in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:527–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.527-540.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIZZINI B., PRUDHOMME R. O., TURPIN A., RAYNAUD M. ESSAI DE MISE EN 'EVIDENCE DE LIAISONS DISULFURE DANS LA TOXINE T'ETANIQUE ET DANS LA TOXINE DIPHT'ERIQUE. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1963 Oct 4;45:925–932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L., Arden S. B. Persisting bacteriophage infections, lysogeny, and phage conversions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):265–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L. Corynebacterium diphtheriae and its relatives. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Dec;34(4):378–422. doi: 10.1128/br.34.4.378-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M., Harper A. A. Action of diphtheria toxin in the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1138–1152. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Goscienski P. J., Hamburger R. N. Characteristics of human antibody to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):130–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.130-136.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers W. H., Reich E. Isolation and characterization of Clostridium botulinum type B toxin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4473–4479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bermek E. Formation of a complex involving ADP-ribosylated human translocation factor, guanosine nucleotide and ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beugnier N., Zanen J. Mise en évidence d'une tyrosine dans le site enzymatique de la toxine diphtérique. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1973 Sep;81(3):581–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. I. Protein synthesis in guinea pig tissues. J Exp Med. 1966 Dec 1;124(6):1107–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.6.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Imhoff J. G. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. II. Protein synthesis in primary heart cell cultures. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1079–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B. Inhibition of protein synthesis after intravenous or intramuscular challenge with diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):418–421. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.418-421.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. V. Protein metabolism in a guinea pig model simulating chronic diphtheritic toxemia. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):556–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.556-560.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. G., Bonventre P. F. Specific reversal of diphtheria toxin mediated inhibition of protein synthesis in guinea pig tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1148–1154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. G., Bonventre P. F. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. III. Effect on subcellular components of protein synthesis from the tissues of intoxicated guinea pigs and rats. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):659–674. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. G., Imhoff J. G., Bonventre P. F. Specificity of diphtheria toxin action on heart and muscle tissues of Guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):686–688. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.686-688.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., Bennett J. V., Feldman R. A. Diphtheria in the United States, 1959-1970. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):172–178. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzzi S., Maistrello I. Inhibition of growth of Erlich tumors in Swiss mice by diphtheria toxin. Cancer Res. 1973 Oct;33(10):2349–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER R. J., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN. I. PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATES IN NORMAL AND INTOXICATED HELA CELLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1007–1018. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER R. J., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN. II. EFFECT OF TOXIN ON AMINO ACID INCORPORATION IN CELL-FREE SYSTEMS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1019–1039. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey T., Leder P., Moldave K., Schlessinger D. Translation: its mechanism and control. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Cole H. A. Diphtheria toxin subunit active in vitro. Science. 1969 Jun 6;164(3884):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3884.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Effect of diphtheria toxin on protein synthesis: inactivation of one of the transfer factors. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Traugh J. A. Inactivation of aminoacyl transferase II by diphtheria toxin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:589–594. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Raeburn S., Maxwell E. S. Aminoacyltransferase II from rat liver. II. Some physical and chemical properties of the purified enzyme and its adenosine diphosphate ribose derivative. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1049–1054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corkill B. The influence of toxaemia on carbohydrate metabolism. J Physiol. 1932 Aug 10;75(4):381–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1932.sp002898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Parikh I., Hollenberg M. D. Affinity chromatography and structural analysis of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin-ganglioside agarose and the biological effects of ganglioside-containing soluble polymers. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4253–4264. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta B. R., Sugiyama H. A common subunit structure in Clostridium botulinum type A, B and E toxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):108–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Groman N. B. Activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Early events in the intoxication of HeLa cells. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):963–969. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.963-969.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Groman N. B. Studies of the activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Poliovirus replication in intoxicated HeLa cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):489–500. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., ALLISON V. D. Diphtheria in the immunized with observations on a diphtheria-like disease associated with nontoxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Hyg (Lond) 1951 Jun-Sep;49(2-3):205–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400044119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton M. D. The Purification and Concentration of Diphtheria Toxin: II. Observations on the Nature of the Toxin. J Bacteriol. 1936 Apr;31(4):367–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.31.4.367-383.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Iglewski B. H. Diphtheria toxin: evidence for presence of fragment B in corynebacteriophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):609–614. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everse J., Gardner D. A., Kaplan N. O., Galasinski W., Moldave K. The formation of a ternary complex between diphtheria toxin, aminoacyltransferase II, and diphosphopyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):899–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN V. J. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):675–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.675-688.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GABLIKS J., SOLOTOROVSKY M. Cell culture reactivity to diphtheria, Staphylococcus, tetanus and Escherichia coli toxins. J Immunol. 1962 Apr;88:505–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., EATON M., BOOHER Z. K. Studies of mono- and polylysogenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.320-325.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., EATON M. Genetic factors in Corynebacterium diphtheriae conversion. J Bacteriol. 1955 Dec;70(6):637–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.6.637-640.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Evidence for the active role of bacteriophage in the conversion of nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae to toxin production. J Bacteriol. 1955 Jan;69(1):9–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.1.9-15.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Evidence for the induced nature of the change from nontoxigenicity to toxigenicity in Corynebacterium diphtheriae as a result of exposure to specific bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1953 Aug;66(2):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.2.184-191.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. The elongation factor 2 content of mammalian cells. Assay method and relation to ribosome number. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):654–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Baseman J. B. Studies on transferase II using diphtheria toxin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:595–602. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Brown R., Kurnick J. T. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VII. Toxin-stimulated hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in mammalian cell extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):1–21. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T. Diphtheria toxin, protein synthesis, and the cell. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Steinhaus D. M. Modification of diphtheria toxin by NAD. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):316–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Uchida T., Singer R. A. Expression of diphtheria toxin genes carried by integrated and nonintegrated phage beta. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):664–668. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff C. G. Chemical structure of a modification of the Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase alpha polypeptides induced by bacteriophage T4 infection. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6181–6190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Dice J. F. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):835–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S., Maxwell E. S. A proposed mechanism for ADP ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II by diphtheria toxin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:609–610. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S., Maxwell E. S. The diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of rat liver aminoacyl transferase. II. General characteristics and mechanism of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 10;245(3):616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S. New form of diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1968 Mar 16;217(5133):1051–1053. doi: 10.1038/2171051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Ames E. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. V. Inhibition of peptide bond formation by toxin and NAD in cell-free systems and its reversal by nicotinamide. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):923–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. 3. Site of toxin action in cell-free extracts. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):899–912. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goor R. S., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. IV. Specificity of the cofactor (NAD) requirement for toxin action in cell-free systems. J Exp Med. 1967 Nov 1;126(5):913–921. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.5.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H., Fleck D. G. An epidemic of diphtheria carriers. Public Health. 1971 Jul;85(5):228–232. doi: 10.1016/s0033-3506(71)80074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto N., Kato I., Sato H. The inhibitory effect of diphtheria toxin on amino acid incorporation by a bacterial cell-free system. Jpn J Exp Med. 1968 Jun;38(3):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hameister H., Richter D. Inhibition of peptide chain elongation in a cell-free system from yeast by pre-incubation of the yeast peptidyl-translocase with diphtheria toxin and NAD. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Apr;351(4):532–536. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1970.351.1.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Genetic analysis of tox+ and tox- bacteriophages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):586–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.586-598.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Hayaishi O. Enzymatic ADP-ribosylation of proteins and regulation of cellular activity. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1973;7:87–127. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152807-2.50011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphoribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II by diphtheria toxin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:603–608. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Kato I., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis by diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Rittenberg M. B. Selective toxicity of diphtheria toxin for malignant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2707–2710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W., Kuchler R. J., Solotorovsky M. Site in cell-free protein synthesis sensitive to diphtheria toxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1089–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1089-1098.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO I., NAKAMURA H., UCHIDA T., KOYAMA J., KATSURA T. Purification of diphtheria toxin. II. The isolation of crystalline toxin-protein and some of its properties. Jpn J Exp Med. 1960 Apr;30:129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATO I., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr An early effect of diphtheria toxin on the metabolism of mammalian cells growing in culture. J Exp Med. 1960 Aug 1;112:329–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Collier R. J., Chung D. W. Interaction of fragment A from diphtheria toxin with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2088–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. In vitro inhibition of diphtheria toxin action by ammonium salts and amines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1552–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1552-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. Mode of inhibition of diphtheria toxin by ammonium chloride. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1557–1562. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1557-1562.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppstech K., Steinbeck R., Klink F. Characteristics of the reaction between diphtheria toxin, pyridine coenzymes and the GTP-splitting transfer factor FI. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Nov;350(11):1377–1384. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1969.350.2.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S., KAPLAN A. S. Action of diphtheria toxin on cells cultivated in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Aug-Sep;95(4):700–702. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampidis T., Barksdale L. Park-Williams number 8 strain of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):77–85. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.77-85.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecroisey A., Bizzini B., Blass J., Raynaud M. Relations entre la structure de la toxine et de l'anatoxine diphtériques. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Apr 17;274(16):2395–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot H. N., Iglewski B. H. Synthesis of diphtheria toxin in E. coli cell-free lysate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan 23;56(2):351–357. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90849-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A., Dirkx J. Fluorescence studies of nucleotides binding to diphtheria toxin and its fragment A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90246-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A., Dirkx J. Liaison de nucléotides à la toxine diphtérique et à son fragment. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1973 Sep;81(3):591–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A., Zanen J., Monier C., Crispeels C., Dirkx J. Partial characterization of diphtheria toxin and its subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. The response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. II. The resistant cell: enhancement of toxin action by poly-L-ornithine. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):541–554. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Crispell J. P. Enzyme treatment of KB cells: the altered effect of diphtheria toxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1446–1452. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M., Kuchler R. J., Solotorovsky M. The response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. I. Amino acid transport, accumulation, and incorporation in normal and intoxicated sensitive cells. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):407–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. 3. Inhibition of protein synthesis studied at the subcellular level. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.61-69.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. IV. Isolation of KB cells resistant to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):487–492. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.487-492.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. V. Concurrent resistance to ribonucleic acid viruses in diphtheria toxin-resistant KB cell strains. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):493–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.493-500.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M., Stinebring W. R. Response of interferon-treated cells to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):747–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.747-752.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K., Galasinski W., Rao P., Siler J. Studies on the peptidyl tRNA translocase from rat liver. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:347–356. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S. Binding of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides to diphtheria toxin. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):635–640. doi: 10.1042/bj1050635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Mattioli A. Interaction of ADP-ribosylated aminoacyl-transferase II with GTP and with ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 27;238(3):493–497. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolten F. L., Cooperband S. R. Selective destruction of target cells by diphtheria toxin conjugated to antibody directed against antigens on the cells. Science. 1970 Jul 3;169(3940):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3940.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, de Borms S. T. Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Different biological properties of the two constituent peptide chains of ricin, a toxic protein inhibiting protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3121–3126. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Refsnes K., Pihl A. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Nature. 1974 Jun 14;249(458):627–631. doi: 10.1038/249627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S. Toxic proteins inhibiting protein synthesis. Naturwissenschaften. 1972 Nov;59(11):497–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00609814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINCHOT G. B., BLOOM W. L. Alterations in the level of muscle phosphocreatine of guinea pigs produced by the injection of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1950 May;184(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLACIDO SOUSA C., EVANS D. G. The action of diphtheria toxin on tissue cultures and its neutralization by antitoxin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Dec;38(6):644–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
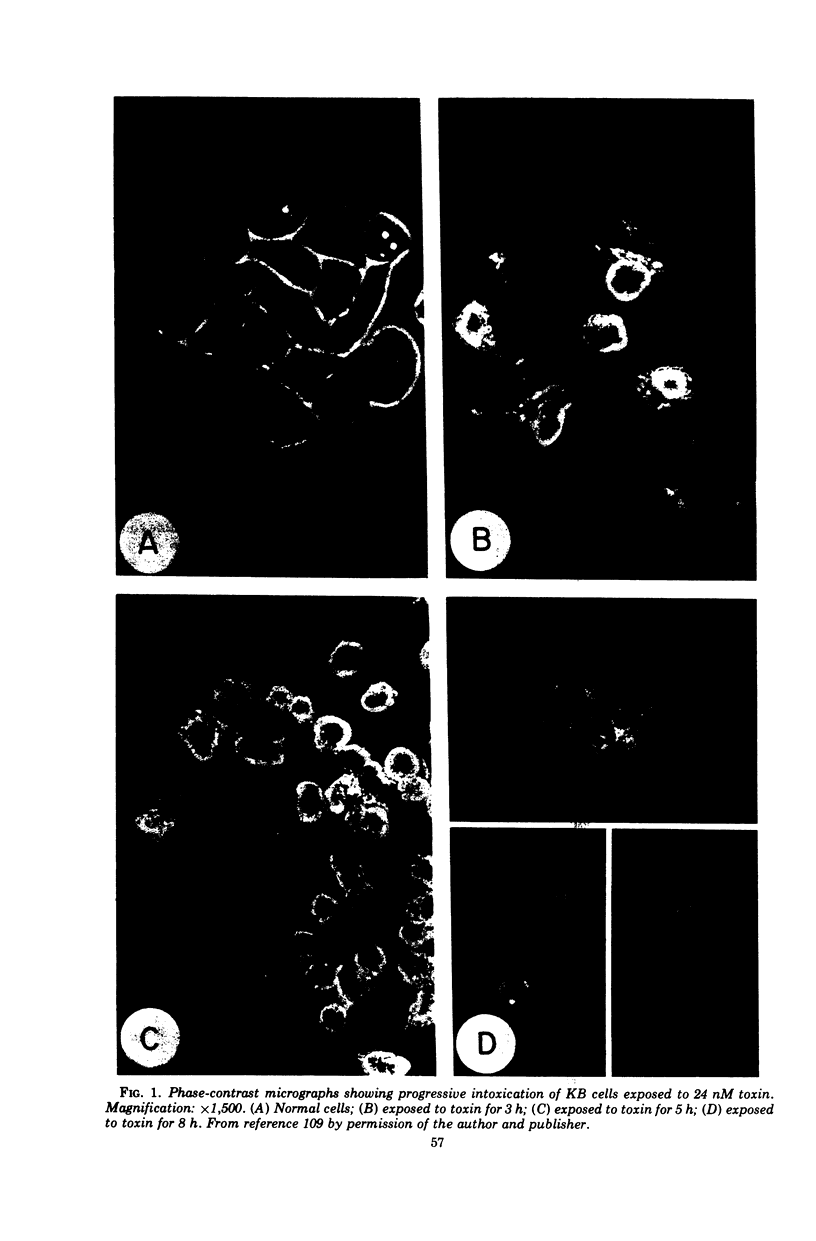
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Brown R. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VI. Site of the action of toxin in living cells. J Exp Med. 1968 Jun 1;127(6):1073–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M. Diphtheria. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):353–358. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M. Studies on Diphtheria Toxin and Its Reaction with Antitoxin. J Bacteriol. 1942 Mar;43(3):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.43.3.273-289.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYNAUD M., BIZZINI B., RELYVELD E. H. COMPOSITION EN AMINO-ACIDES DE LA TOXINE DIPHT'ERIQUE PURIFI'EE. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47:261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELYVELD E. H., BEN EFRAIM S. [Diphtheria toxin]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1959 Nov;97:697–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn S., Collins J. F., Moon H. M., Maxwell E. S. Aminoacyltransferase II from rat liver. I. Purification and enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1041–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn S., Goor R. S., Collins J. F., Maxwell E. S. Alteration in the ionic properties of aminoacyltransferase II from rat liver by NAD+ and diphtheria toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):294–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90722-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn S., Goor R. S., Schneider J. A., Maxwell E. S. Interaction of aminoacyl transferase II and guanosine triphosphate: inhibition by diphtheria toxin and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1428–1434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relyveld E. H. Formation de la toxine diphtérique lourde. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jan 12;270(2):410–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D., Lipmann F. Separation of mitochondrial and cytoplasmic peptide chain elongation factors from yeast. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5065–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Henriksen O., Maxwell E. S. Elongation factor 2. Amino acid sequence at the site of adenosine diphosphate ribosylation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5088–5093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Maxwell E. S. Chemical properties of elongation factor 2. Amino acid composition, NH 2 -terminal residue, and sulfhydryl reactivity. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7023–7028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS N., HENDEE E. D. The effect of diphtheria toxin on the metabolism of HeLa cells. J Exp Med. 1959 Feb 1;109(2):145–163. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelinger C. B., Imhoff J. G., Bonventre P. F. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VI. Inhibition of protein synthesis induced by local infection with toxingenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jan;142(1):41–45. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-36953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samagh B. S., Gregory K. F. Antibody to lactate dehydrogenase. V. Use as a carrier for introducing diphtheria toxin into mouse tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 26;273(1):188–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulson M. E., Rideau C., Raeburn S. Diphtheria toxin: requirement for active protein synthesis for inactivation of aminoacyl transferase II in the intact mammalian cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):268–271. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90644-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L. Competitive binding of adenine and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide to diphtheria toxin. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):730–732. doi: 10.1042/bj1070730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A. Studies on diphtheria toxin. The effect of GTP on the toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of rat liver aminoacyl transferase. II. Chem Biol Interact. 1971 Apr;3(2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(71)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimura T. Poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1973;13:127–151. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Das Gupta R., Yang K. H. Disulfide-toxicity relationship of botulinal toxin types A, E, and F. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jul;143(3):589–591. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Collier R. J. Binding of transfer factor II to ribosomal RNA and inhibition of the binding by guanosine nucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1437–1444. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Collier R. J. Interaction of transferase II with polynucleotides and inhibition of the interaction by guanosine nucleotides. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2357–2366. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugh J. A., Collier R. J. Interaction of transferase II with the 60 s ribosomal subunit. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):285–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugawa A., Ohsumi Y., Kato I. Inhibitory effect of diphtheria toxin on amino acid incorporation in Escherichia coli cell-free system. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):152–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.152-157.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Mutation in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by temperate phage . Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 1;233(35):8–11. doi: 10.1038/newbio233008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. 3. Reconstitution of hybrid "diphtheria toxin" from nontoxic mutant proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3851–3854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. II. Kinetic studies on intoxication of HeLa cells by diphtheria toxin and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3845–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Reconstitution of diphtheria toxin from two nontoxic cross-reacting mutant proteins. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):901–903. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANHEYNINGEN W. E., ARSECULERATNE S. N. EXOTOXINS. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1964;18:195–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.18.100164.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiester M. J., Bonventre P. F., Grupp G. Estimate of myocardial damage induced by diphtheria toxin. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):354–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONEDA M. A new culture method designed for kinetic studies on diphtheria toxin production. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Apr;38(2):190–193. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YONEDA M., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Some effects of iron deficiency on the extracellular products released by toxigenic and nontoxigenic strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.256-264.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanen J., Depuydt F., Dirkx J. Action d'agents dénaturants sur la toxine diphtérique. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1968 Jul;76(3):601–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]