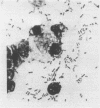
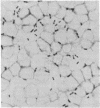
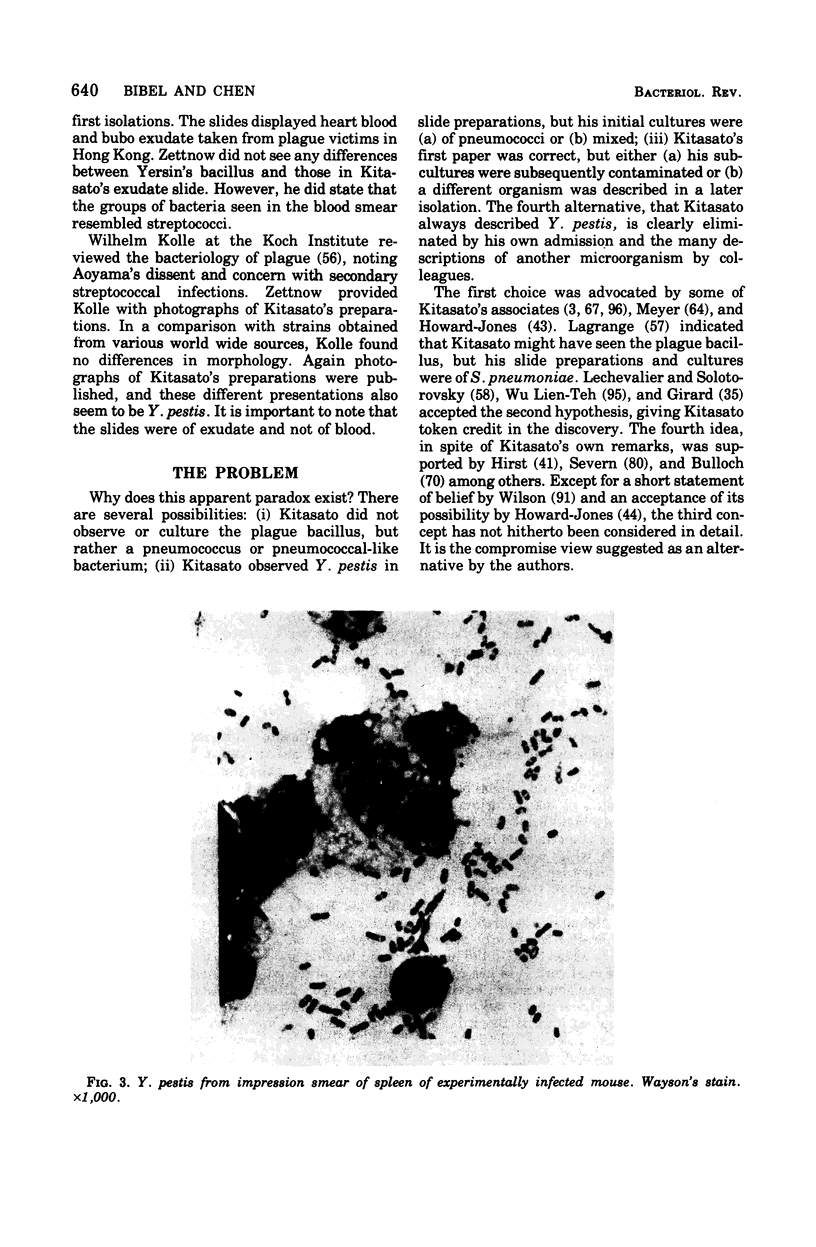
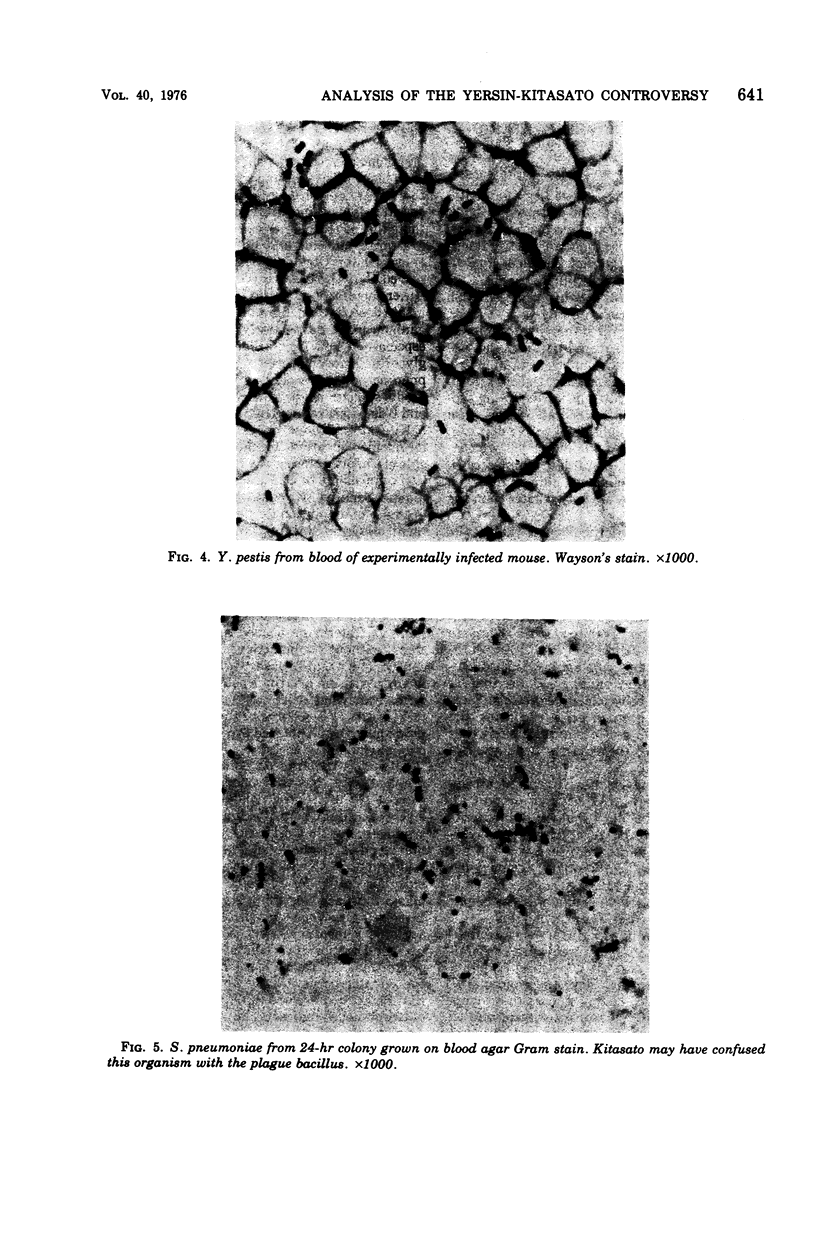
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMIES C. R. The envelope substance of Pasteurella pestis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):259–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUSTRIAN R. The Gram stain and the etiology of lobar pneumonia, an historical note. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Sep;24(3):261–265. doi: 10.1128/br.24.3.261-265.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., DAVIS D. H., DEVIGNAT R., GIRARD G., GOHAR M. A., KARTMAN L., MEYER K. F., PARKER M. T., POLLITZER R., PRINCE F. M. Recommended laboratory methods for the diagnosis of plague. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;14(3):457–509. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTHOLOMEW J. W., MITTWER T. The Gram stain. Bacteriol Rev. 1952 Mar;16(1):1–29. doi: 10.1128/br.16.1.1-29.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAUGH D. C., QUAN S. F. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis using specific bacteriophage lyophilized on strips of filter paper; a preliminary report. Am J Clin Pathol. 1953 Jun;23(6):619–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T. H., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. VII. A hemagglutination test with the protein fraction of Pasteurella pestis: a serologic comparison of virulent and avirulent strains with observations on the structure of the bacterial cells and its relationship to infection and immunity. J Immunol. 1954 Apr;72(4):282–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. H., Meyer K. F. An evaluation of Pasteurella pestis fraction-1-specific antibody for the confirmation of plague infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(6):911–918. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISLER D. M., KUBIK G., PRESTON H. Colonial morphology and virulence of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.41-47.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNNISON J. B., LARSON A., LAZARUS A. S. Rapid differentiation between Pasteurella pestis and Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis by action of bacteriophage. J Infect Dis. 1951 May-Jun;88(3):254–255. doi: 10.1093/infdis/88.3.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg M. I. Laboratory diagnosis of plague infection. Health Lab Sci. 1968 Jan;5(1):38–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Jones N. Kitasato, Yersin, and the plague bacillus. Clio Med. 1975 Apr;10(1):23–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Jones N. Was Shibasaburo Kitasato the co-discoverer of the plague bacillus? Perspect Biol Med. 1973 Winter;16(2):292–307. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1973.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartman Leo, Martin Albert R., Hubbert William T., Collins Richard N., Goldenberg Martin I. Epidemiologic features and results of field studies. Public Health Rep. 1967 Dec;82(12):1084–1094. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., WINTER C. C. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis with fluorescent antibody. III. Staining Pasteurella pestis in tissue impression smears. J Infect Dis. 1959 May-Jun;104(3):288–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/104.3.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGATA N. Wer hat die Pestbazillen zuerst entdeckt? Kitasato? Yersin? Oder Kitasato und Yersin? Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1955 Jun;163(2-3):171–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KNAPP W., GOLDENBERG M. I., HUDSON B. W., LAWTON W. D., CHEN T. H., KARTMAN L. ISOLATION OF A STRAIN OF PASTEURELLA PSEUDOTUBERCULOSIS FROM ALASKA IDENTIFIED AS PASTEURELLA PESTIS: AN IMMUNOFLUORESCENT FALSE POSITIVE. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:424–432. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Birch-Andersen A., Berger U. Fine structure and taxonomic position of Neisseria haemolysans (Thjotta and Boe 1938) or Gemella haemolysans (Berger 1960). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(3):375–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. E., THAL E. A TAXONOMIC STUDY OF THE GENUS PASTEURELLA USING A NUMERICAL TECHNIQUE. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:213–223. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokhey S. S., Habbu M. K. Optimum and Limiting Temperatures for the Growth of the Plague Bacillus in Broth. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):25–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.25-32.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. C., MOODY M. D. Rapid identification of Pasteurella pestis with fluorescent antibody. II. Specific identification of Pasteurella pestis in dried smears. J Infect Dis. 1959 May-Jun;104(3):281–287. doi: 10.1093/infdis/104.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]