Abstract
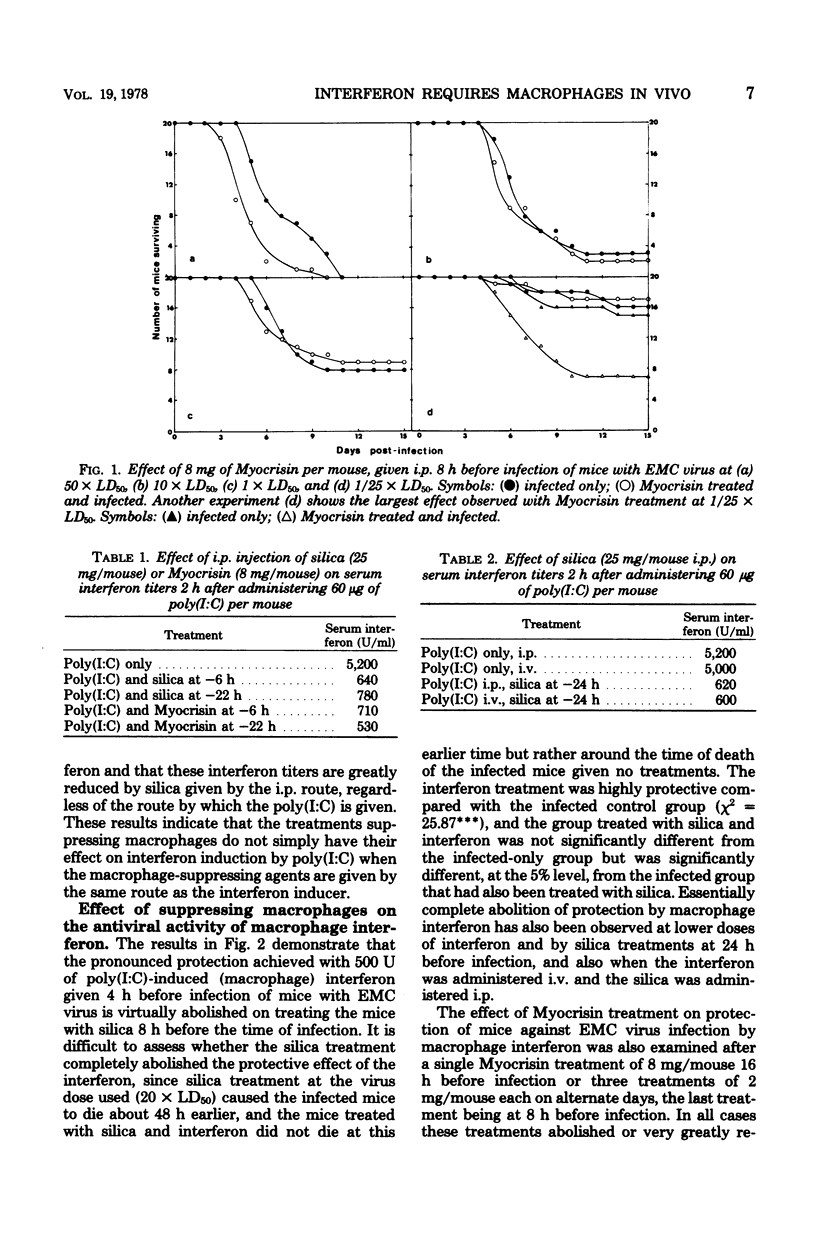
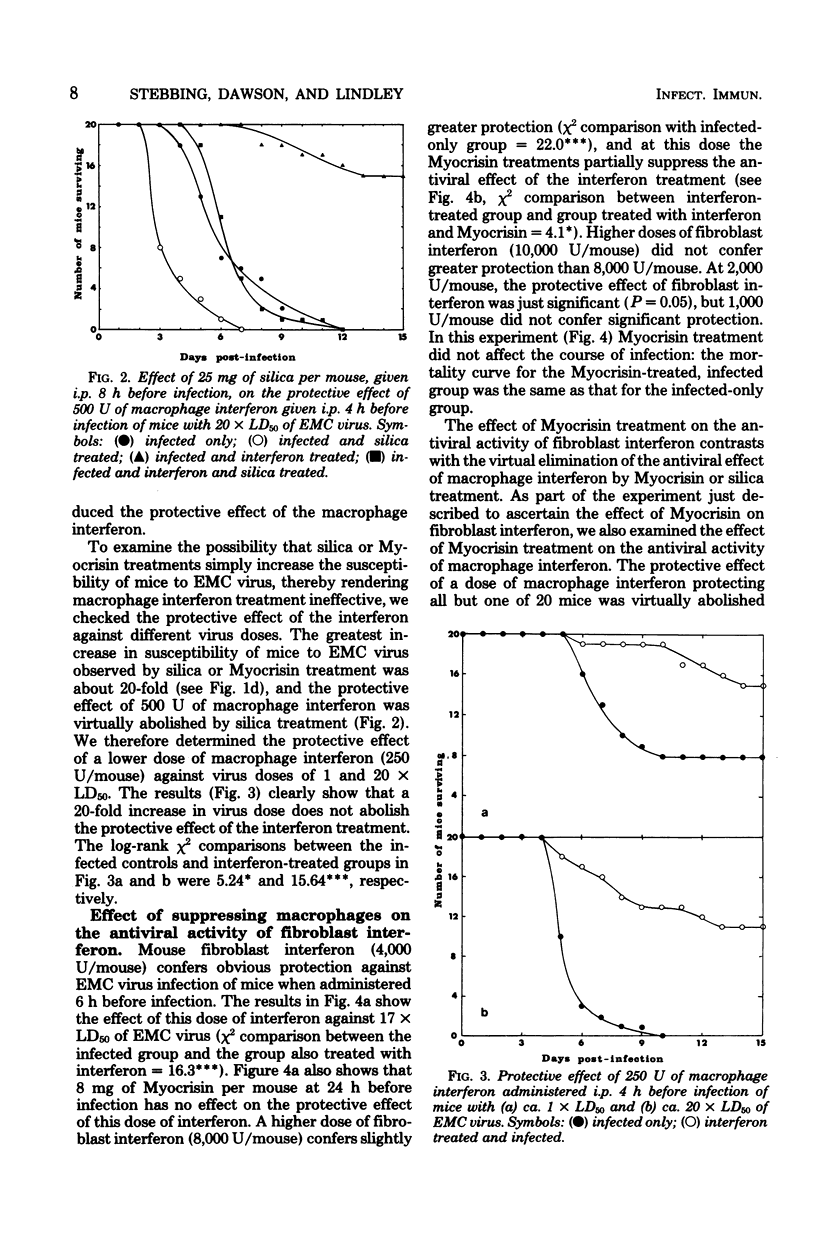
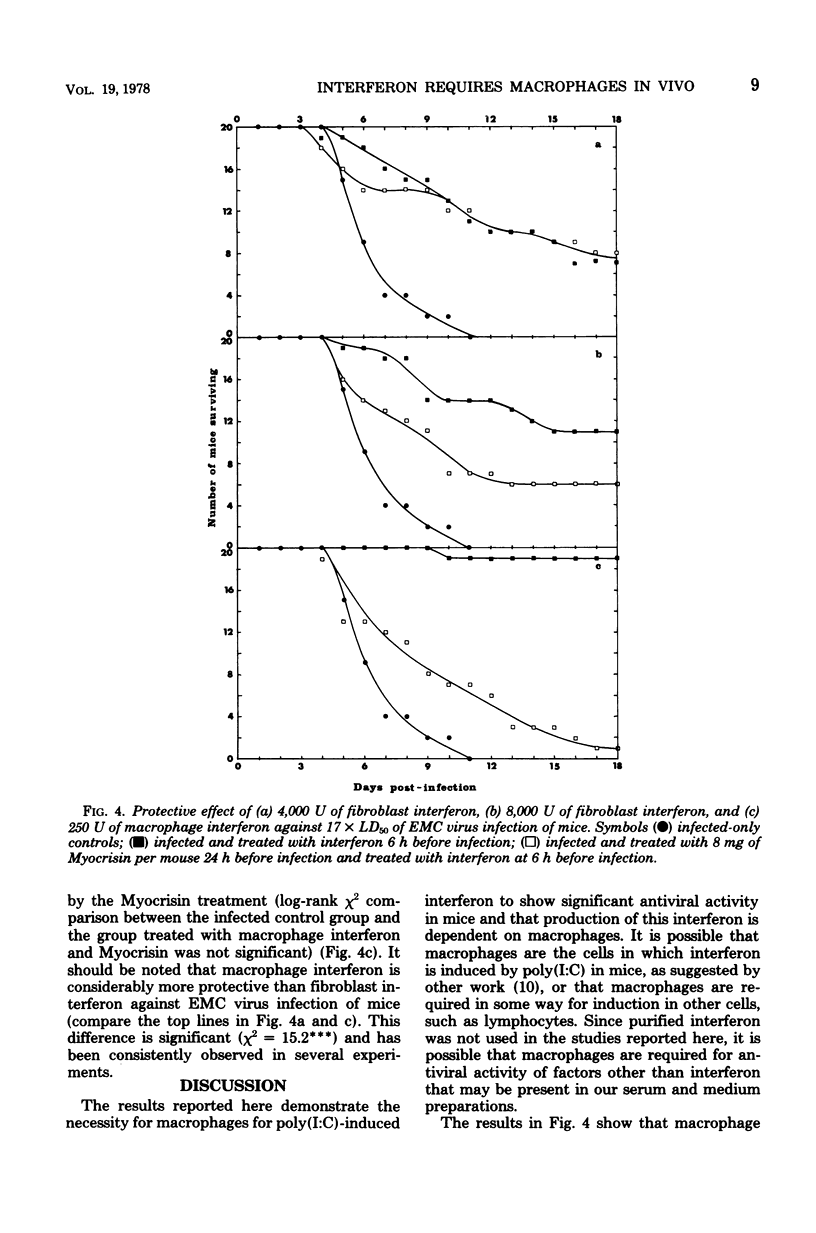
Suppression of macrophages in mice by treatments with silica or auro-thiomalate (Myocrisin) reduced production of serum interferon by polyriboinosinic acid:polyribocytidylic acid by 85 to 90%, indicating that this double-stranded polynucleotide caused interferon production primarily in macrophages. Suppression of macrophages in mice by silica or Myocrisin treatment did not significantly affect the susceptibility of mice to encephalomyocarditis virus, although at virus doses around 20 times the 50% lethal dose they died about 48 h earlier. Macrophage interferon protected mice from encephalomyocarditis virus infection at much lower doses than fibroblast interferon, and treatment of mice with silica or Myocrisin abolished the protection conferred by macrophage interferon, whereas these treatments had a much smaller effect on the protection afforded by fibroblast interferon. The requirement for macrophages for interferon to be effective in mice can explain why macrophage suppression can cause normally nonlethal viruses to kill adult mice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C. On the role of mononuclear phagocytes in immunity against viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):15–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allner K., Bradish C. J., Fitzgeorge R., Nathanson N. Modifications by sodium auro-thio-malate of the expression of virulence in mice by defined strains of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):221–228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang F. B., Warwick A. MOUSE MACROPHAGES AS HOST CELLS FOR THE MOUSE HEPATITIS VIRUS AND THE GENETIC BASIS OF THEIR SUSCEPTIBILITY. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1065–1075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy V. G., Billiau A., De Somer P. Human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons show different dose-response curves in assay of cell protection. J Gen Virol. 1976 May;31(2):251–255. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN G. T., KOPROWSKI H. Study of the mechanism of innate resistance to virus infection. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:333–373. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Brouty-boye D., Tovey M. Pronounced antiviral activity of human interferon on bovine and porcine cells. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):543–545. doi: 10.1038/251543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I., Tovey M. G., Bandu M. E., Maury C., Brouty-Boyé D. Role of interferon in the pathogenesis of virus diseases in mice as demonstrated by the use of anti-interferon serum. I. Rapid evolution of encephalomyocarditis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1305–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Zisman B., Allison A. C. Macrophages and age-dependent resistance to Herpes simplex virus in mice. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1160–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jullien P., De Maeyer-Guignard J., De Maeyer E. Interferon synthesis in x-irradiated animals v. Origin of mouse serum interferon induced by polyinosinic-polycytidylic Acid and encephalomyocarditis virus. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1023–1028. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1023-1028.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. ASPECTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRUS DISEASES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:30–71. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.30-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C. Conservatism of the approximation sigma (O-E)2-E in the logrank test for survival data or tumor incidence data. Biometrics. 1973 Sep;29(3):579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. The role of antibody and host cells in the resistance of mice against infection by coxsackie B-3 virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):329–338. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Carey N. H. Anti-viral activity of single-stranded homopolynucleotides against encephalomyocarditis virus and Semliki Forest virus in adult mice without interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):21–39. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Kaminski F. Investigation of the anti-viral mechanism of poly I and poly C against encephalomyocarditis virus infection in the absence of interferon induction in mice. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jul;32(1):25–35. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Kaminski F., Lindley I. J. Protection of mice against encephalomyocarditis virus infection by preparations of transfer RNA. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):73–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stebbing N., Grantham C. A., Lindley I. J., Eaton M. A., Carey N. H. In vivo antiviral activity of polynucleotide mimics of strategic regions in viral RNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:682–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb22004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd Distinct molecular species of interferons. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L., Allison A. C. Correlation of persistent mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-3) infection with its effect on mouse macrophage cultures. Arch Virol. 1976;50(4):279–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01317953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisman B., Wheelock E. F., Allison A. C. Role of macrophages and antibody in resistance of mice against yellow fever virus. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):236–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Groen G., Vanden Berghe D. A., Pattyn S. R. Interaction of mouse peritoneal macrophages with different arboviruses in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):353–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


