Abstract
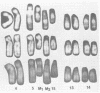
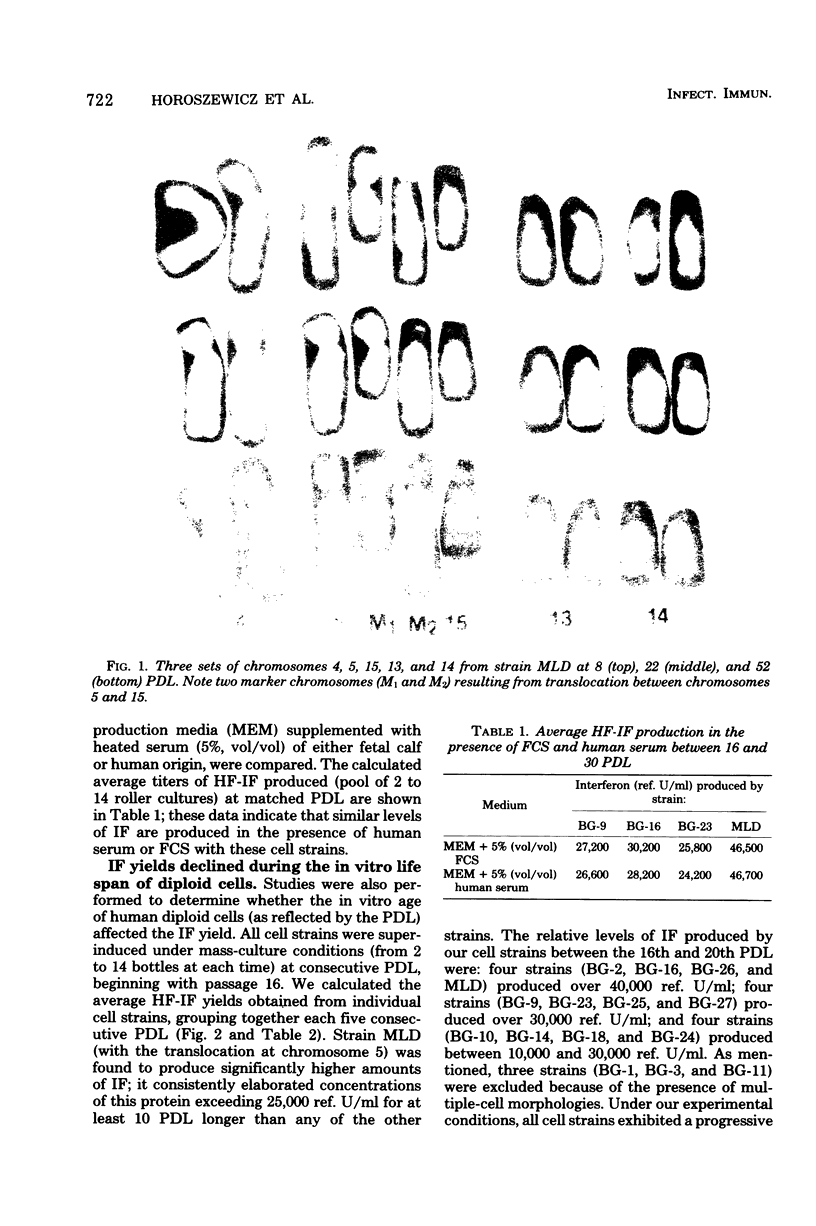
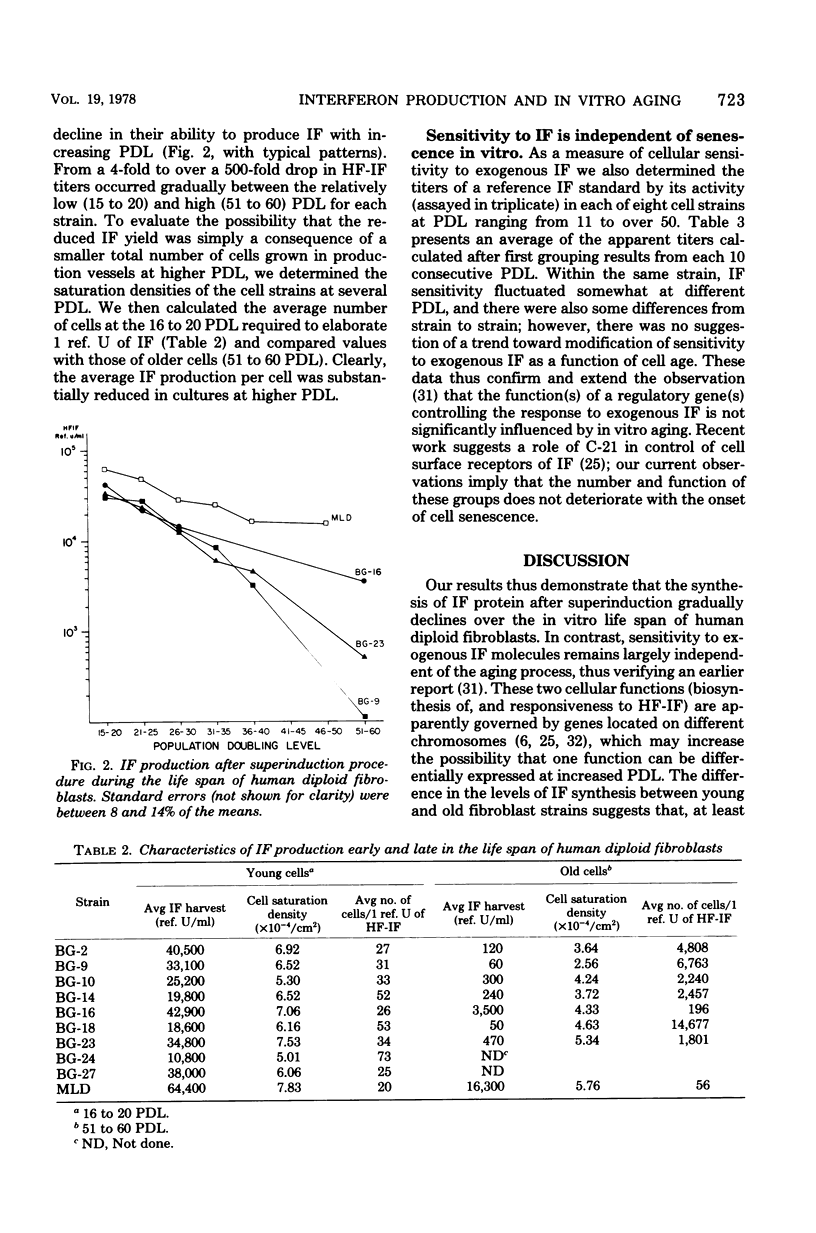
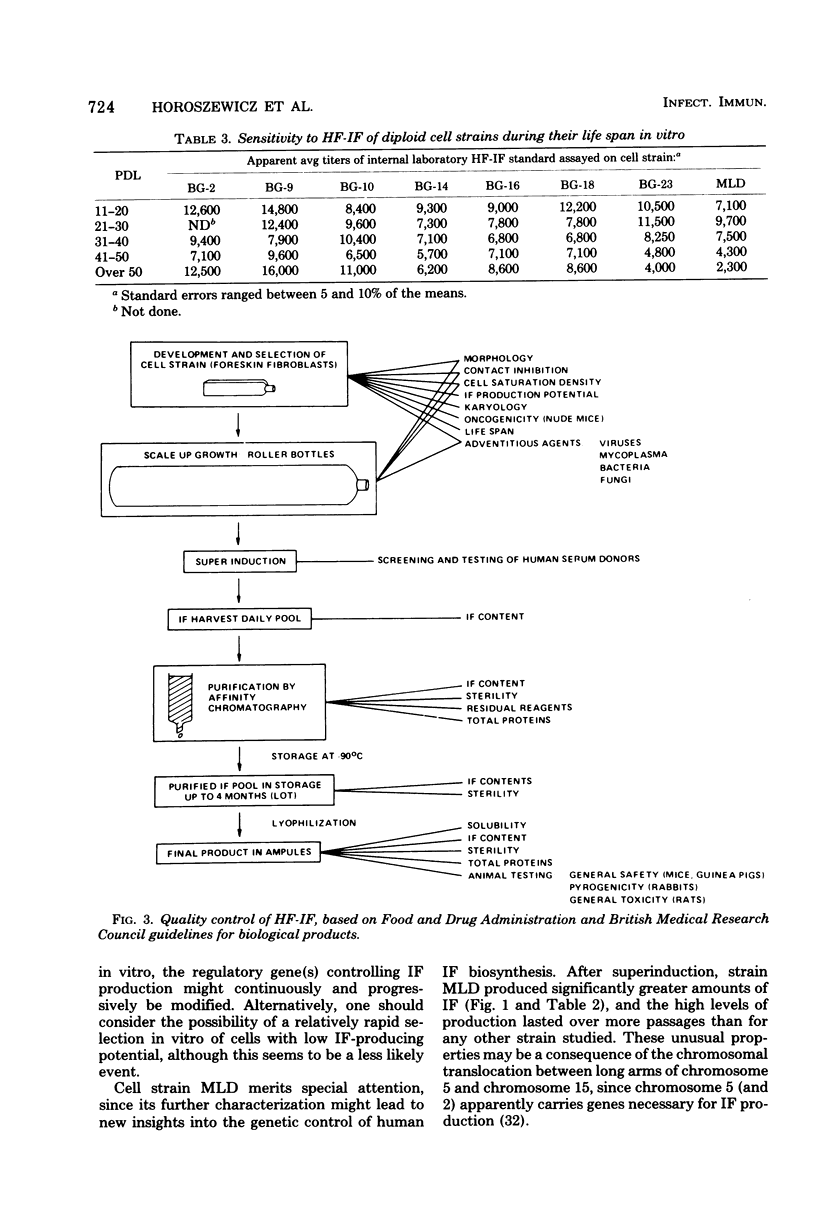
To develop resources for large-scale production of human fibroblast interferon, we isolated, cryopreserved, and characterized 15 new strains of human diploid foreskin fibroblasts. Their life spans in vitro ranged from 52 to 72 population doublings. We based the selection of cell strains for mass interferon production on the number of population doublings during which consistently high yields of interferon were obtained after "superinduction" in roller bottles; our data show that aging in vitro leads to significant decline in amounts of interferon produced. In contrast, susceptibility to interferon remains largely unaffected by in vitro senescence. Karyotypic analysis indicated that the best interferon-producing strain, MLD (over 60,000 reference units/ml), has a translocation between chromosomes 5 and 15.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Lidin B., Strander H., Cantell K. Spontaneous interferon production and Epstein-Barr virus antigen expression in human lymphoid cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1975 Aug;28(2):219–223. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-2-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvin A. M., Yeager A. S., Merigan T. C. Effect of leukocyte interferon on urinary excretion of cytomegalovirus by infants. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A205–A210. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Joniau M., De Somer P. Mass production of human interferon in diploid cells stimulated by poly-I:C. J Gen Virol. 1973 Apr;19(1):1–8. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomgren H., Cantell K., Johansson B., Lagergren C., Ringborg U., Strander H. Interferon therapy in Hodgkin's disease. A case report. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(6):527–532. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Pitha P. M., Marshall L. W., Tazawa I., Tazawa S., Ts'o P. O. Structural requirements of the rI n -rC n complex for induction of human interferon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90560-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Vignal M., Couillin P., Van Cong N., Boué J., Boué A. Chromosomal localization of human genes governing the interferon-induced antiviral state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Huang J. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human interferon with concanavalin A-agarose. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6354–6355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human, mouse, and rabbit interferons with immobilized hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7620–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Edy V. G., De Vlieger H., Eeckels R., Desmyter J. Intrathecal administration of interferon in neonatal herpes. J Pediatr. 1975 May;86(5):736–739. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., De Groote J., Desmet V. J., Billiau A., Ray M. B., Bradburne A. F., Edy V. G., De Somer P. Administration of human fibroblast interferon in chronic hepatitis-B infection. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):645–647. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92460-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Pollard R. B., Lutwick L. I., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Effect of human leukocyte interferon on hepatitis B virus infection in patients with chronic active hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1976 Sep 2;295(10):517–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197609022951001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L., MOORHEAD P. S. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Dec;25:585–621. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., Davey M. W., O'Malley J. A., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Molecular structure of human fibroblast and leukocyte interferons: probe by lectin and hydrophobic chromatography. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1124-1130.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski W. J., von Muenchhausen W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Binding of human interferons to immobolized Cibacron Blue F3GA: The nature of molecular interaction. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5182–5187. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaighn M. E., Prince A. M. Production of albumin and other serum proteins by clonal cultures of normal human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Forsgren M., Hård af Segerstad S., Strander H., Cantell K. Administration of interferon to an infant with congenital rubella syndrome involving persistent viremia and cutaneous vasculitis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Jan;65(1):105–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorhead P. S., Nicholls W. W., Perkins F. T., Hayflick L. Standards of karyology for human diploid cells. J Biol Stand. 1974 Apr;2(2):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(74)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson-Rees W. A., Flandermeyer R. R. Inter- and intraspecies contamination of human breast tumor cell lines HBC and BrCa5 and other cell cultures. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1343–1344. doi: 10.1126/science.557237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Bash D., Ruddle F. H. Antibodies to a cell-surface component coded by human chromosome 21 inhibit action of interferon. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):139–141. doi: 10.1038/260139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H., Cantell K., Carlström G., Ingimarsson S., Jakobsson P., Nilsonne U. Acute infections in interferon-treated patients with osteosarcoma: preliminary report of a comparative study. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A245–A248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strander H., Cantell K., Carlström G., Jakobsson P. A. Clinical and laboratory investigations on man: systemic administration of potent interferon to man. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Sep;51(3):733–742. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulkowski E., Davey M. W., Carter W. A. Interaction of human interferons with immobilized hydrophobic amino acids and dipeptides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 10;251(17):5381–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Chou E. L., Lundh N. Regulation of chromosome 21-directed anti-viral gene(s) as a consequence of age. Nature. 1975 Sep 25;257(5524):310–312. doi: 10.1038/257310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Creagan R. P., Ruddle F. H. The somatic cell genetics of human interferon: assignment of human interferon loci to chromosomes 2 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Hazards of human leukocyte interferon therapy. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 2;296(22):1295–1296. doi: 10.1056/nejm197706022962217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]