Abstract
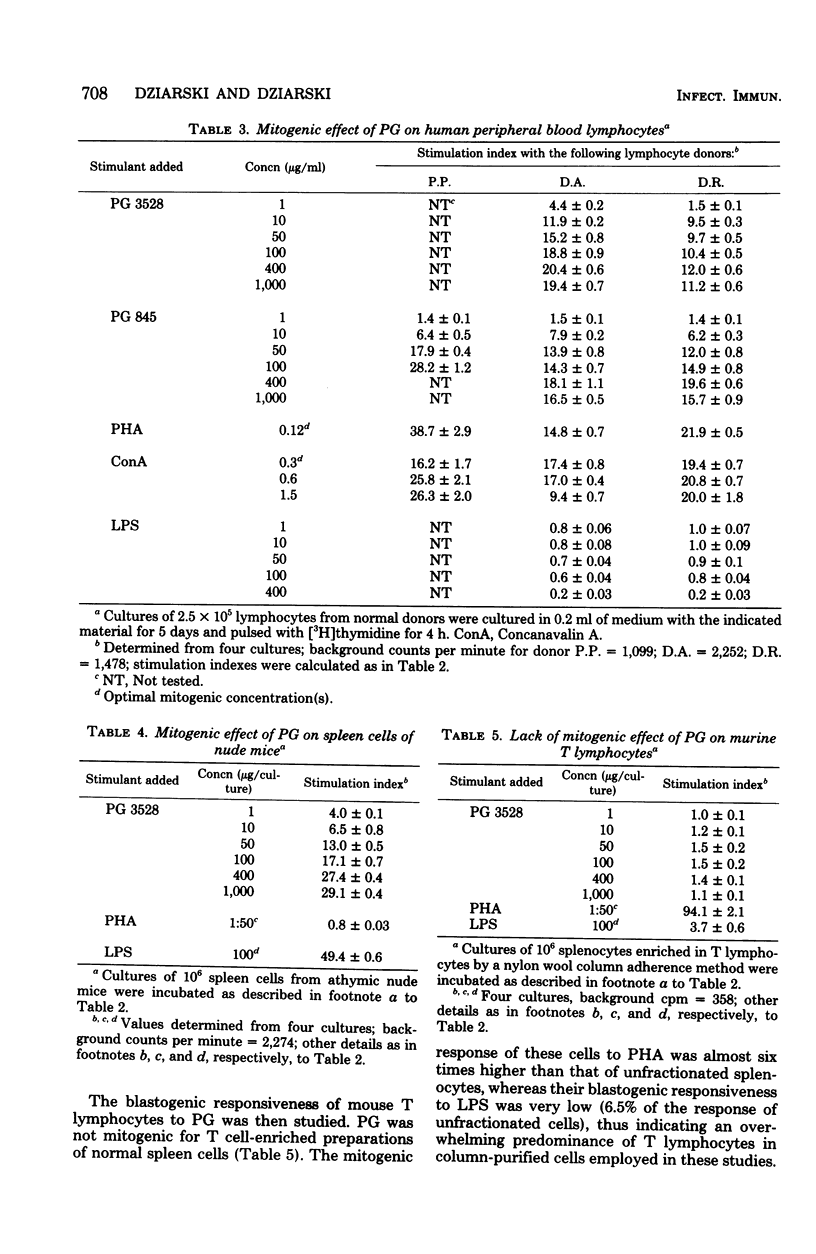
Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan displayed a marked dose-dependent mitogenic activity for mouse splenocytes and human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro, as measured by increased [3H]thymidine incorporation. Similarly it was mitogenic for athymic nude mouse spleen cells, whereas no blastogenic effect was observed in T cell-enriched and B cell-depleted mouse lymphocyte cultures. These data demonstrate that peptidoglycan-responding cells in mouse spleen cell cultures are B lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bokisch V. A. Interaction of peptidoglycans with anti-IgGs and with complement. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):320–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEDID L., SKARNES R. C., PARANT M. Characterization of a Cr51-labeled endotoxin and its identification in plasma and urine after parenteral administration. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:561–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciorbaru R., Petit J. F., Lederer E., Zissman E., Bona C., Chedid L. Presence and subcellular localization of two distinct mitogenic fractions in the cells of Nocardia rubra and Nocardia opaca: preparation of soluble mitogenic peptidoglycan fractions. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1084–1090. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1084-1090.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Rodriguez G. E., Kind P. D., Campbell P. A. Listeria cell wall fraction: a B cell mitogen. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1132–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Bona C., Chedid L., Fleck J., Nauciel C., Martin J. P. Mitogenic effect of bacterial peptidoglycans possessing adjuvant activity. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):268–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damais C., Parant M., Chedid L. Nonspecific activation of murine spleen cells in vitro by a synthetic immunoadjuvant (N-acetyl-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine). Cell Immunol. 1977 Nov;34(1):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Stimulation of reticuloendothelial system and toxicity to macrophages of Staphylococcus aureus cell wall, peptidoglycan, and teichoic acid. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1977 Jul;238(3):320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Svedjelund A., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte stimulation by protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):207–213. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Boackle R. J., Schwab J. H. Activation of the alternate complement pathway by peptidoglycan from streptococcal cell wall. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):296–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.296-303.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heymer B. Biological properties of the peptidoglycan. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):245–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holton J. B., Schwab J. H. Adjuvant properties of bacterial cell wall mucopeptides. J Immunol. 1966 Jan;96(1):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollès P., Migliore-Samour D., Maral R., Floc'h F., Werner G. H. Low molecular weight water-soluble peptidoglycans as adjuvants and immunostimulants. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Watanabe Y., Shimono T., Narita T., Kato K. Immunoadjuvant activities of cell walls, their water-soluble fractions and peptidoglycan subunits, prepared from various gram-positive bacteria, and of synthetic n-acetylmuramyl peptides. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):302–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauciel C., Fleck J. Adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycans. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIM J. J., PERRY S. EFFECTS OF ENDOTOXINS ON CULTURED LEUKOCYTES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Apr;118:1014–1019. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-30033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Adler W. H., Smith R. T. The mitogenic effects of endotoxin and staphylococcal enterotoxin B on mouse spleen cells and human peripheral lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1453–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J. Endotoxin-like properties of the peptidoglycan. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):230–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specter S., Cimprich R., Friedman H., Chedid L. Stimulation of an enhanced in vitro immune response by a synthetic adjuvant, muramyl dipeptide. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Tarumi Y., Ikenaka K. Mitogenic activity of adjuvant-active N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine and its analogues. Biken J. 1977 Jun;20(2):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


