Abstract
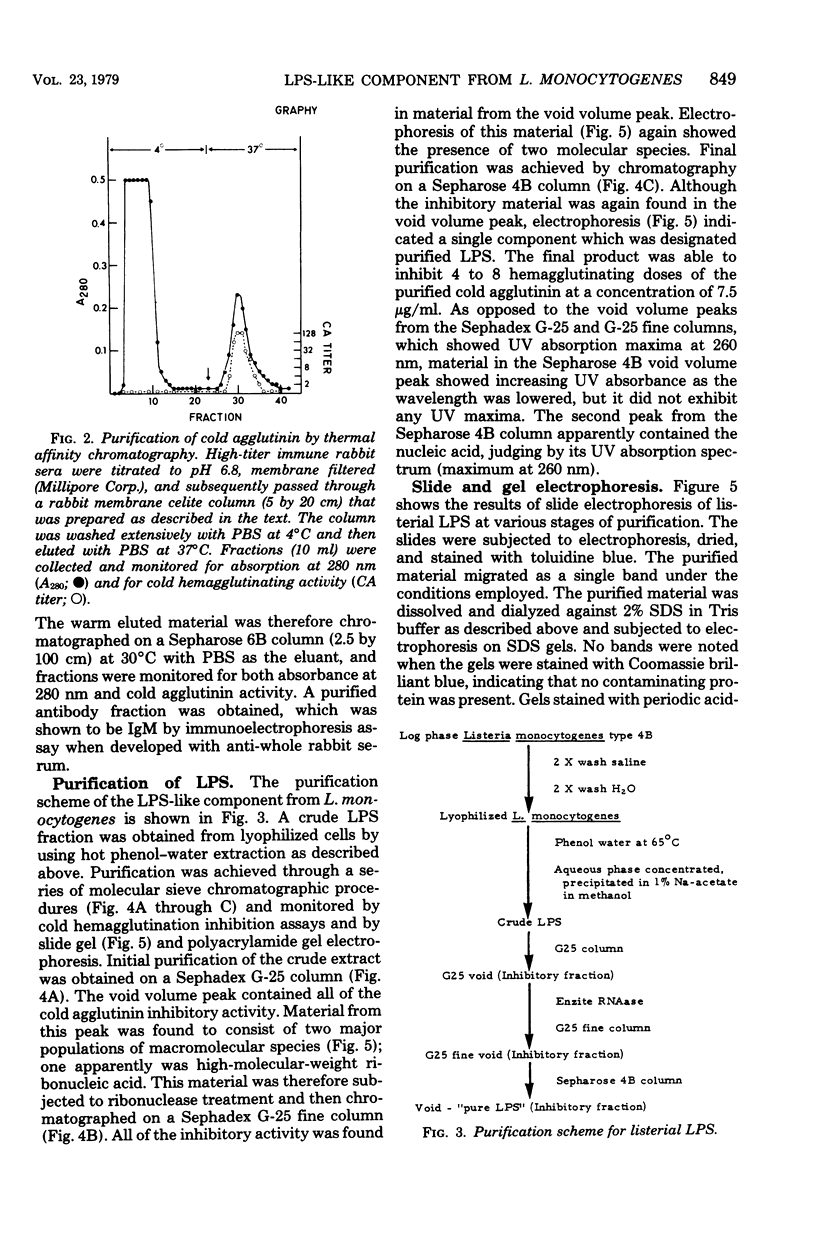
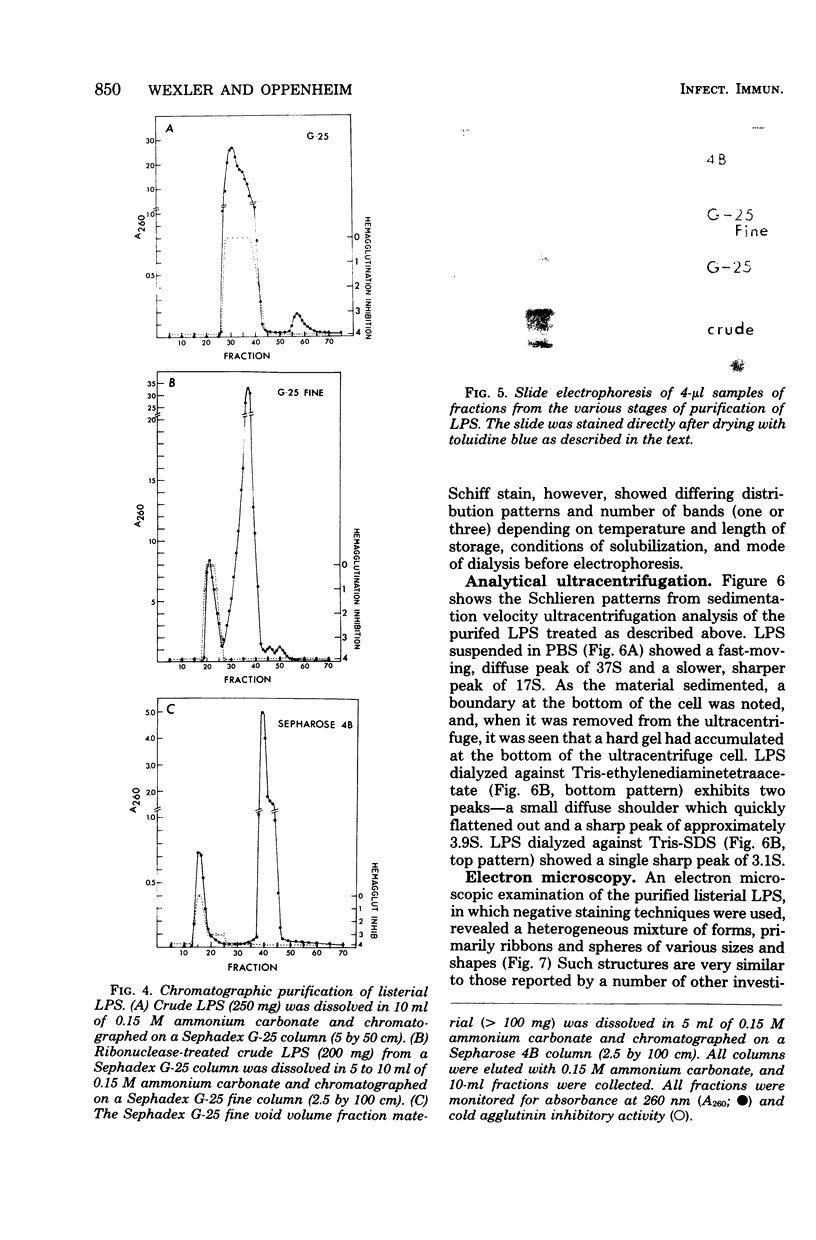
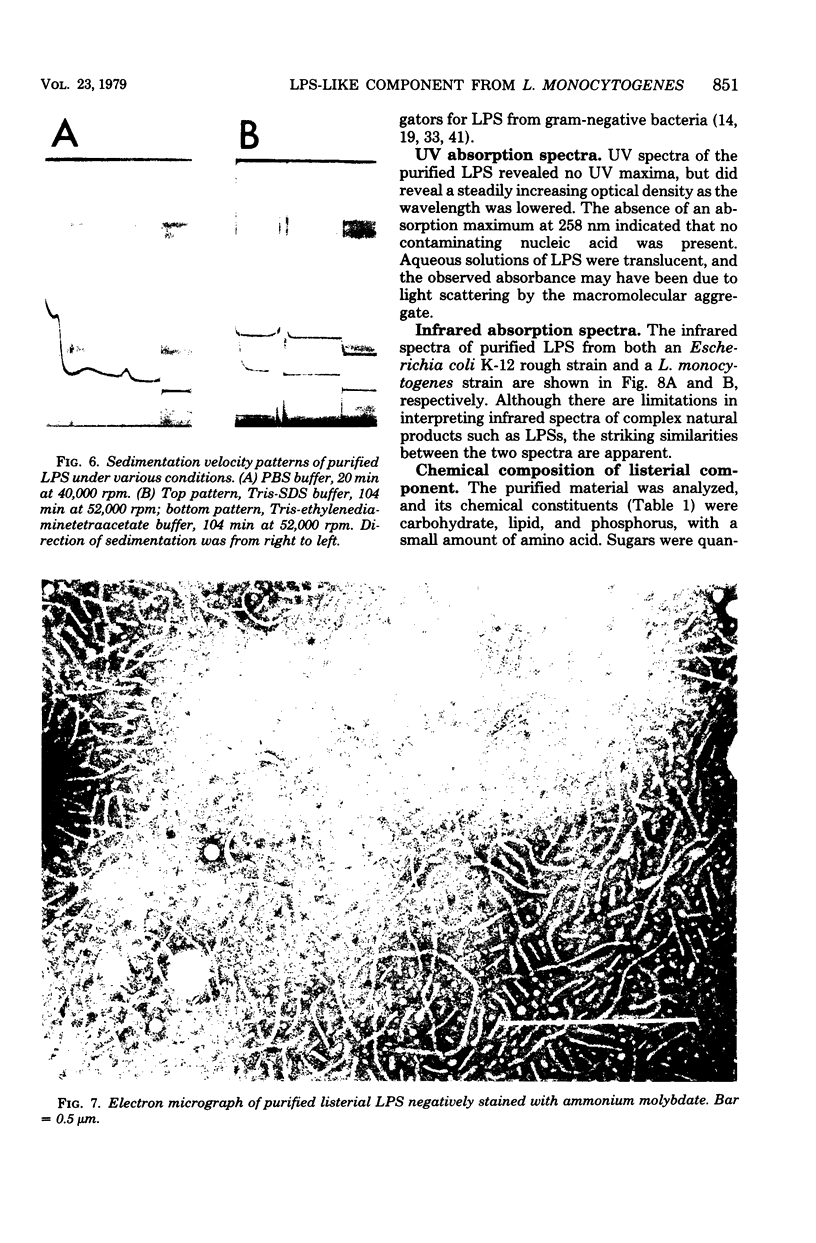
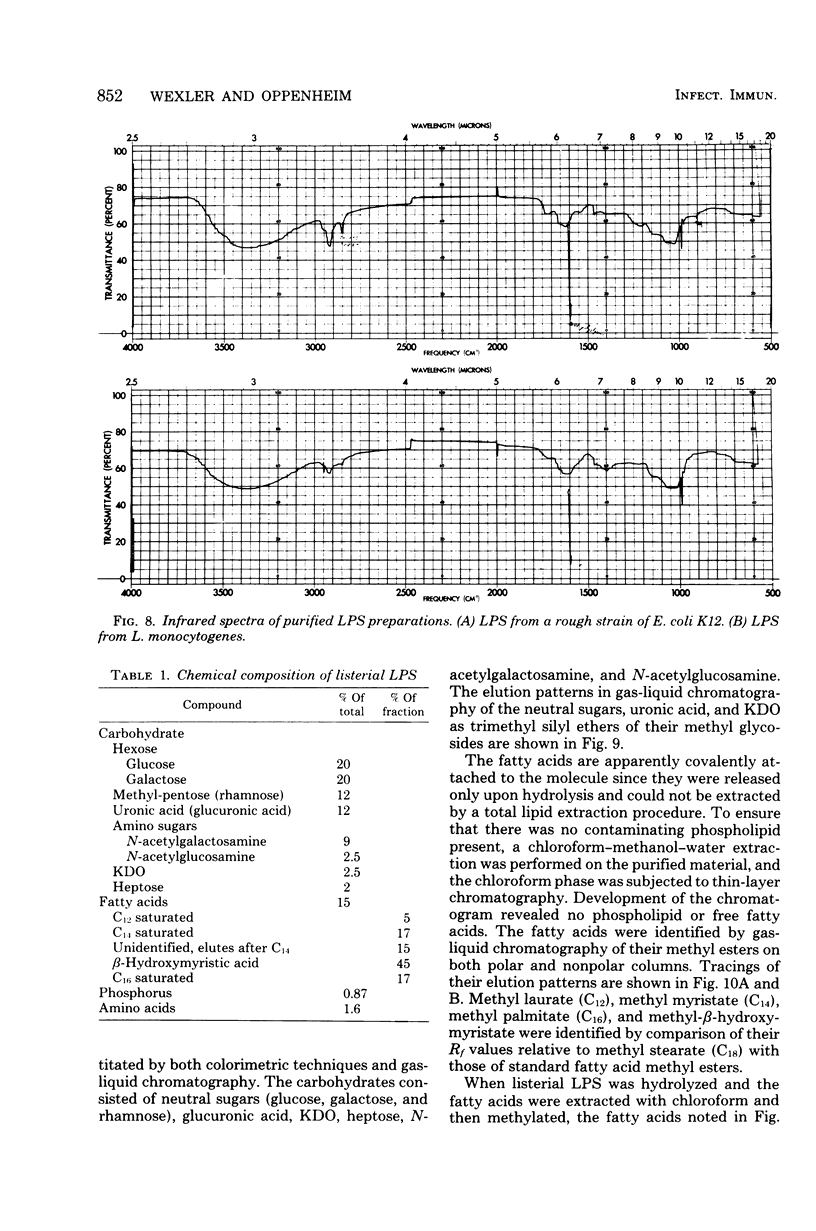
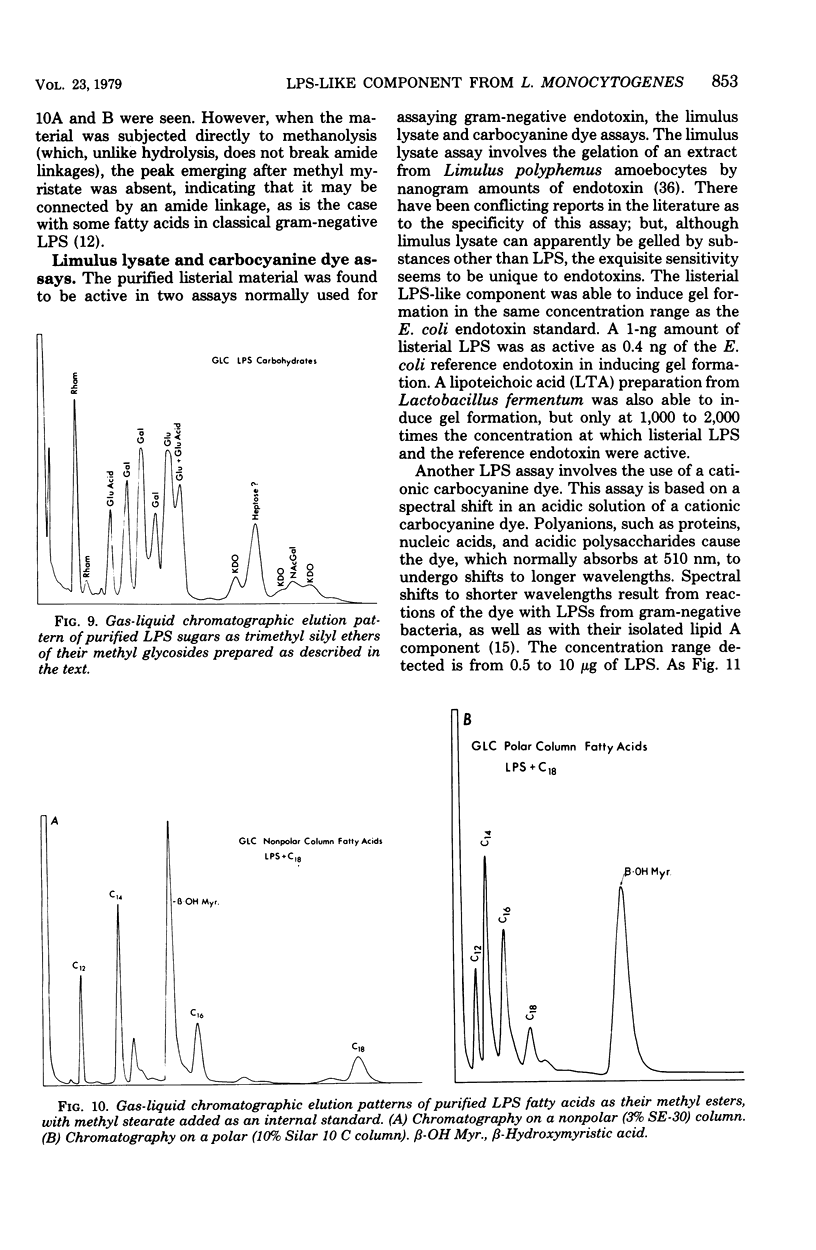
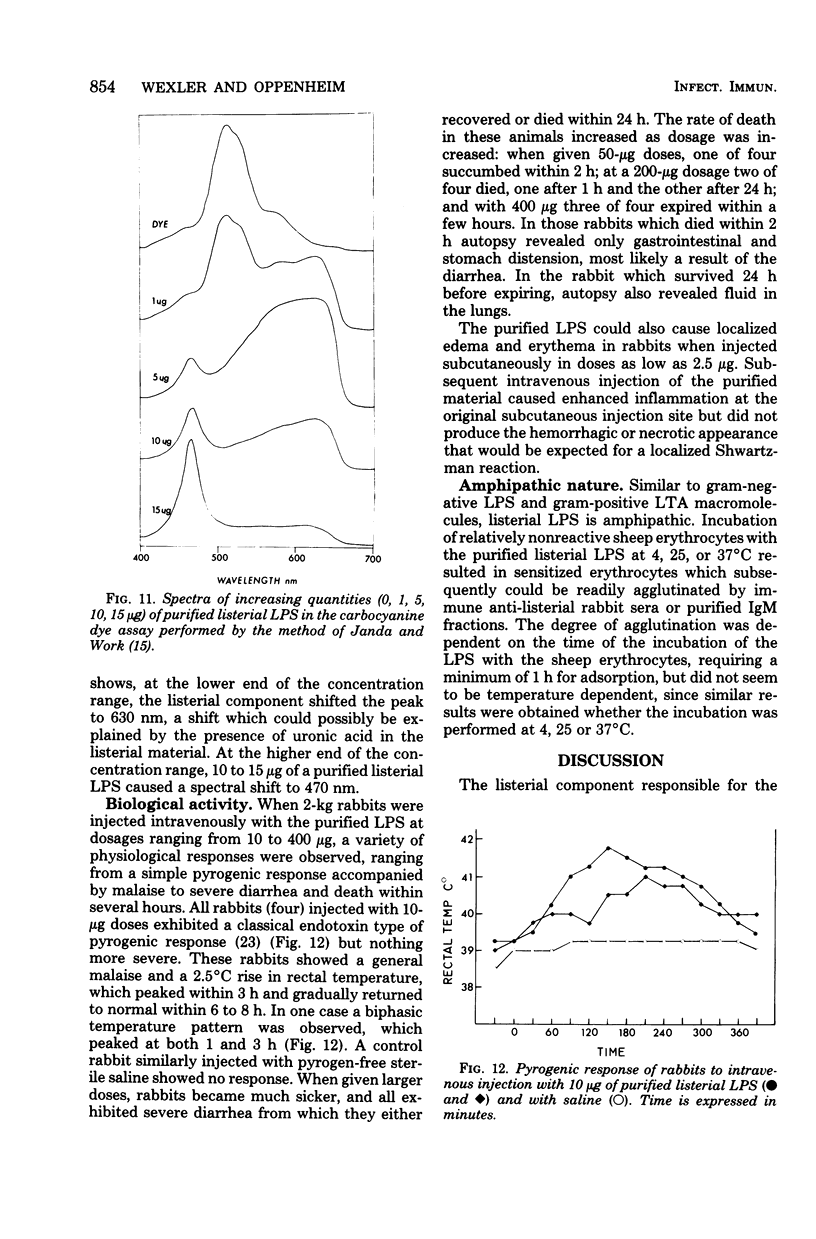
The bacterial component responsible for the induction of transient cold agglutinin syndrome in rabbits after intravenous injection of heat-killed Listeria monocytogenes type 4B has been purified and biologically and chemically characterized. A purified immunoglobulin M cold agglutinin was prepared from high-titer sera resulting from the immunization of rabbits with heat-killed L. monocytogenes type 4B and was subsequently used to monitor the purification of the bacterial component responsible for its induction. The bacterial component was isolated from a hot phenol-water extract of lyophilized L. monocytogenes type 4B by multiple molecular sieve chromatography. Upon chemical analysis the purified material was found to be strikingly similar in chemical composition to gram-negative lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. The material contained 15% total fatty acid (of which 50% was beta-hydroxymyristic acid), 40 to 45% neutral sugar (glucose, galactose, and rhamnose), 11.5% amino sugar, 12% uronic acid, 2.5% 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonic acid, 2% heptose, 0.87% phosphorus, and 1.6% amino acid, thereby accounting for 85 to 90% of the weight of the component. Electron micrographs of the purified material were similar to those of lipopolysaccharide preparations from gram-negative organisms. The purified material exist in aqueous solutions as large aggregates, but can be dissociated into a single smaller subunit (3.1S) by dialysis against sodium dodecyl sulfate buffer. The listerial component was toxic and pyrogenic to rabbits, producing symptoms typical of gram-negative endotoxins. Activity in the limulus lysate gelation assay and in the carbocyanine dye assay provides a further link of this material with classical gram-negative endotoxins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Bickel W. D., Haskins W. T., Milner K. C., Ribi E., Rudbach J. A. Frequency of occurrence of native hapten among enterobacterial species. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1427–1433. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1427-1433.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. An assay for total hexosamine and a differential assay for glucosamine and galactosamine. Clin Biochem. 1976 Dec;9(6):269–274. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(76)80075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTEA N., YAKULIS V., HELLER P. EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCTION OF COLD AGGLUTININS IN RABBITS. Blood. 1965 Sep;26:323–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin A. R., Jr, Siddique I. H. Certain chemical and biological properties of phenol extracts from Listeria monocytogenes. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Nov;37(11):1331–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costea N., Yakulis V. J., Heller P. Inhibition of cold agglutinins (anti-I) by M. pneumoniae antigens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Feb;139(2):476–479. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costea N., Yakulis V. J., Heller P. The mechanism of indction of cold agglutinins by mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1971 Mar;106(3):598–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe W. G. The colorimetric micro-determination of long-chain fatty acids. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88(1):7–10. doi: 10.1042/bj0880007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. W., Zey P. N. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharide isolated from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.838-844.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORN R. J., YAKULIS V. J., LEMKE C. E., CHOMET B. Cold agglutinins in Listeria monocytogenes infections. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957 Apr;99(4):573–580. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1957.00260040073008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Production of cold agglutinins in rabbits induced by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes or Streptococcus MG. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Aug;81(4):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopic study of lipopolysaccharide from an avian strain of Escherichia coli O18. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):238–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.238-243.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCILWAIN P., EVELETH D. F., DOUBLY J. A. PHARMACOLOGIC STUDIES OF A TOXIC CELLULAR COMPONENT OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. Am J Vet Res. 1964 May;25:774–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner K. C., Finkelstein R. A. Bioassay of endotoxin: correlation between pyrogenicity for rabbits and lethality for chick embryos. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):529–536. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mára M., Julăk J., Patocka F. Isolation and chemical properties of biologically active fractions of the surface of Listeria monocytogenes. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mára M., Patocka F., Julák J., Potuzníková B. Contribution to knowledge of factors participating in virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. II. Study of the chemical nature of complex Ei. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(1):29–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Warner R. C. Physicochemical studies on a lipopolysaccharide from the cell wall of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4994–5001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P., Salton M. R. Isolation and characterization of a mannan from mesosomal membrane vesicles of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):214–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patocka F., Mára M., Potuźníková B., Jirásek A., Mencíková E. Biological properties of surface components of Listeria monocytogenes (Ei factor). J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(3):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. S. Preparation of endotoxin. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):80–80. doi: 10.1038/209080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shands J. W., Jr, Graham J. A., Nath K. The morphologic structure of isolated bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique I. H., Srivastava K. K. Cell wall and cytoplasmic components of Listeria monocytogenes. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Apr;34(4):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique I. H., Ying L. C., Chung R. A. Studies on diphosphopyridine nucleotidase and platelet damaging factor in an extracellular product of Listeria monocytogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Oct;16(10):909–916. doi: 10.1139/m70-157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Zopf D. A., Wistar R., Jr, Ginsburg V. A human cold agglutinin which binds lacto-N-neotetraose. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):717–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser J., Drews G., Ladwig R. Localization and biological and physicochemical properties of the cell wall lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.346-353.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]