Abstract
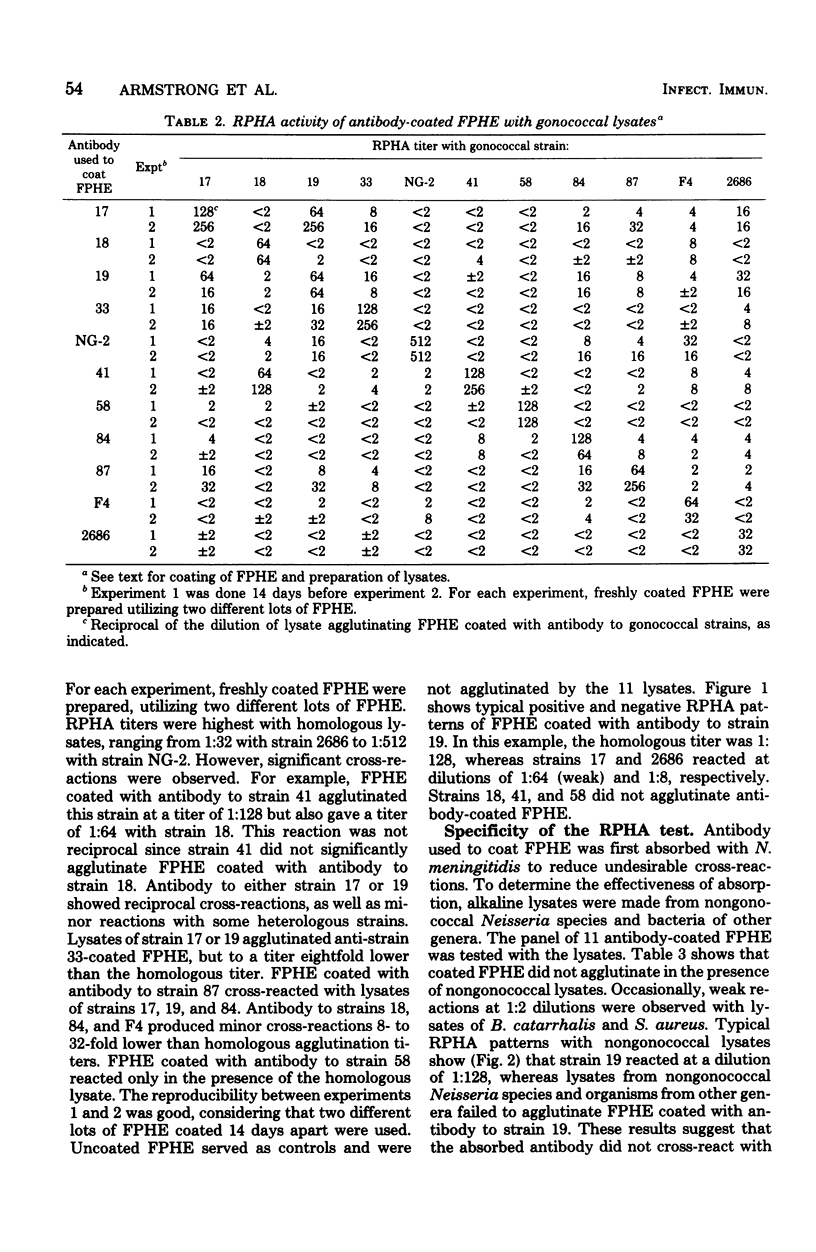
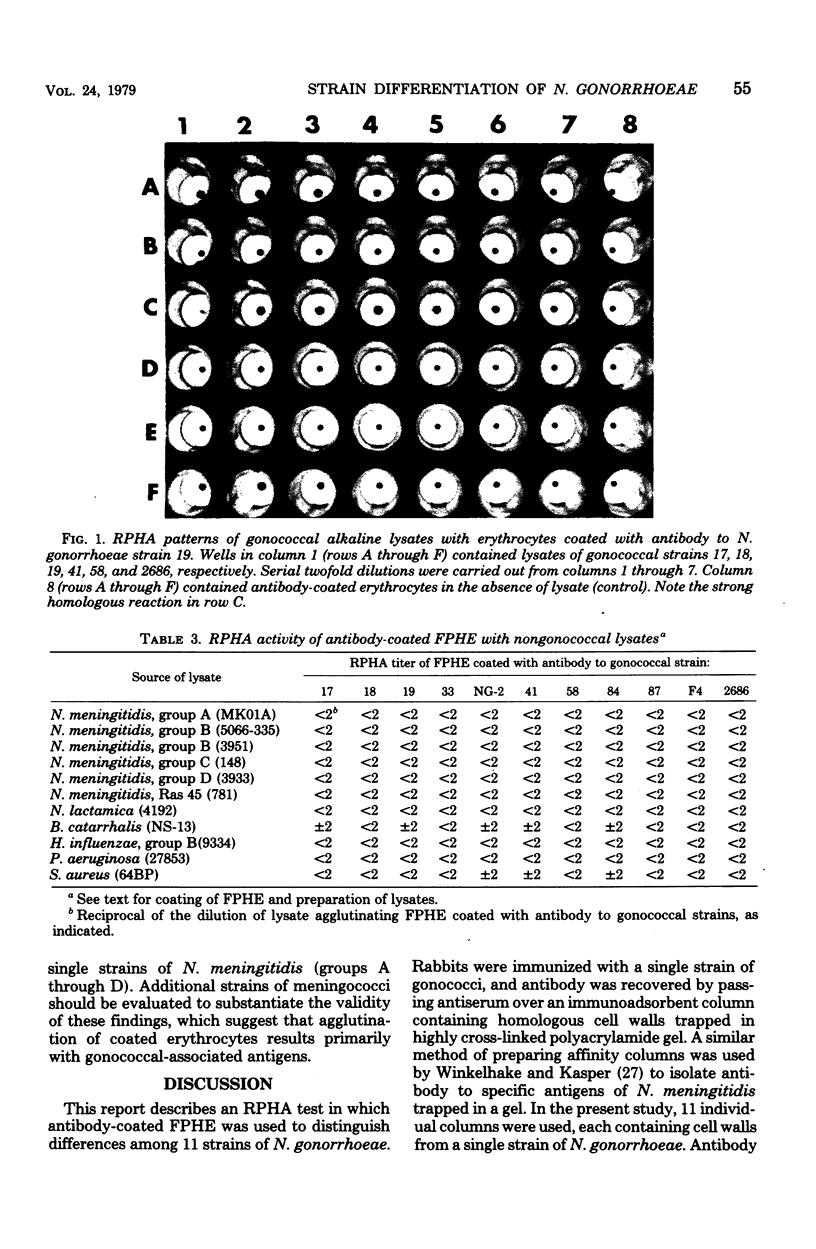
A reverse passive hemagglutination test that utilizes human erythrocytes coated with antibody to gonococci was developed to distinguish differences among 11 strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Different rabbits were immunized with each strain of gonococcus. Antibody was purified by passing antiserum over an immunoadsorbent column containing homologous cell walls trapped in a cross-linked polyacrylamide gel. Antibody, after absorption with N. meningitidis, was used for coating 11 individual suspensions of erythrocytes, each with antibody to one gonococcal strain. The panel of coated erythrocytes was added to microtiter trays containing dilutions of homologous bacterial lysate and lysates from 10 heterologous strains. Agglutination titers were highest with homologous lysates, although cross-reactions occurred among some heterologous lysates. Lysates of nongonococcal Neisseria species and of other genera did not agglutinate coated erythrocytes. The reverse passive hemagglutination test can be a useful procedure to distinguish differences among strains of N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A. Serogrouping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of four immunologically distinct acidic polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):377–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J., Wong K. H., Bullard J. C., Logan L. C. Immunological and serological diversity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: immunotyping of gonococci by cross-protein in guinea pig subcutaneous chambers. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1293–1296. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1293-1296.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M. Antigenic heterogeneity of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrel S., Barandun S. Protein-containing polyacrylamide gels: their use as immunoadsorbents of high capacity. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jan;8(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90420-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELSSON D. THE DEMONSTRATION OF N. GONORRHOEAE WITH THE AID OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODIES. 4. STUDIES BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE AND DOUBLE DIFFUSION-IN-GEL TECHNIQUE ON THE ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN N. GONORRHOEAE AND OTHER NEISSERIA STRAINS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:267–276. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson D., Kronvall G. Slide agglutination method for the serological identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with anti-gonococcal antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):368–374. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.368-374.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geizer I. Studies on serotyping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975 Jul;232(2-3):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata A. A., Brandriss M. W. Passive hemagglutination procedures for protein and polysaccharide antigens using erythrocytes stabilized by aldehydes. J Immunol. 1968 Mar;100(3):641–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata A. A., Emerick A. J., Boley W. F. Hepatitis B virus antigen detection by reverse passive hemagglutination. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jul;143(3):761–763. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata A. A., Ronspies S. J., Petruska J. C., Hargie M., Jr, Schenck J. R., Stall W. T. Passive hemagglutination procedure for group A streptococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson R. I. Typing the gonococcus. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 11;3(5714):107–107. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5714.107-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. S. Evaluation of the gono-tect fluorescent antibody system for confirmation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Health Lab Sci. 1975 Jul;12(3):215–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidberry H. D., Sadoff J. C. Pyocin sensitivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and its feasibility as an epidemiological tool. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):628–637. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.628-637.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Griffiss J. M., Rose D., Brooks G. F., Artenstein M. S. Clinical correlation of strain differentiation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134(2):128–134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Artenstein M. S. Cross-reactivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis and the nature of antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Holmes K. K., Knapp J. S., Ott S., Kyzer D. D. Immunologic classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with micro-immunofluorescence. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):795–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhake J. L., Kasper D. L. Affinity chromatography of anti-meningococcal antiserum. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):824–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]