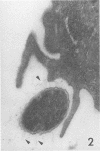
Abstract
The degree of piliation of 20 clinical isolates of Escherichia coli was correlated with their susceptibility to phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Piliation was quantitated by negative staining, and phagocytosis was quantitated by a monolayer technique. Ingestion was confirmed by electron microscopy. In the absence of source of opsonins, there was a positive correlation between the degree of piliation and susceptibility to phagocytosis (y = 0.83x + 19.58; correlation coefficient = 0.65; P < 0.01). Heavily piliated strains were no longer phagocytized after their pili were removed by ultraviolet irradiation. Phagocytosis was reduced 75% in the presence of 0.1 M d-mannose, an agent which competitively inhibits binding of pili to cell surfaces. l-Mannose, d-glucose, and d-galactose were much less inhibitory. The viability of piliated organisms was reduced by 1 log after 1 h of incubation with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Addition of 10% fresh human serum increased both the rate and completeness of killing. These observations suggest that polymorphonuclear leukocytes may interact with the pili of E. coli to promote phagocytosis. This phenomenon may have clinical relevance in situations where normal opsonic activity is poor, such as the renal medulla.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar-Shavit Z., Ofek I., Goldman R., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Mannose residues on phagocytes as receptors for the attachment of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhi. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):455–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessis M. Necrotaxis. Chemotaxis towards an injured cell. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1974;19:369–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNEW I., BRAUDE A. I. Depression of phagocytosis by solutes in concentrations found in the kidney and urine. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI104652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Cohn Z. A. Effects of concanavalin A on mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Stimulation of endocytic activity and inhibition of phago-lysosome formation. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1364–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. The effect of cytochalasin B and colchicine on concanavalin A induced vacuolation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Silverstein S. C. Segmental response of the macrophage plasma membrane to a phagocytic stimulus. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):323–336. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther G. R., Wang J. L., Yahara I., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Concanavalin A derivatives with altered biological activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1012–1016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., STRAUSS B. STUDIES ON HEAT-LABILE OPSONIN IN RABBIT SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Beachey E. H., Bisno A. L. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to phagocytosis: relationship to colonial morphology and surface pili. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):310–316. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old D. C. Inhibition of the interaction between fimbrial haemagglutinins and erythrocytes by D-mannose and other carbohydrates. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):149–157. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Ukena T. E., Berlin R. D. Effects of phagocytosis and colchicine on the distribution of lectin-binding sites on cell surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):394–398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Phagocytosis: the engulfment stage. Semin Hematol. 1968 Apr;5(2):134–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEDDEN W. I. Fimbriae and haemagglutinating activity in strains of Proteus hauseri. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:1–7. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salit I. E., Gotschlich E. C. Type I Escherichia coli pili: characterization of binding to monkey kidney cells. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1182–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J. Host-parasite interaction in the rat renal pelvis: a possible role for pili in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1696–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Ofek I. Influence of pili on the virulence of Proteus mirabilis in experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):664–667. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P. How do phagocytes eat? Ann Intern Med. 1978 Sep;89(3):398–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-3-398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Mason R. J., Pollard T. D., Vaughan M. Isolation and properties of phagocytic vesicles. II. Alveolar macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):604–614. doi: 10.1172/JCI106850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Pollard T. D., Mason R. J., Vaughan M. Isolation and properties of phagocytic vesicles from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1745–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI106664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Sparks E., Young D., King G. Studies on Gonococcus infection. X. Pili and leukocyte association factor as mediators of interactions between gonococci and eukaryotic cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1352–1361. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1352-1361.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. V. Capping, cell movement, and microtubular function in normal and lectin-treated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1207–1220. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J. Redistribution and fate of Ig complexes on surface of B lymphocytes: functional implications and mechanisms. Transplant Rev. 1973;14:184–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1973.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Contact angles and phagocytosis of non-opsonized bacteria. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Sep;12(3):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Fine structural alterations induced in platelets by adenosine diphosphate. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):604–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Recognition and response in mononuclear and granular phagocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Sep;25(3):355–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F., Good R. J. The influence of the shape of phagocytes on their adhesiveness. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(6):627–636. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]