Abstract
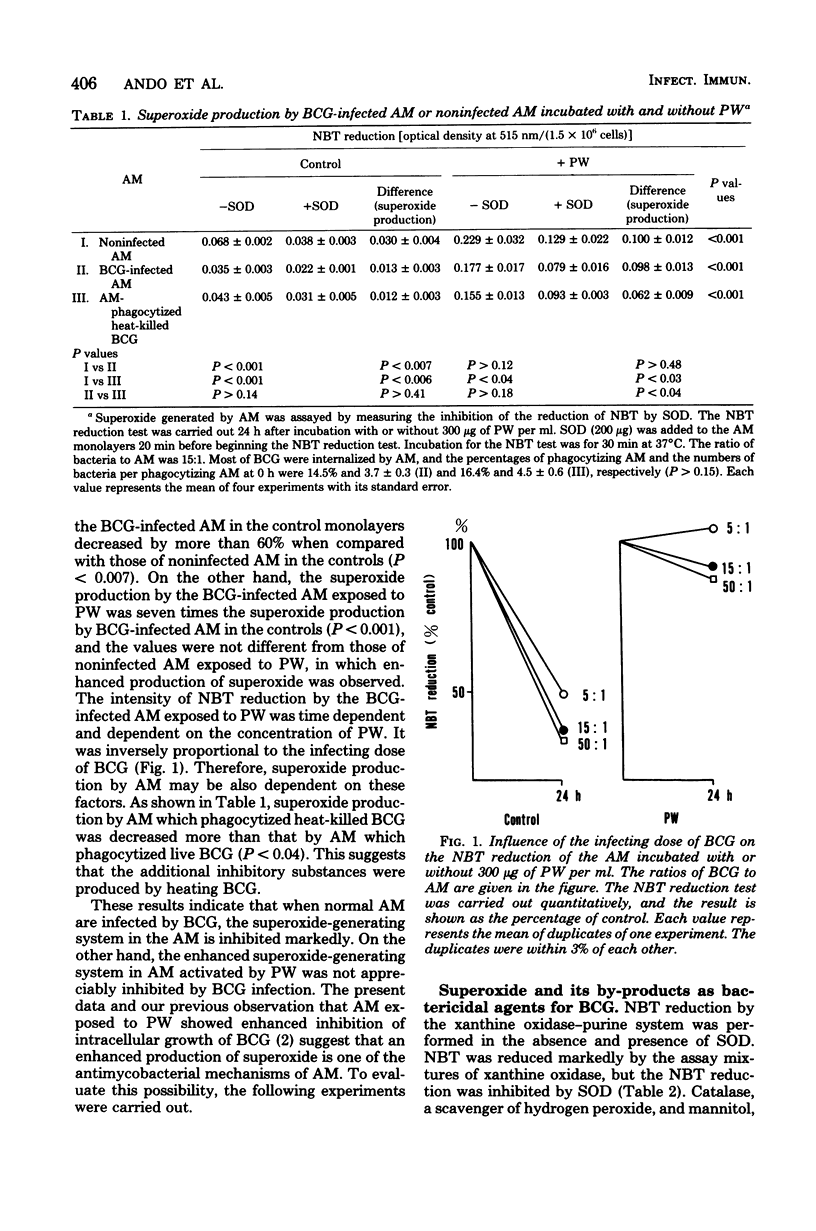
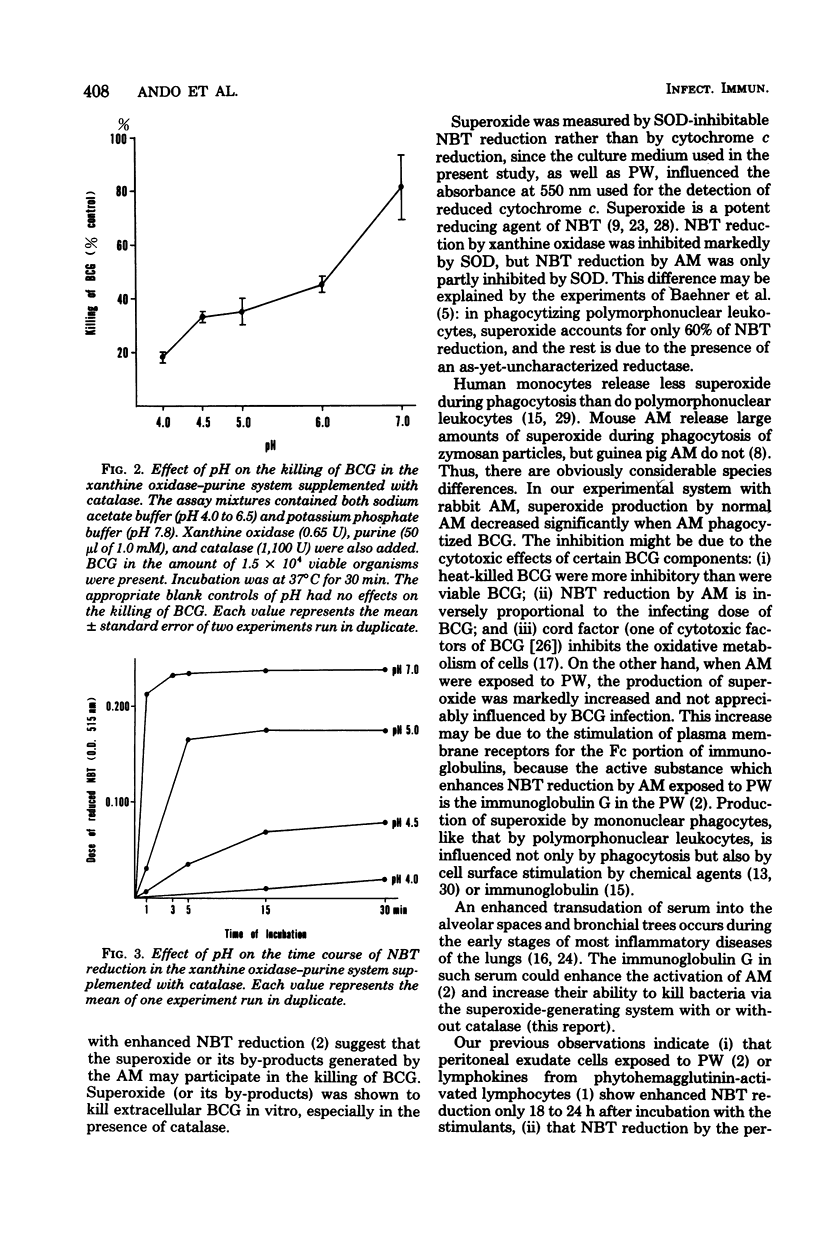
The superoxide production of BCG-infected and noninfected alveolar macrophages was measured by superoxide dismutase-inhibitable nitro blue tetrazolium reduction. The cells were incubated with or without cell-free bronchial lavage fluid (pulmonary washings). When control alveolar macrophages were infected by BCG, superoxide production was decreased markedly, probably due to bacterial cytotoxic factors. In contrast, the production of superoxide in alveolar macrophages exposed to pulmonary washings was increased and not appreciably influenced by BCG infection. Superoxide production by alveolar macrophages was dependent on time and on the protein concentration in the pulmonary washings. In controls, it was inversely proportional to the infecting dose of BCG. We observed previously that alveolar macrophages activated by pulmonary washings inhibited intracellular growth of BCG. We now present evidence that enhanced production of superoxide contributes to such inhibition, especially in the presence of catalase at acid pH. These findings are pertinent to the defense of inflamed lungs, where serum and serum immunoglobulin G transuded from blood into alveolar spaces probably induce such activation on alveolar macrophages.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando M., Suga M., Shima K., Sugimoto M., Higuchi S. Different effects of phytohemagglutinin-activated lymphocytes and their culture supernatants on macrophage function. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1442–1448. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1442-1448.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando M., Suga M., Shima K., Sugimoto M., Tokuomi H. Activation of alveolar macrophages exposed to lavage-procured immunoglobulin G obtained from normal rabbit lungs. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):476–484. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.476-484.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T., Kipnes R. S. Biological defense mechanisms. Evidence for the participation of superoxide in bacterial killing by xanthine oxidase. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Murrmann S. K., Davis J., Johnston R. B., Jr The role of superoxide anion and hydrogen peroxide in phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolic reactions. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):571–576. doi: 10.1172/JCI108126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Whitten D. M., Babior B. M. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):593–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drath D. B., Karnovsky M. L. Superoxide production by phagocytic leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):257–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee J. B., Vassallo C. L., Bell P., Kaskin J., Basford R. E., Field J. B. Catalase-dependent peroxidative metabolism in the alveolar macrophage during phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1280–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI106340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Cerqueira M., Lind S., Kaplan H. B. Evidence that the superoxide-generating system of human leukocytes is associated with the cell surface. J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;59(2):249–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI108635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Godzik C. A., Cohn Z. A. Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Lehmeyer J. E., Guthrie L. A. Generation of superoxide anion and chemiluminescence by human monocytes during phagocytosis and on contact with surface-bound immunoglobulin G. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B. Expression of immune mechanisms in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):347–379. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Fukushi K. Studies of a biochemical lesion in experimental tuberculosis in mice. X. Mitochondrial swelling induced by cord factor in vivo and accompanying biochemical change. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jul;100(1):42–46. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial activity of catalase at acid pH. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):571–574. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. W. Reactions of superoxide anion, catechols, and cytochrome c. Can J Biochem. 1970 Aug;48(8):935–939. doi: 10.1139/o70-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLL H., BLOCH H. Studies on the chemistry of the cord factor of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):251–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park B. H., Fikrig S. M., Smithwick E. M. Infection and nitroblue-tetrazolium reduction by neutrophils. A diagnostic acid. Lancet. 1968 Sep 7;2(7567):532–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAJAGOPALAN K. V., HANDLER P. HEPATIC ALDEHYDE OXIDASE. II. DIFFERENTIAL INHIBITION OF ELECTRON TRANSFER TO VARIOUS ELECTRON ACCEPTORS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:2022–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagone A. L., Jr, King G. W., Metz E. N. A comparison of the metabolic response to phagocytosis in human granulocytes and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1352–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI108403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsan M., McIntyre P. A. The requirement for membrane sialic acid in the stimulation of superoxide production during phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1308–1316. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


