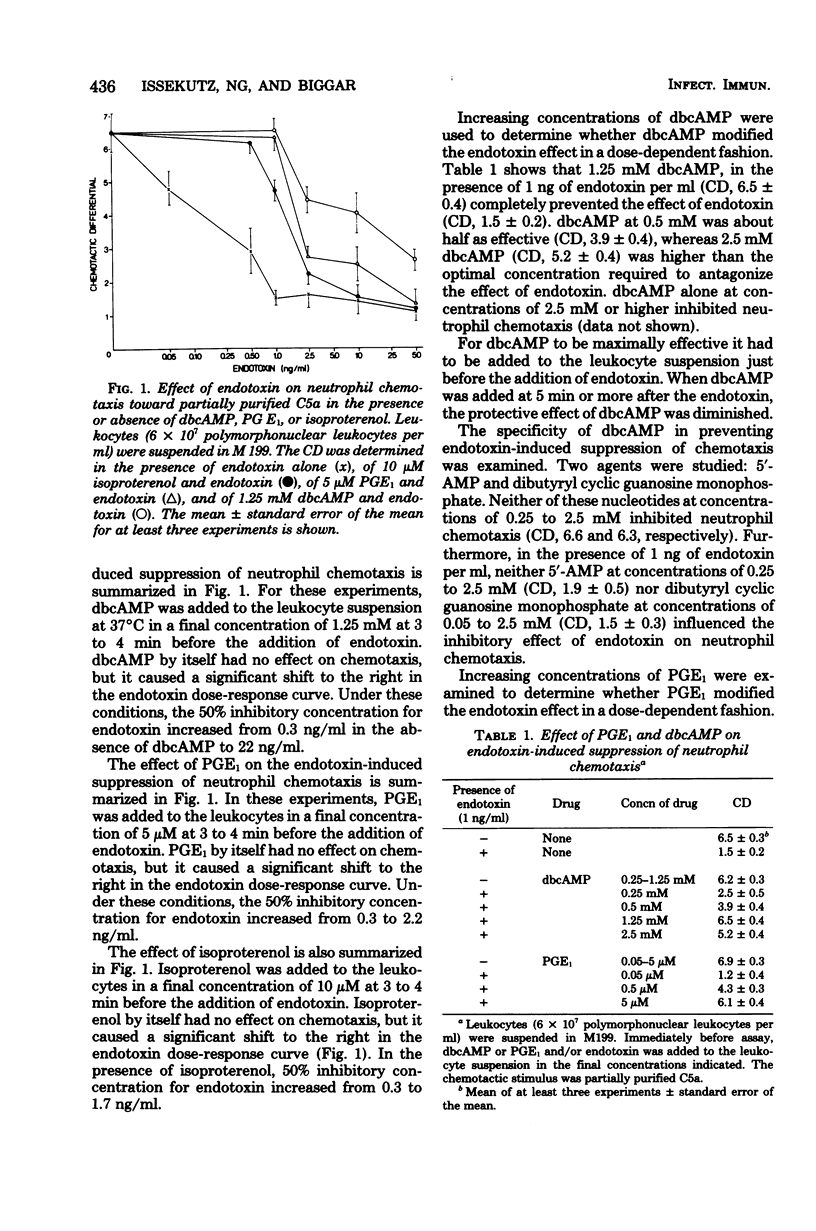
Abstract
We reported previously that Escherichia coli endotoxin inhibited human neutrophil chemotaxis toward C5a. This effect of endotoxin was antagonized by anti-inflammatory steroids. We now report that dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, prostaglandin E1, isoproterenol, and cholera toxin also antagonize the suppression of chemotaxis by endotoxin. Each compound inhibited the effect of endotoxin in a dose-dependent fashion. To be effective, each compound except cholera toxin had to be present at the time of endotoxin challenge. Furthermore, propranolol blocked the protective effect of isoproterenol against endotoxin but not the protective effect of dibutyrl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate or prostaglandin E1. Dibutyryl cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate, adenosine 5'-monophosphate, phenylephrine, prostaglandin F2 alpha, and carbachol did not modify the suppression of chemotaxis by endotoxin. Anti-inflammatory steroids and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate are thought to stabilize phospholipids in certain cell membranes. This phospholipid-stabilizing action may contribute, at least in part, to the protective effect against endotoxin-mediated suppression of neutrophil chemotaxis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergman M. J., Guerrant R. L., Murad F., Richardson S. H., Weaver D., Mandell G. L. Interaction of polymorphonuclear neutrophils with Escherichia coli. Effect of enterotoxin on phagocytosis, killing, chemotaxis, and cyclic AMP. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):227–234. doi: 10.1172/JCI108931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein L. M., Weissmann G., Zurier R. Effects of cholera enterotoxin on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and neutrophil function. Comparison with other compounds which stimulate leukocyte adenyl cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):698–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI107231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONTI C. R., CLUFF L. E., SCHEDER E. P. Studies on the pathogenesis of staphylococcal infection. IV. The effect of bacterial endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:845–860. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:127–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., Hill H. R., Quie P. G., Gogan N., Goldberg N. D. Cyclic GMP and cell movement. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):458–460. doi: 10.1038/245458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimber P. E., Rafter G. W. The interaction of Escherichia coli endotoxin with leukocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):14–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90510-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. I. Generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1564–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J. Steroid hormones, anti-inflammatory steroids and prostaglandins. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1976 Aug;8(4):337–348. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(76)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch G. E., Nichols W. K., Hill H. R. Cyclic nucleotide changes in human neutrophils induced by chemoattractants and chemotactic modulators. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbaczyńska-Cedro K., Staszewska-Barczak J. Suppression of the release of prostaglandin-like substances by hydrocortisone in vivo. Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):517–531. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Estensen R. D., Quie P. G., Hogan N. A., Goldberg N. D. Modulation of human neutrophil chemotactic responses by cyclic 3',5'-guanosine monophosphate and cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Metabolism. 1975 Mar;24(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Biggar W. D. Influence of serum-derived chemotactic factors and bacterial products on human neutrophil chemotaxis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):212–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.212-220.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. G., Perry M. B. Improved techniques for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):29–34. doi: 10.1139/m76-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Schmitges C. J., Chandrabose K., Cuatrecases P. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and prostacyclin inhibit membrane phospholipase activity in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):828–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logsdon P. J., Middleton E., Jr, Coffey R. G. Stimulation of leukocyte adenyl cyclase by hydrocortisone and isoproterenol in asthmatic and nonasthmatic subjects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Jul;50(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire E. D., Wallis R. B. The role of bacterial contamination in the isolation of apparent anti-inflammatory factors from rabbit anti-lymphocytic serum. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Feb;59(2):261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkes M., Stanford N., Chi M. M., Roth G. J., Raz A., Needleman P., Majerus P. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate inhibits the availability of arachidonate to prostaglandin synthetase in human platelet suspensions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):449–454. doi: 10.1172/JCI108659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W., Huber M. G., Baumann M. L. Alterations in cyclic AMP metabolism in human bronchial asthma. 3. Leukocyte and lymphocyte responses to steroids. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1342–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI107306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I., Rosenblatt J., Becker E. L. The role of cyclic AMP in the chemotactic responsiveness and spontaneous motility of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. The inhibition of neutrophil movement and the elevation of cyclic AMP levels by catecholamines, prostaglandins, theophylline and cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1126–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Walker J. R. Anti-inflammatory activity of bacterial endotoxin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1977 Nov;29(11):702–704. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1977.tb11441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Adye J. C. Endotoxin-binding substances from human leukocytes and platelets. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):978–986. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.978-986.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Territo M. C., Golde D. W. Granulocyte function in experimental human endotoxemia. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Wiik A., Garcia M. L., Williams R. C., Jr Enhancement of human neutrophil migration by prostaglandin E2. Cell Immunol. 1978 Apr;37(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


