Abstract
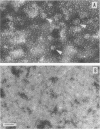
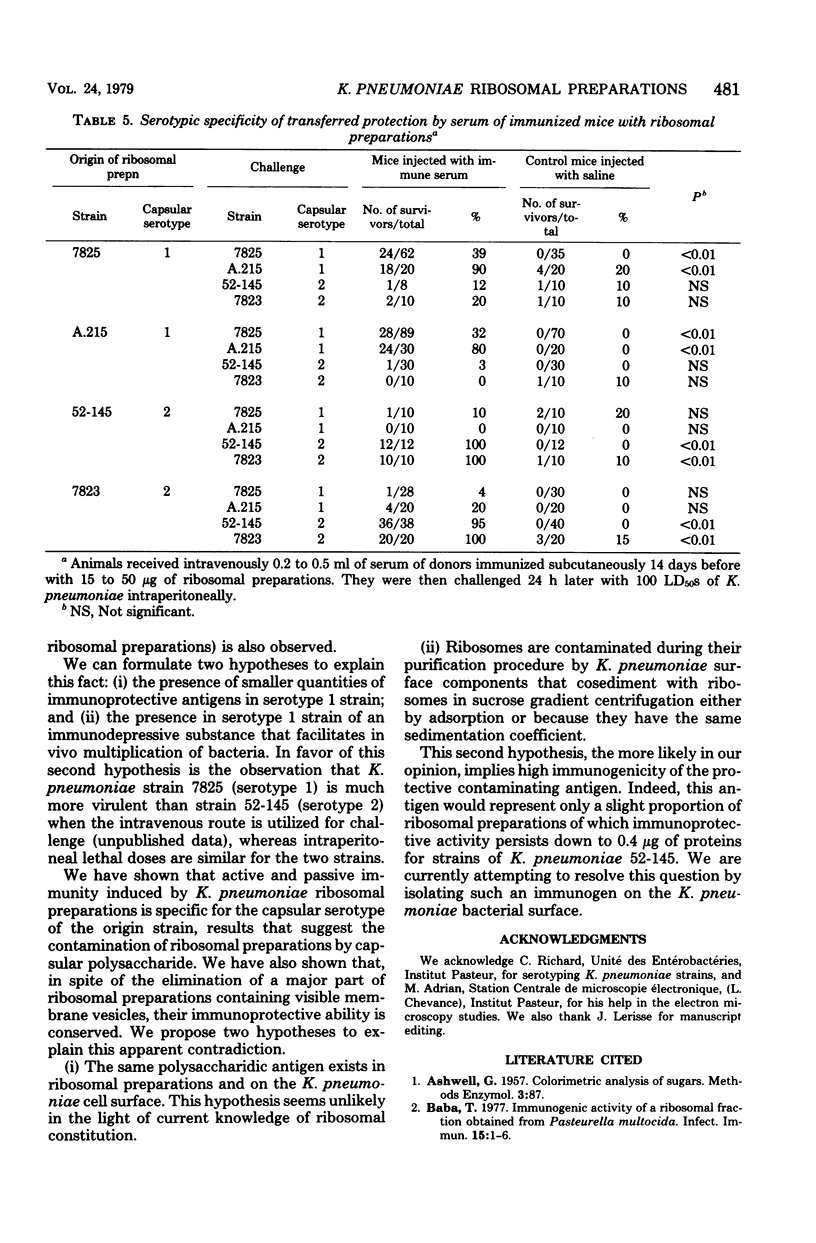
Klebsiella pneumoniae ribosomal preparations protect mice immunized by the subcutaneous route against an intraperitoneal challenge of 100 50% lethal doses. The minimal protective doses are 5 and 0.4 micrograms of proteins for preparations extracted from strains of capsular serotypes 1 and 2, respectively. This difference in protective activity is also found in bacteria killed by Formalin. The protective activity of these preparations is not diminished by their purification on sucrose gradient, which eliminates most of the membrane vesicles which are visible by electron microscopy. The use of four strains of K. pneumoniae belonging to capsular serotypes 1 and 2 allowed us to show that the immunoprotective capacity of the ribosomal preparations was specific to the capsular serotype of the origin strain. This was confirmed by experiments in which the serum of immunized mice was transferred passively. The experimental data favor the presence in the ribosomal preparation of antigens belonging to the bacterial surface and resisting elimination by ultracentrifugation on sucrose gradient. Those surface antigens (possibly capsular polysaccharide) at least play a role in the orientation of the specificity of the protection induced by the ribosomal preparations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba T. Immunogenic activity of a ribosomal fraction obtained from Pasteurella multocida. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.1-6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbel M. J. The immunogenic activity of ribosomal fractions derived from Brucella abortus. J Hyg (Lond) 1976 Feb;76(1):65–74. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400054954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit C., Tewari R. P. Immunogenicity of Ribosomal Preparations from Yeast Cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1091-1097.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Protection of suckling mice from experimental cholera by maternal immunization: comparison of the efficacy of whole-cell, ribosomal-derived, and enterotoxin immunogens. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.167-172.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoops P., Prather N. E., Berry J., Ravel J. M. Evidence for an extrinsic immunogen in effective ribosomal vaccines from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1184–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1184-1192.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Gregory B., Naylor J., Actor P. Isolation of protective somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa) ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):156–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.156-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman M. M. Direct evidence for the presence of lipopolysaccharide components in Pseudomonas ribosomal vaccine. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):471–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.471-473.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn M., Tewari R. P., Solotorovsky M. Immunoprotective activity of ribosomes from Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):453–460. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.453-460.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Johnson W. Role of endotoxin contamination in ribiosomal vaccines prepared from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.98-104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard C. Etude antigénique et biochimique de 500 souches de Klebsiella. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1973;31(4):295–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomal vaccines isolated from group A, type 14 Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1195-1202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendsen C. L., Johnson W. Humoral immunity to Streptococcus pneumoniae induced by a pneumococcal ribosomal protein fraction. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):345–354. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.345-354.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R. P., Lynn M., Birnbaum A. J., Solotorovsky M. Characterization of the immunoprotective antigen of ribosomal preparations from Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.58-65.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari R. P., Sharma D., Solotorovsky M., Lafemina R., Balint J. Adoptive transfer of immunity from mice immunized with ribosomes or live yeast cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):789–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.789-795.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Weiss E. Response of mice to injection of ribosomal fraction from group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.355-363.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Eisenstein T. K. Biological properties of an immunogenic pneumococcal subcellular preparation. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):750–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.750-757.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Snyder I. S. Protection against pneumococcal infection by a ribosomal preparation. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.16-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Berry L. J. Immunity induced by ribosomal extracts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):66–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. NATURE OF THE LABILE IMMUNOGENIC SUBSTANCE IN THE PARTICULATE FRACTION ISOLATED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1030-1037.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]