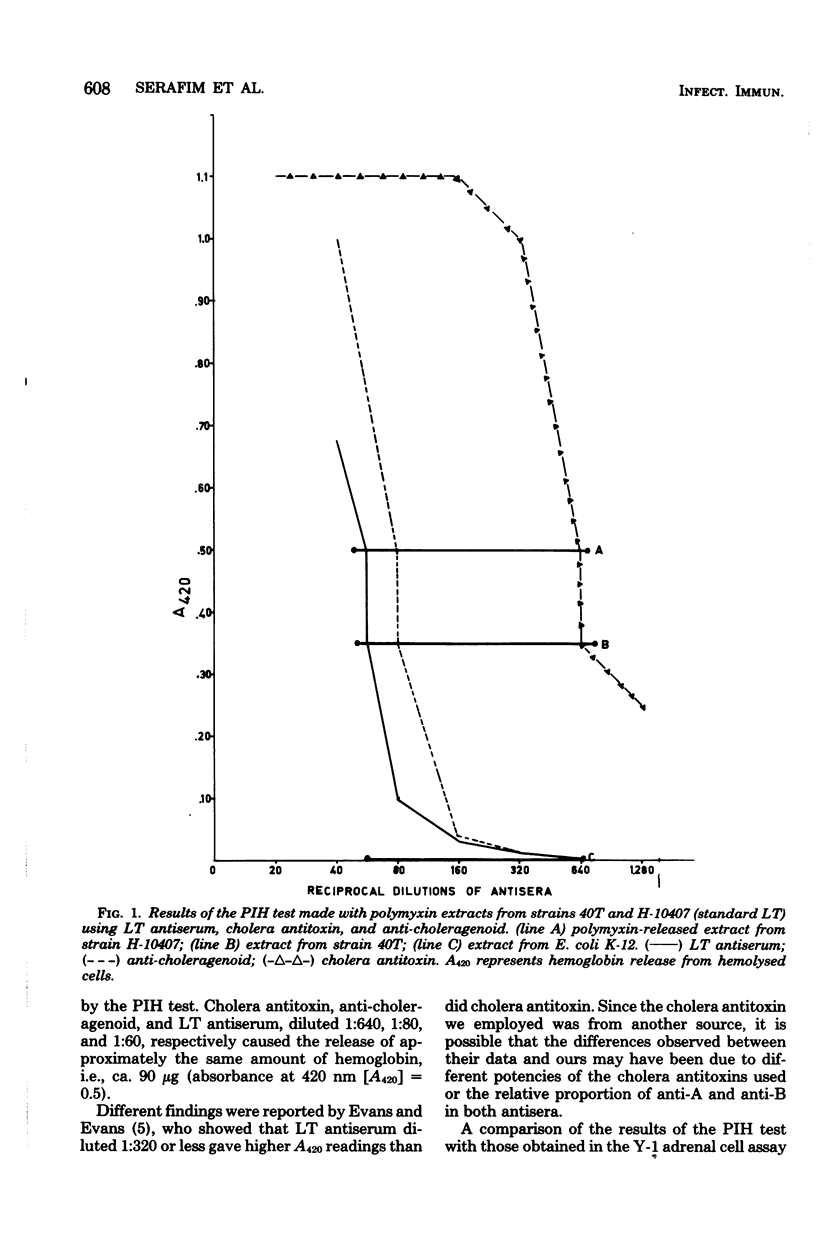
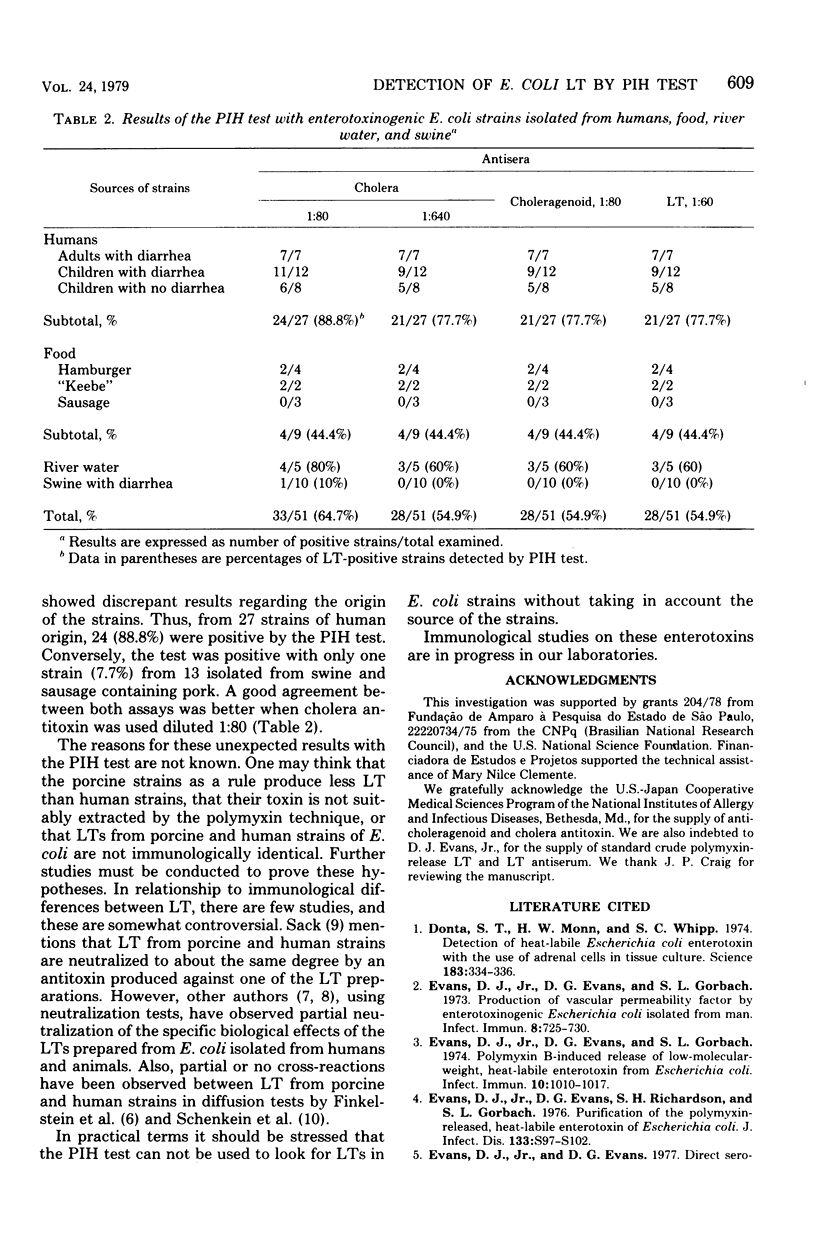
Abstract
Fifty-one strains of Escherichia coli isolated from humans, swine, food, and water and identified as enterotoxinogenic by the Y-1 adrenal cell assay, were examined for heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) production by the passive immune hemolysis test. Cholera antitoxin, anti-choleragenoid and anti-LT were used as antisera. Cholera antitoxin was much more potent than anti-choleragenoid and LT antiserum in the detection of LT-positive strains. All strains isolated from pigs and sausage were negative in tests made with LT antiserum. A few strains isolated from humans, food, and water also gave negative results. These data showed that the passive immune hemolysis test is not as efficient as the Y-1 adrenal cell assay in the detection of enterotoxinogenic E. coli strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Polymyxin B-Induced Release of Low-Molecular-Weight, Heat-Labile Enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1010-1017.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkein I., Green R. F., Santos D. S., Maas W. K. Partial purification and characterization of a heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1710–1720. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1710-1720.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


