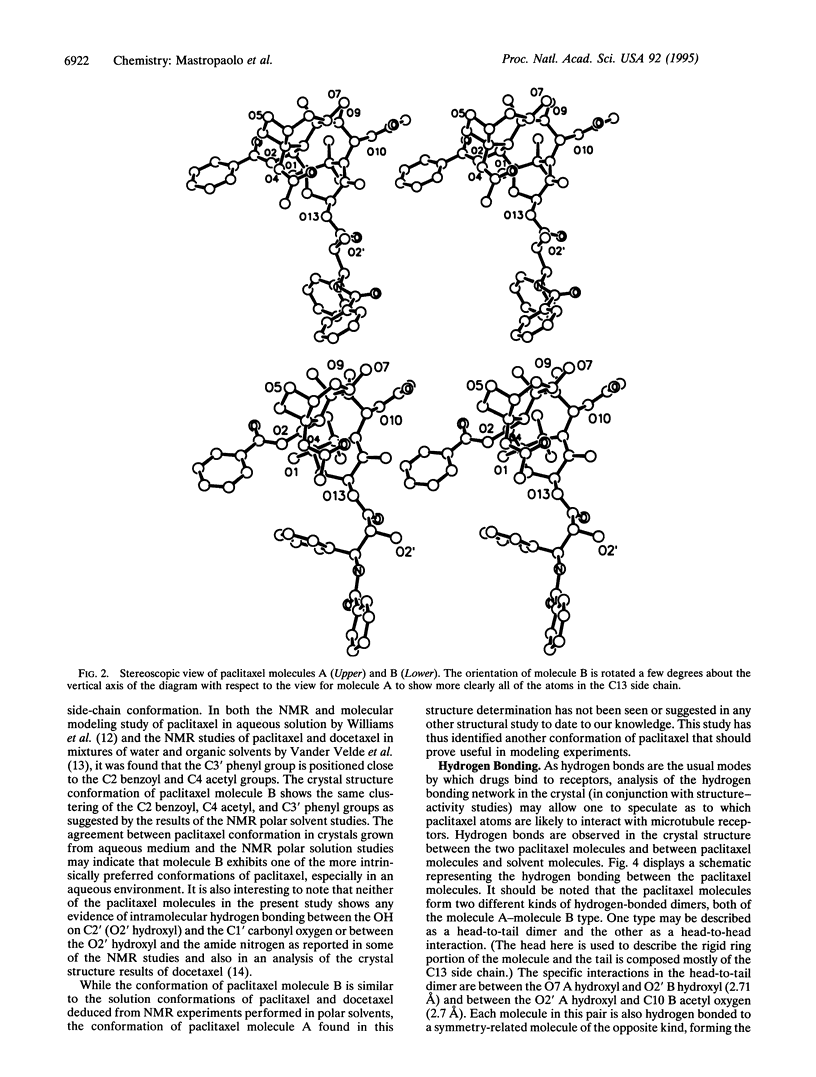
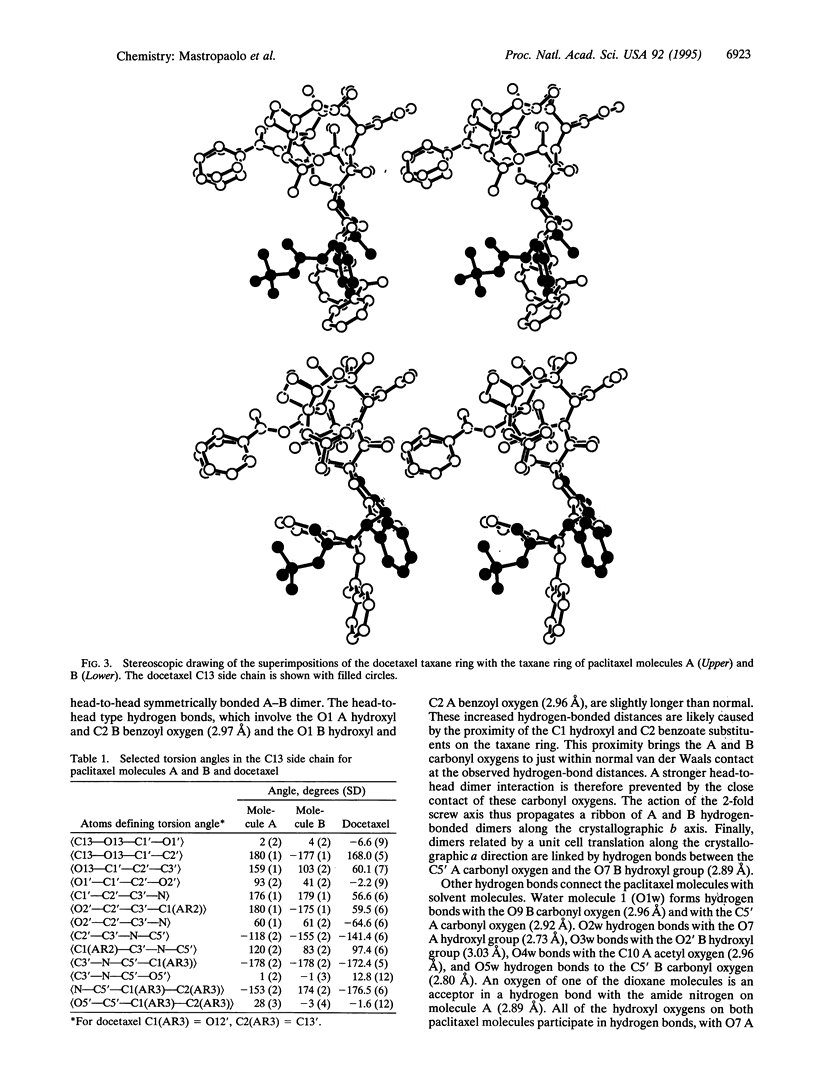
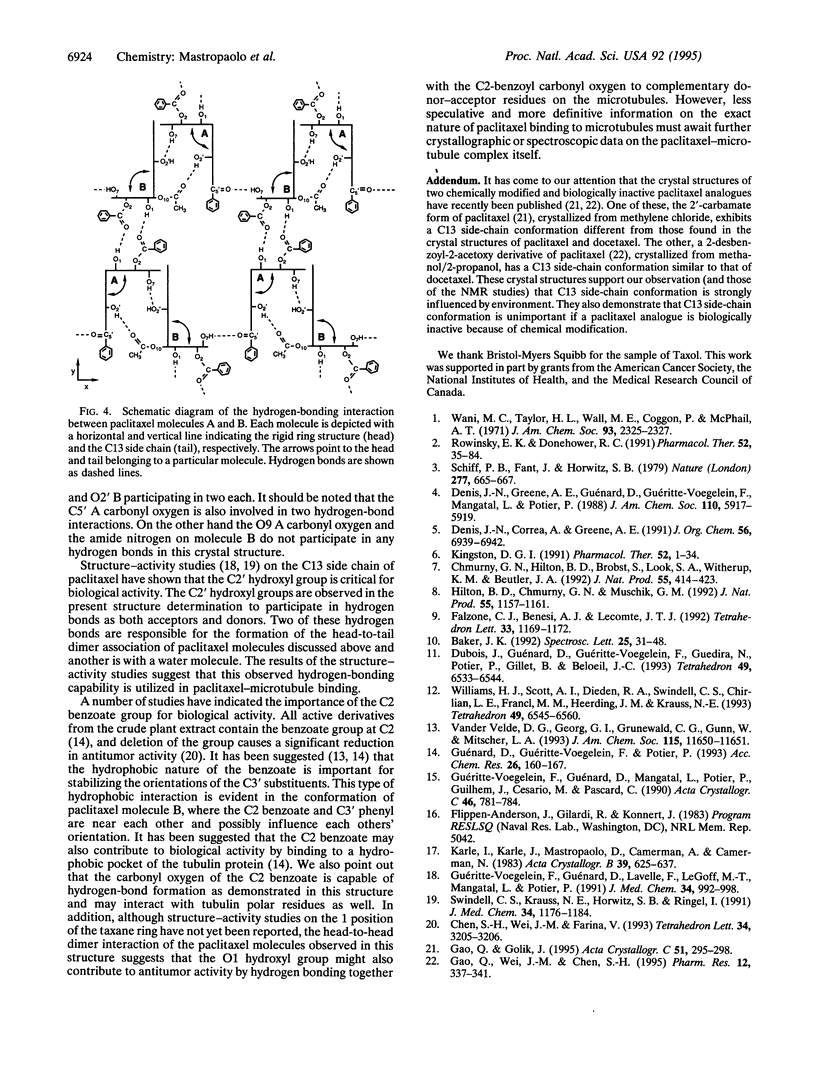
Abstract
Paclitaxel (formerly called taxol), an important anticancer drug, inhibits cell replication by binding to and stabilizing microtubule polymers. As drug-receptor interactions are governed by the three-dimensional stereochemistries of both participants, we have determined the crystal structure of paclitaxel to identify its conformational preferences that may be related to biological activity. The monoclinic crystals contain two independent paclitaxel molecules in the asymmetric unit plus several water and dioxane solvent molecules. Taxane ring conformation is very similar in both paclitaxel molecules and is similar to the taxane ring conformation found in the crystal structure of the paclitaxel analogue docetaxel (formerly called taxotere). The two paclitaxel molecules have carbon-13 side-chain conformations that differ from each other and from that of the corresponding side chain in the docetaxel crystal structure. The carbon-13 side-chain conformation of one paclitaxel molecule is similar to what was proposed from NMR studies done in polar solvents, while that of the other paclitaxel molecule is different and hitherto unobserved. The paclitaxel molecules interact with each other and with solvent atoms through an extensive network of hydrogen bonds. Analysis of the hydrogen-bonding network together with structure-activity studies may suggest which atoms of paclitaxel are important for binding to microtubule receptors.
Full text
PDF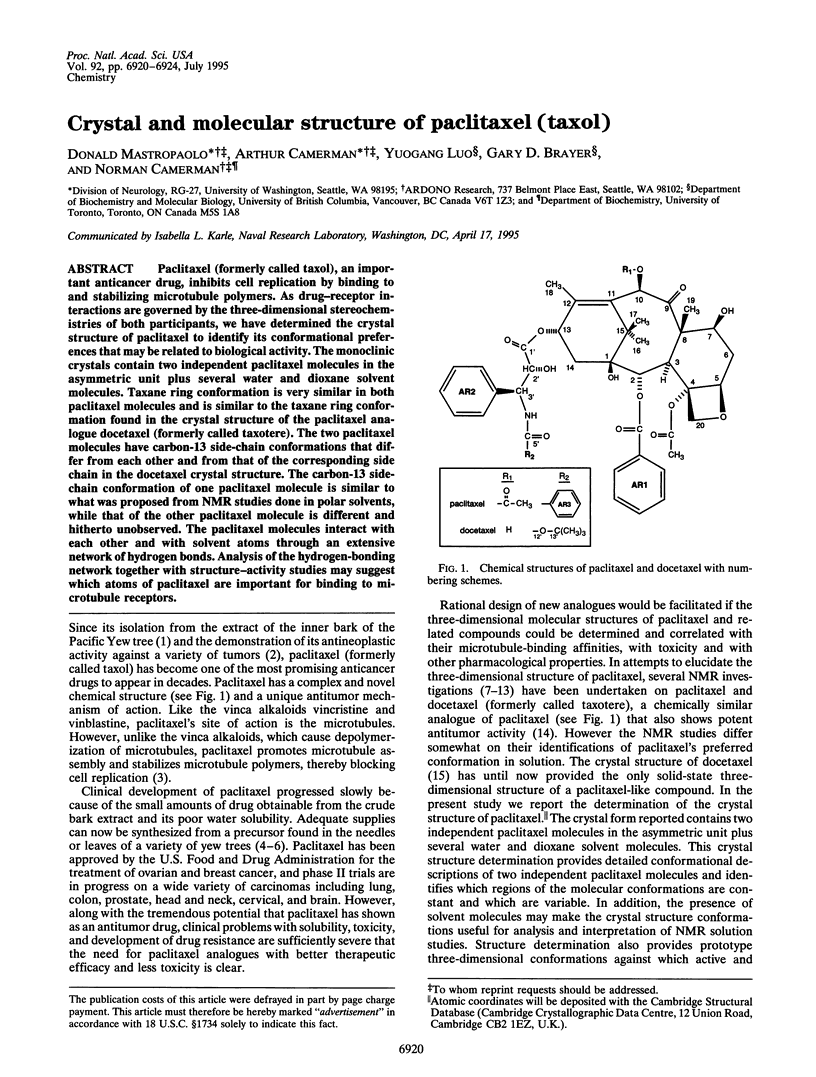

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chmurny G. N., Hilton B. D., Brobst S., Look S. A., Witherup K. M., Beutler J. A. 1H- and 13C-nmr assignments for taxol, 7-epi-taxol, and cephalomannine. J Nat Prod. 1992 Apr;55(4):414–423. doi: 10.1021/np50082a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao Q., Wei J. M., Chen S. H. Crystal structure of 2-debenzoyl, 2-acetoxy paclitaxel (Taxol): conformation of the paclitaxel side-chain. Pharm Res. 1995 Mar;12(3):337–341. doi: 10.1023/a:1016236014766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guéritte-Voegelein F., Guénard D., Lavelle F., Le Goff M. T., Mangatal L., Potier P. Relationships between the structure of taxol analogues and their antimitotic activity. J Med Chem. 1991 Mar;34(3):992–998. doi: 10.1021/jm00107a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton B. D., Chmurny G. N., Muschik G. M. Taxol: quantitative internuclear proton-proton distances in CDCl3 solution from nOe data: 2D nmr ROESY buildup rates at 500 MHz. J Nat Prod. 1992 Aug;55(8):1157–1161. doi: 10.1021/np50086a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston D. G. The chemistry of taxol. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Oct;52(1):1–34. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90085-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowinsky E. K., Donehower R. C. The clinical pharmacology and use of antimicrotubule agents in cancer chemotherapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Oct;52(1):35–84. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(91)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff P. B., Fant J., Horwitz S. B. Promotion of microtubule assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):665–667. doi: 10.1038/277665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindell C. S., Krauss N. E., Horwitz S. B., Ringel I. Biologically active taxol analogues with deleted A-ring side chain substituents and variable C-2' configurations. J Med Chem. 1991 Mar;34(3):1176–1184. doi: 10.1021/jm00107a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wani M. C., Taylor H. L., Wall M. E., Coggon P., McPhail A. T. Plant antitumor agents. VI. The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from Taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 May 5;93(9):2325–2327. doi: 10.1021/ja00738a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


