Abstract
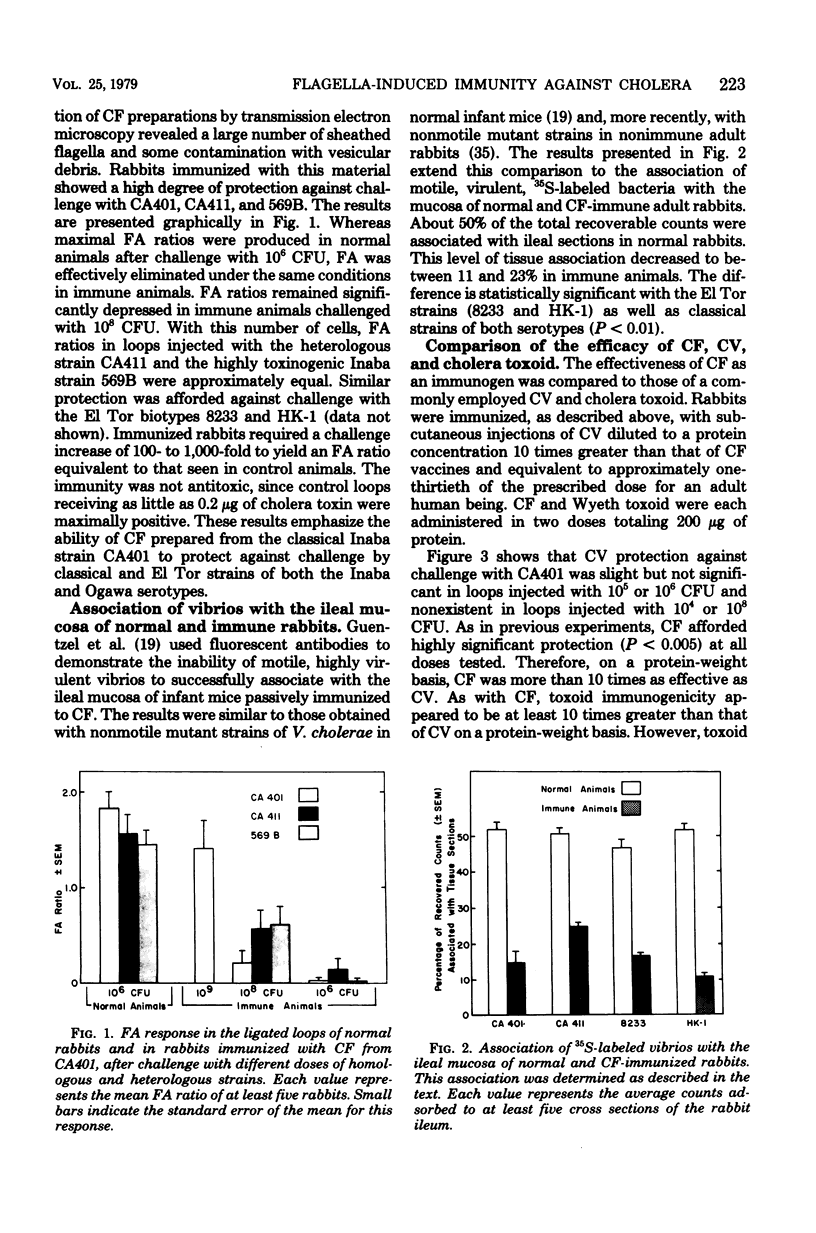
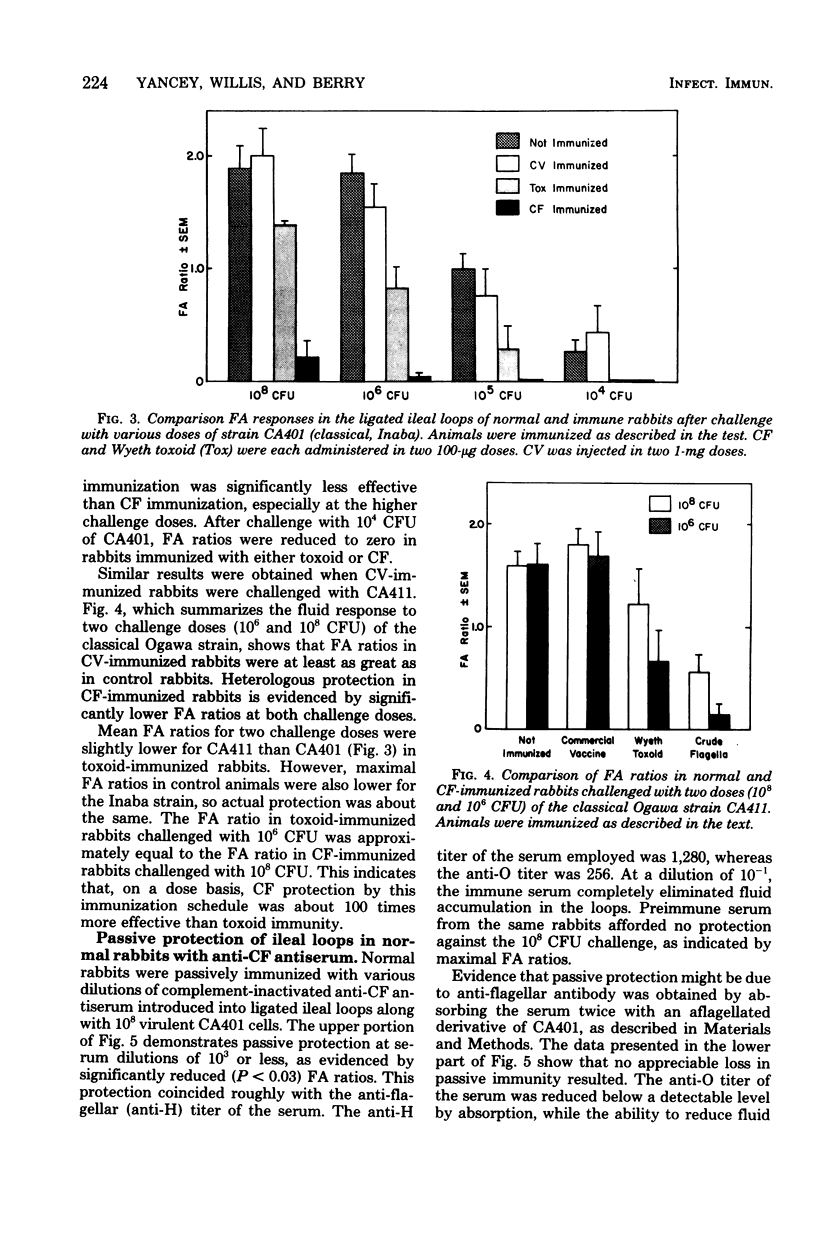
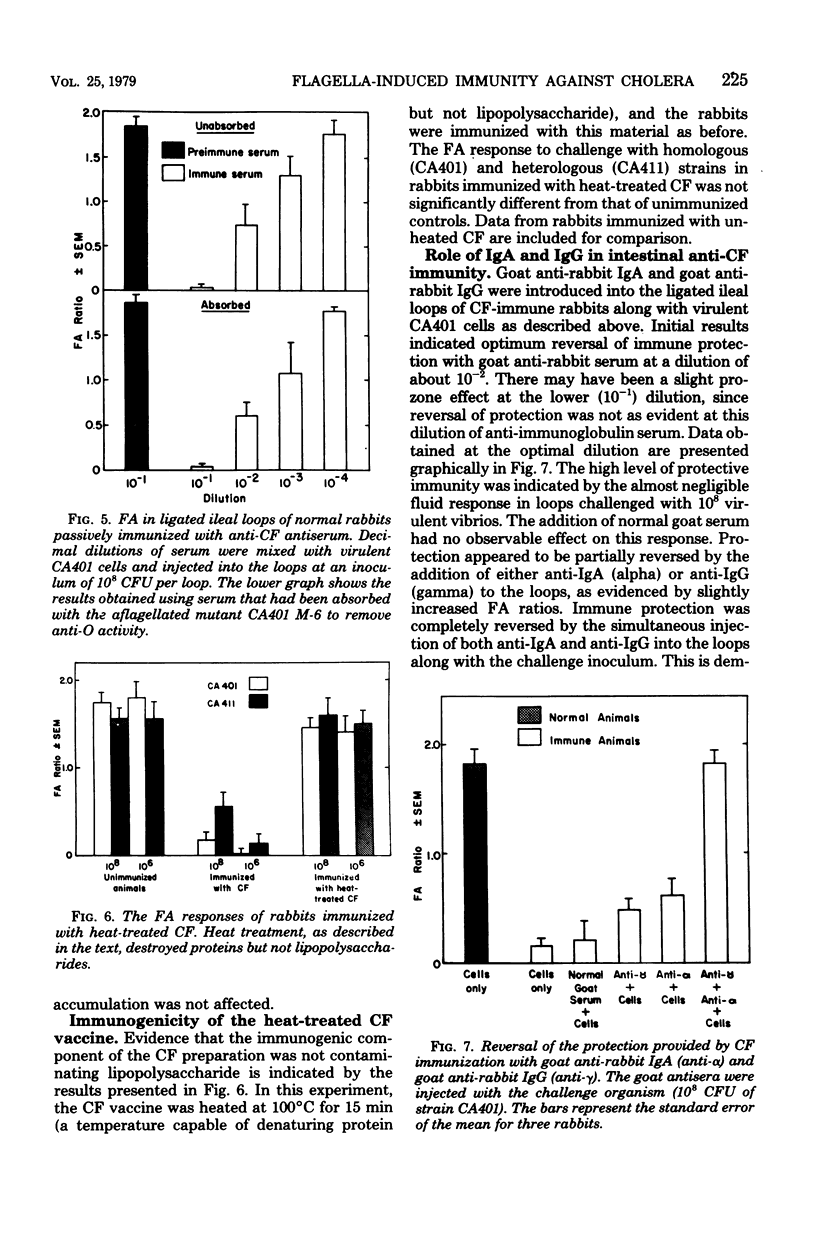
The adult rabbit ligated ileal loop model was used to evaluate the prophylactic potential of a crude flagellar (CF) vaccine produced from the classical. Inaba strain CA401. A greater than 1,000-fold increase in the challenge inoculum was required to induce an intestinal fluid response in actively immunized adult rabbits equivalent to that produced in unimmunized animals. Similar protection was afforded against challenge with classical and El Tor biotypes of both Inaba and Ogawa serotypes. Highly virulent 35S-labeled vibrios were inhibited in their ability to associated with the intestinal mucosa of CF-immunized rabbits. The protection conferred by CF immunization was found to be superior to that of a commercial bivalent vaccine and also to that of glutaraldehyde-treated cholera toxoid. The critical immunogenic component of CF appears to be a flagella-derived protein. The immunogenicity of CF was destroyed by heat treatment, and absorption of CF-immune serum with aflagellated mutant vibrios did not diminish its ability to confer a high level of passive protection. The intestinal protection of CF-immunized rabbits was completely reversed by the introduction of both goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulins A and G, but by neither alone.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azurin J. C., Cruz A., Pesigan T. P., Alvero M., Camena T., Suplido R., Ledesma L., Gomez C. Z. A controlled field trial of the effectiveness of cholera and cholera El Tor vaccines in the Philippines. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(5):703–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENENSON A. S., ISLAM M. R., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd RAPID IDENTIFICATION OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE BY DARKFIELD MICROSCOPY. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:827–831. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baselski V. S., Parker C. D. Intestinal distribution of Vibrio cholerae in orally infected infant mice: kinetics of recovery of radiolabel and viable cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):518–525. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.518-525.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benenson A. S., Saad A., Mosley W. H., Ahmed A. Serological studies in cholera. 3. Serum toxin neutralization--rise in titre in response to infection with Vibrio cholerae, and the level in the "normal" population of East Pakistan. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(2):287–295. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cash R. A., Music S. I., Libonati J. P., Snyder M. J., Wenzel R. P., Hornick R. B. Response of man to infection with Vibrio cholerae. I. Clinical, serologic, and bacteriologic responses to a known inoculum. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das Gupta A., Sinha R., Shrivastava D. L., De S. P., Taneja B. L., Rao M. S., Abou-Gareeb A. H. Controlled field trial of the effectiveness of cholera and cholera El Tor vaccines in Calcutta. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;37(3):371–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks E. R., Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Evaluation of surface components of Vibrio cholerae as protective immunogens. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):533–538. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.533-538.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eubanks E. R., Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Virulence factors involved in the intraperitoneal infection of adult mice with Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):457–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.457-463.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R., GANGAROSA E. J. ORAL IMMUNIZATION AND PRODUCTION OF COPROANTIBODY IN HUMAN VOLUNTEERS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:724–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the ligated ileal loop model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):464–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.464-467.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Hollingsworth R. C. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the rat foot edema model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):468–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.468-473.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: comparison of immunity induced perorally and parenterally in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):647–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGAROSA E. F., BEISEL W. R., BENYAJATI C., SPRINZ H., PIYARATN P. The nature of the gastrointestinal lesion in asiatic cholera and its relation to pathogenesis: a biopsy study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1960 Mar;9:125–135. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1960.9.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Field L. H., Eubanks E. R., Berry L. J. Use of fluorescent antibody in studies of immunity to cholera in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.539-548.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Månsson J., Svennerholm L. Interaction of cholera toxin and membrane GM1 ganglioside of small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2520–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Mechanisms of disease and immunity in cholera: a review. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 (Suppl):S105–S112. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: adhesion to isolated rabbit brush border membranes and hemagglutinating activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):232–239. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.232-239.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Contribution of the K88 antigen of Escherichia coli to enteropathogenicity; protection against disease by neutralizing the adhesive properties of K88 antigen. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1441–1449. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley W. H., McCormack W. M., Ahmed A., Chowdhury A. K., Barui R. K. Report of the 1966-67 cholera vaccine field trial in rural East Pakistan. 2. Results of the serological surveys in the study population--the relationship of case rate to antibody titre and an estimate of the inapparent infection rate with Vibrio cholerae. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(2):187–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup R. S., Chisari F. V. Response of monkeys to immunization with cholera toxoid, toxin, and vaccine: reversion of cholera toxoid. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):471–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. S., Bonde G., McCann T., Rubin B. A., Tint H. Development of a purified cholera toxoid. II. Preparation of a stable, antigenic toxoid by reaction of purified toxin with glutaraldehyde. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):304–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.304-317.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancey R. J., Willis D. L., Berry L. J. Role of motility in experimental cholera in adult rabbits. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.387-392.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


