Abstract
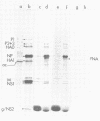
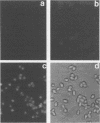
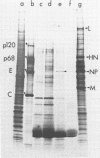
Chicken erythrocytes can be infected by the fowl plague (Rostock) strain (FP/R) of influenza type A, Newcastle disease virus (NDV), and Semliki Forest virus (SFV). Only NDV and SFV produced infectious progeny, albeit at low levels. Infection by FP/R was monitored by de novo synthesis of viral proteins, and the proteins synthesized could be identified by comparison with infected chicken fibroblast cells. FP/R synthesized far greater amounts of viral protein than did NDV or SFV.
Full text
PDF

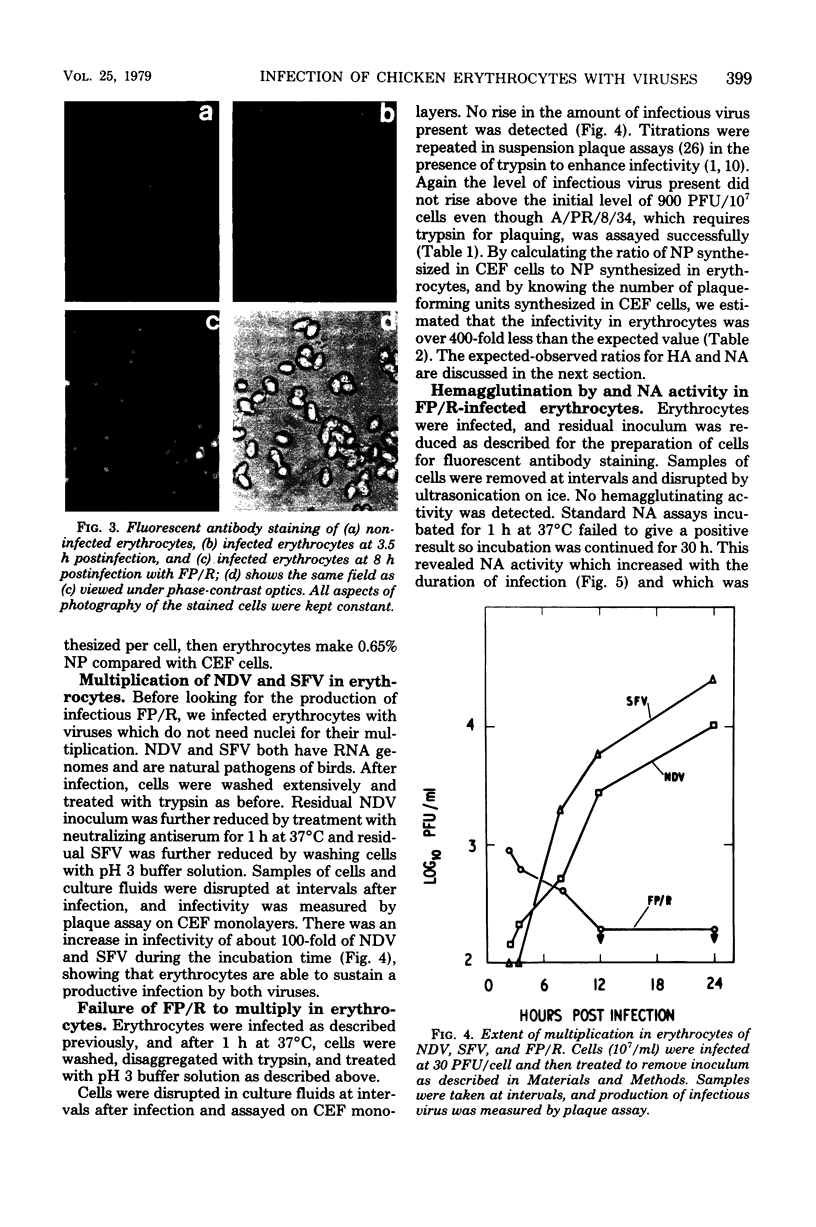
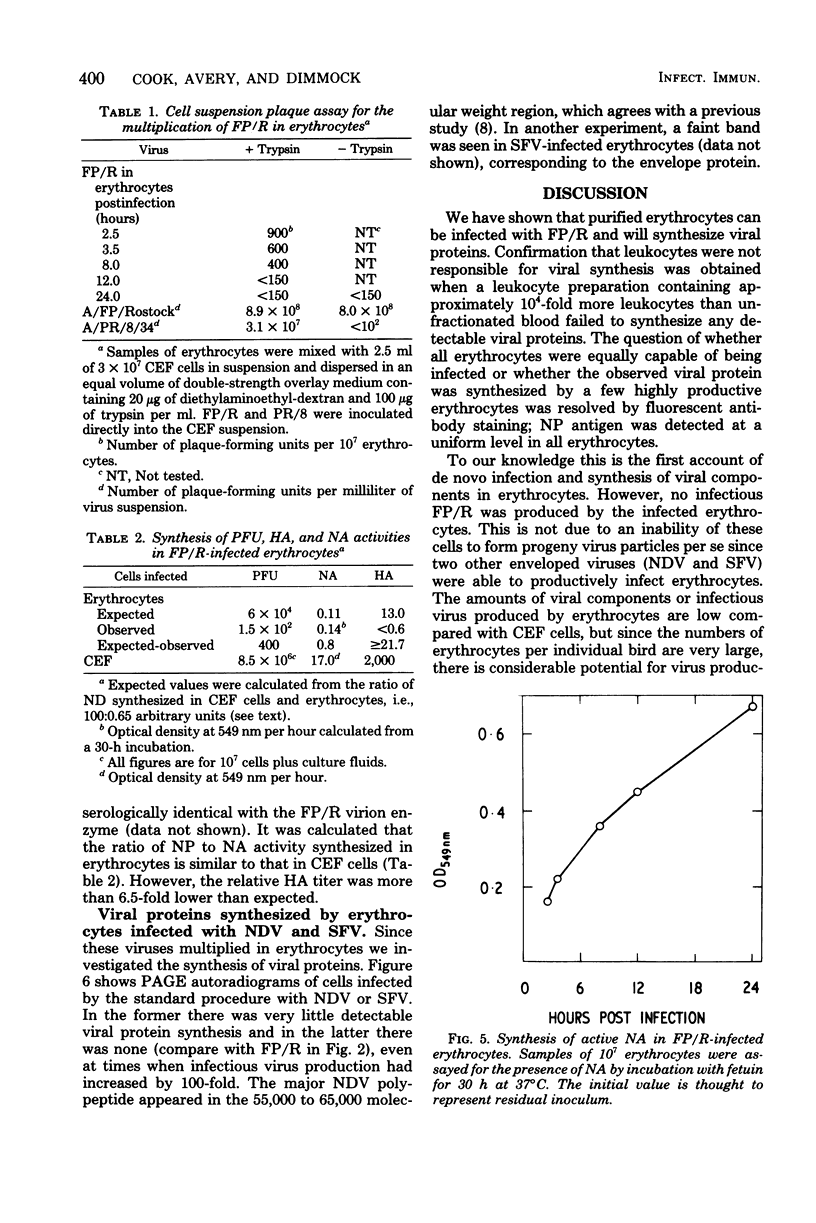
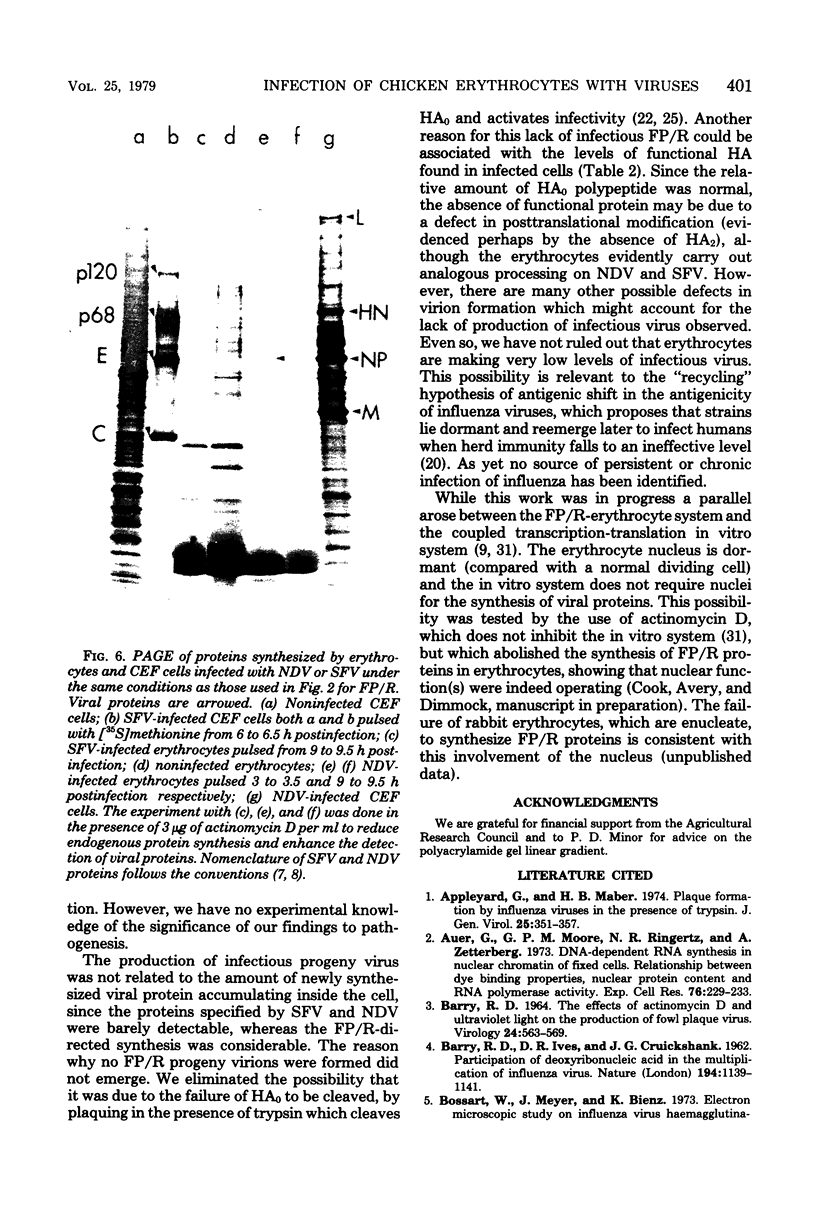

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleyard G., Maber H. B. Plaque formation by influenza viruses in the presence of trypsin. J Gen Virol. 1974 Dec;25(3):351–357. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-3-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer G., Moore G. P., Ringertz N. R., Zetterberg A. DNA-dependent RNA synthesis in nuclear chromatin of fixed cells: relationship between dye-binding properties, nuclear protein content and RNA polymerase activity. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90440-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D., IVES D. R., CRUICKSHANK J. G. Participation of deoxyribonucleic acid in the multiplication of influenza virus. Nature. 1962 Jun 23;194:1139–1140. doi: 10.1038/1941139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRY R. D. THE EFFECTS OF ACTINOMYCIN D AND ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATION ON THE PRODUCTION OF FOWL PLAGUE VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:563–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton C. J., Porter A., Kennedy S. I. Defective-interfering particles of Semliki Forest virus: intracellular events during interference. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):397–416. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. A method for producing plaques in agar suspensions of animal cells. Virology. 1955 Nov;1(4):397–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., Wit L. D., Horisberger M. Cell-free coupling of influenza virus RNA transcription and translation. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.247-255.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons R. W., Oshiro L. S., Johnson H. N., Lennette E. H. Intra-erythrocytic location of Colorado tick fever virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Nov;17(2):185–195. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-2-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A., Pringle C. R., Wunner W. H., Skehel J. J. Virus replication in enucleate cells: vesicular stomatitis virus and influenza virus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. The reactivation of the red cell nucleus. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):23–32. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Tata J. R. Template-engaged and free RNA polymerases during Xenopus erythroid cell maturation. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):496–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglis S. C., Carroll A. R., Lamb R. A., Mahy B. W. Polypeptides specified by the influenza virus genome I. Evidence for eight distinct gene products specified by fowl plague virus. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. C., Avery R. J., Dimmock N. J. Failure of an influenza virus to initiate infection in enucleate BHK cells. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1155–1161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1155-1161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. C., Dimmock N. J. Fowl plaque virus replication in mammalian cell-avian erythrocyte heterokaryons: studies concerning the actinomycin D and ultra-violet light sensitive phase in influenza virus replication. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):210–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90255-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy S. I., Burke D. C. Studies on the structural proteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jan;14(1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madgwick W. J., Maclean N., Baynes Y. A. RNA synthesis in chicken erythrocytes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 2;238(83):137–139. doi: 10.1038/newbio238137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. Inhibition of synthesis of influenza virus proteins: evidence of two host-cell-dependent events during multiplication. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. Selective inhibition of influenza virus protein synthesis by inhibitors of DNA function. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):393–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. The coupling of transcription from influenza virions to translation in vitro. Arch Virol. 1979;59(3):201–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01317415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. The multiplication of influenza virus in enucleated BHK cells fused with chicken erythrocytes. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):336–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morser M. J., Kennedy S. I., Burke D. C. Virus-specified polypeptides in cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:19–29. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro L. S., Dondero D. V., Emmons R. W., Lennette E. H. The development of Colorado tick fever virus within cells of the haemopoietic system. J Gen Virol. 1978 Apr;39(1):73–79. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Ritchey M. B., Schulman J. L. Mapping of the influenza virus genome. II. Identification of the P1, P2, and P3 genes. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):114–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
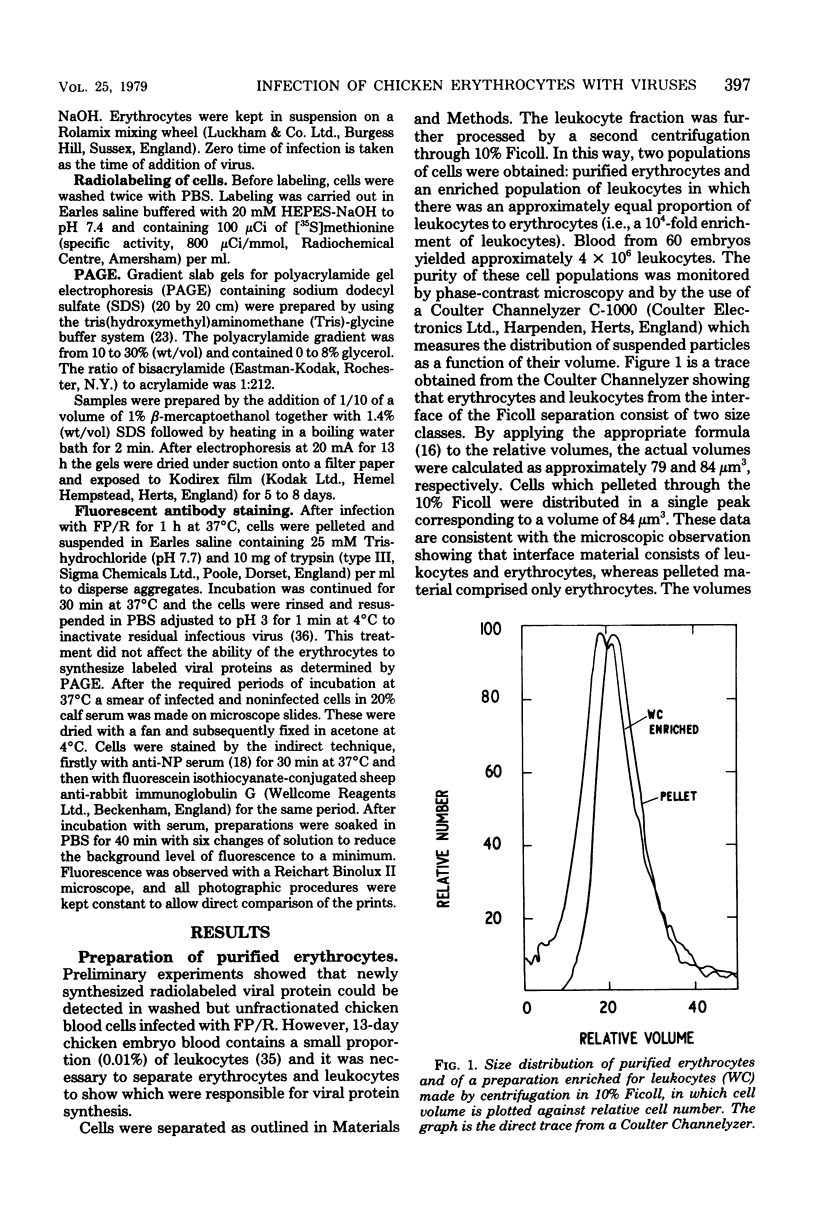
- Stephenson J. R., Hudson J. B., Dimmock N. J. Early events in influenza virus multiplication. II. Penetration of virus into cells at 4 degrees. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobita K., Kilbourne E. D. Genetic recombination for antigenic markers of antigenically different strains of influenza B virus. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):347–352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.347-352.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Preparation and properties of antibody directed specifically against the neuraminidase of influenza virus. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):49–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]