Abstract
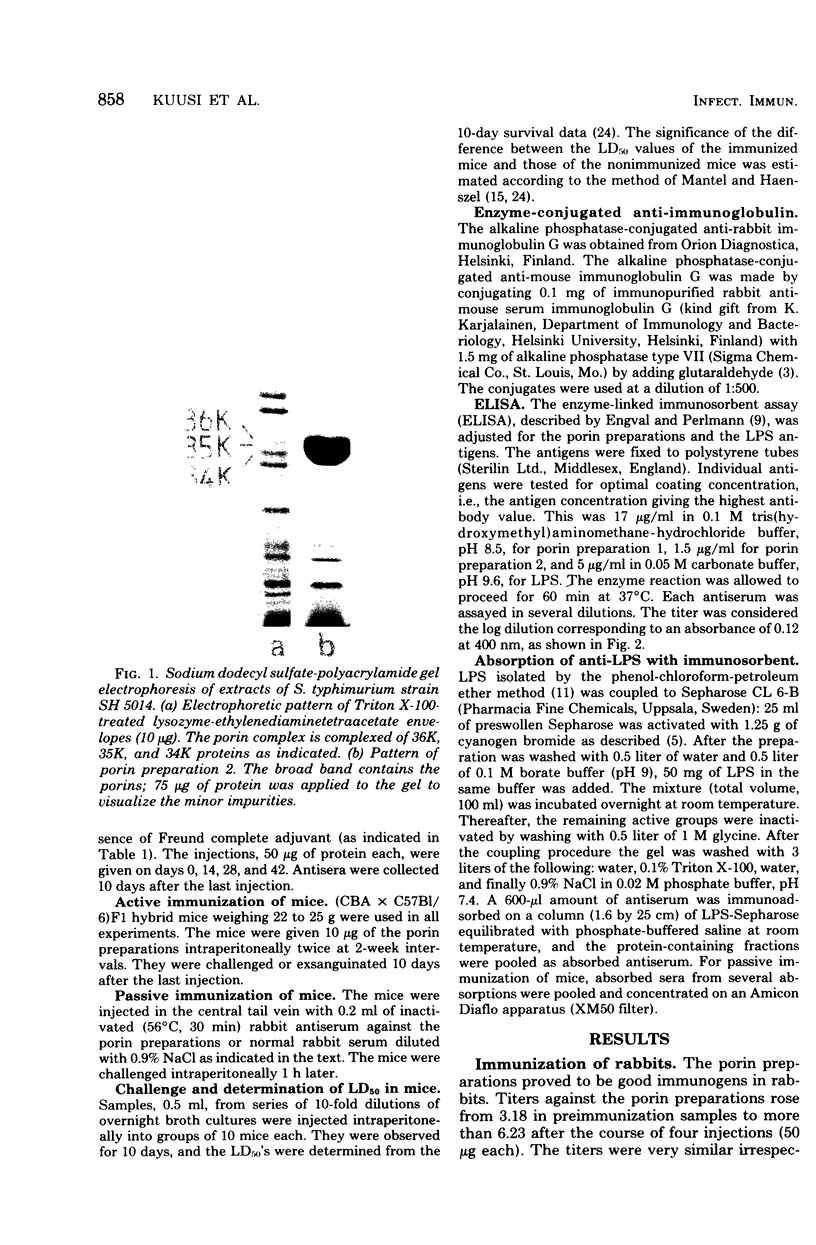
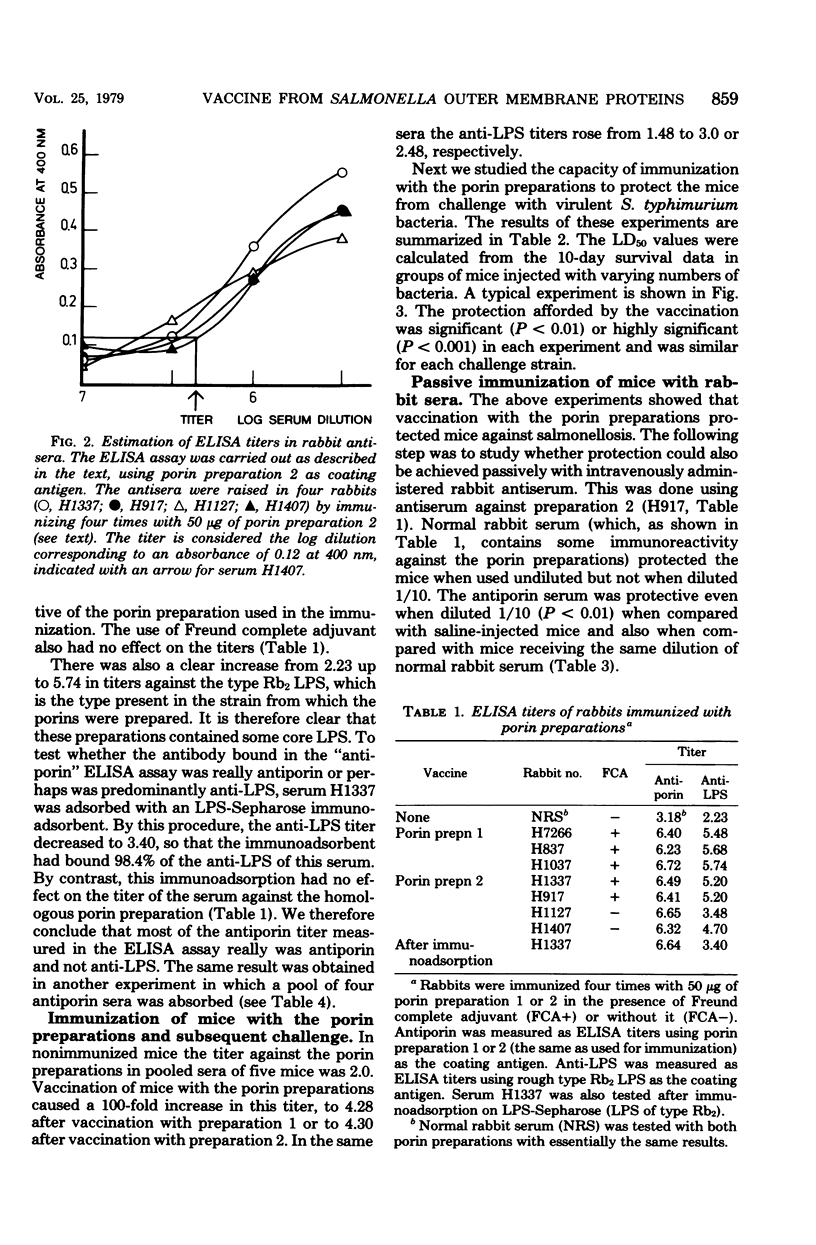
Porin (outer membrane protein) preparations extracted from a rough (Rb2) mutant of Salmonella typhimurium proved to be good immunogens in mice and rabbits. The antibody response achieved was measured by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay techniques. High titers of both antiporin and antilipopolysaccharide were detected in both species. The rabbit antiserum raised against the porins and the porin preparations themselves had a highly significant protective capacity against intraperitoneal Salmonella infection of mice. Absorption of the rabbit antiporin serum with lipopolysaccharide immunosorbent did not change its protective capacity in a passive immunization experiment, suggesting that the antiporin antibody preparations were the active components.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Resolution of bacterial proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on slabs. Membrane, soluble, and periplasmic fractions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austrian R. Pneumococcal infection and pneumococcal vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1977 Oct 27;297(17):938–939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710272971712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber C., Eylan E., Heiber R. The protective role of proteins from Salmonella typhimurium in infection of mice with their natural pathogen. Rev Immunol (Paris) 1972 Apr-Jun;36(3):77–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CVJETANOVIC B., UEMURA K. THE PRESENT STATUS OF FIELD AND LABORATORY STUDIES OF TYPHOID AND PARATYPHOID VACCINES WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STUDIES SPONSORED BY WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:29–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K., Angerman C. R. Immunity to experimental Salmonella infection: studies on the protective capacity and immunogenicity of lipopolysaccharide, acetone-killed cells, and ribosome-rich extracts of Salmonella typhimurium in C3H/HeJ and CD-1 mice. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1010–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch C. E., Parkes L., McNelis R. M., Gotschlich E. C. Protection against group B meningococcal disease. I. Comparison of group-specific and type-specific protection in the chick embryo model. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):319–329. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greisman S. E., DuBuy J. B., Woodward C. L. Experimental gram-negative bacterial sepsis: reevaluation of the ability of rough mutant antisera to protect mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Jul;158(3):482–490. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Immunization with R mutants of S. Minnesota. I. Protection against challenge with heterologous gram-negative bacilli. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):601–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae T. Outer membrane of Salmonella. Isolation of protein complex that produces transmembrane channels. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2176–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Lounatmaa K., Sarvas M., Mäkelä P. H., Nakae T. Bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium deficient in two major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):941–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.941-955.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A., Wilson B. M. Protective effects of a supernatant factor from Salmonella typhimurium on Salmonella typhimurium infection of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.125-131.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen M. V., Nurminen M., Johansson V., Makela P. H. Mouse virulence of Salmonella typhimurium mutants deficient in two major outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):454–458. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.454-458.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V. Mouse virulence of Salmonella strains: the effect of different smooth-type O side-chains. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):255–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Stevens P., Ingram J. Functional role of antibody against "core" glycolipid of Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):850–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



