Abstract
We have identified verotoxin 1 (VT1) as the active component within an antineoplastic bacteriocin preparation from Escherichia coli HSC10 studied over two decades. Recombinant VT1 can simulate the toxicity of anticancer proteins (ACP), and the antineoplastic activity of ACP (and VT1) was abrogated by treatment with anti-VT1 antibody. Similarly, VT1 mimics the protective effect of ACP in a murine metastatic fibrosarcoma model. Prior immunization with VT1 B subunit prevents the effect of VT1 or ACP in this model. The activity of ACP against a variety of human ovarian cell lines was mimicked by VT1, and multidrug-resistant variants were significantly hypersensitive. Primary ovarian tumors and metastases contain elevated levels of globotriaosylceramide compared with normal ovaries, and overlay of frozen tumor sections showed selective VT binding to tumor tissue and the lumen of invading blood vessels. Our contention that VT1 could provide an additional approach to the management of certain human neoplasms is discussed.
Full text
PDF

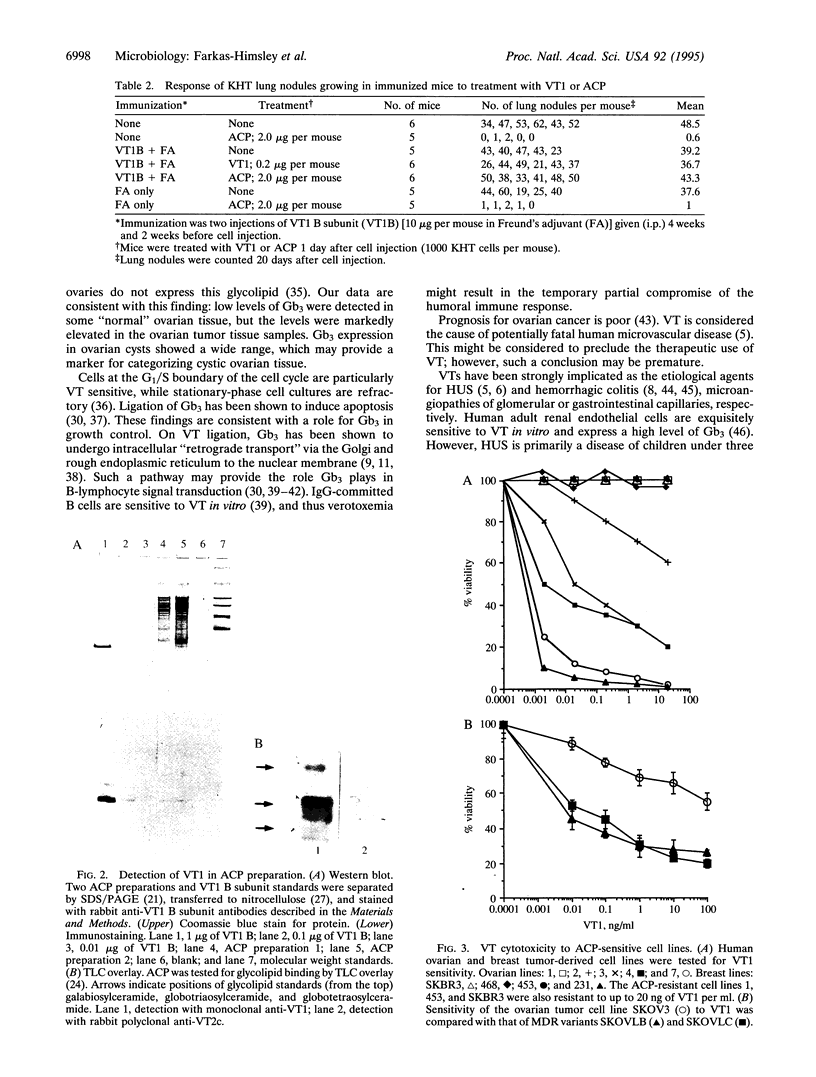
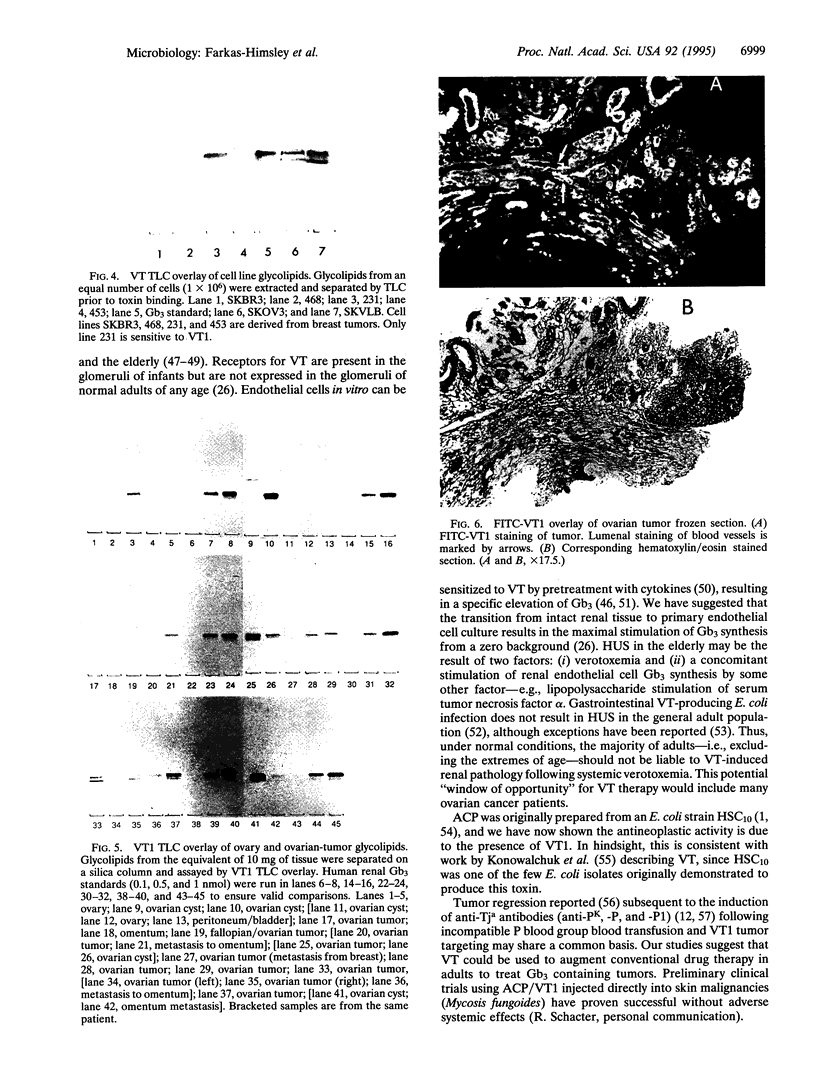

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd B., Richardson S., Gariepy J. Serological responses to the B subunit of Shiga-like toxin 1 and its peptide fragments indicate that the B subunit is a vaccine candidate to counter action of the toxin. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):750–757. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.750-757.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd B., Tyrrell G., Maloney M., Gyles C., Brunton J., Lingwood C. Alteration of the glycolipid binding specificity of the pig edema toxin from globotetraosyl to globotriaosyl ceramide alters in vivo tissue targetting and results in a verotoxin 1-like disease in pigs. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1745–1753. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G., Naik M., Ling V. P-glycoprotein expression in multidrug-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2790–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A., Madrid-Marina V., Estrov Z., Freedman M. H., Lingwood C. A., Dosch H. M. Expression of glycolipid receptors to Shiga-like toxin on human B lymphocytes: a mechanism for the failure of long-lived antibody response to dysenteric disease. Int Immunol. 1990;2(1):1–8. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes F. P., Barrett T. J., Green J. H., Aloisio C. H., Spika J. S., Strockbine N. A., Wachsmuth I. K. Affinity purification and characterization of Shiga-like toxin II and production of toxin-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1926–1933. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1926-1933.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas-Himsley H., Cheung R. Bacterial proteinaceous products (bacteriocins) as cytotoxic agents of neoplasia. Cancer Res. 1976 Oct;36(10):3561–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas-Himsley H., Yu H. Purified colicin as cytotoxic agent of neoplasia: comparative study with crude colicin. Cytobios. 1985;42(167-168):193–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghislain J., Lingwood C. A., Fish E. N. Evidence for glycosphingolipid modification of the type 1 IFN receptor. J Immunol. 1994 Oct 15;153(8):3655–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin P. M., Ostroff S. M., Tauxe R. V., Greene K. D., Wells J. G., Lewis J. H., Blake P. A. Illnesses associated with Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. A broad clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Nov 1;109(9):705–712. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-9-705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin P. M., Tauxe R. V. The epidemiology of infections caused by Escherichia coli O157:H7, other enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and the associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Epidemiol Rev. 1991;13:60–98. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head S. C., Karmali M. A., Lingwood C. A. Preparation of VT1 and VT2 hybrid toxins from their purified dissociated subunits. Evidence for B subunit modulation of a subunit function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3617–3621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. P., Farkas-Himsley H. Further studies of the action of a partially purified bacteriocin against a murine fibrosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 1;51(5):1359–1365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A., de Grandis S., Friesen J., Karmali M., Petric M., Congi R., Brunton J. L. Cloning and expression of the genes specifying Shiga-like toxin production in Escherichia coli H19. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):375–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.375-379.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H., Bezanson G. S. Cytotoxic Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with haemorrhagic colitis in Canada. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):76–76. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Levine P., Watanabe K., Hakomori S. Recent studies of glycolipid and glycoprotein profiles and characterization of the major glycolipid antigen in gastric cancer of a patient of blood group genotype pp (Tja-) first studied in 1951. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):5249–5254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A. Infection by verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jan;2(1):15–38. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai K., Galton J., Terasaki P. I., Wakisaka A., Kawahara M., Root T., Hakomori S. I. Tissue distribution of the Pk antigen as determined by a monoclonal antibody. J Immunogenet. 1985 Aug-Oct;12(4-5):213–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1985.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khine A. A., Lingwood C. A. Capping and receptor-mediated endocytosis of cell-bound verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin). 1: Chemical identification of an amino acid in the B subunit necessary for efficient receptor glycolipid binding and cellular internalization. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Nov;161(2):319–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041610217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoo S. K., Battistutta D., Hurst T., Sanderson B., Ward B. G., Free K. The prognostic value of clinical, pathologic, and biologic parameters in ovarian cancer. Cancer. 1993 Jul 15;72(2):531–537. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930715)72:2<531::aid-cncr2820720233>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE P., BOBBITT O. B., WALLER R. K., KUHMICHEL A. Isoimmunization by a new blood factor in tumor cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jul;77(3):403–405. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law H., Lingwood C. A. Use of fluorescent standards in protein transfer and immunoblotting. Accurate estimation of the molecular weight of immunoreactive species. Anal Biochem. 1985 Sep;149(2):404–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90590-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. C., Kundu S. K., Degasperi R., Li Y. T. Accumulation of globotriaosylceramide in a case of leiomyosarcoma. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):925–927. doi: 10.1042/bj2400925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman E., Heuser E., Donnell G. N., Landing B. H., Hammond G. D. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Clinical and pathological considerations. N Engl J Med. 1966 Aug 4;275(5):227–236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196608042750501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Richardson S., Petric M., Brunton J. L., De Grandis S., Karmali M. Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8834–8839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A. Verotoxin-binding in human renal sections. Nephron. 1994;66(1):21–28. doi: 10.1159/000187761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A. Verotoxins and their glycolipid receptors. Adv Lipid Res. 1993;25:189–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Wasfy G., Han H., Huesca M. Receptor affinity purification of a lipid-binding adhesin from Helicobacter pylori. Infect Immun. 1993 Jun;61(6):2474–2478. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2474-2478.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Yiu S. K. Glycolipid modification of alpha 2 interferon binding. Sequence similarity between the alpha 2 interferon receptor and verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) B-subunit. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):25–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2830025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louise C. B., Obrig T. G. Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin, interleukin-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4173–4179. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4173-4179.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney M. D., Lingwood C. A. CD19 has a potential CD77 (globotriaosyl ceramide)-binding site with sequence similarity to verotoxin B-subunits: implications of molecular mimicry for B cell adhesion and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli pathogenesis. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):191–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangeney M., Lingwood C. A., Taga S., Caillou B., Tursz T., Wiels J. Apoptosis induced in Burkitt's lymphoma cells via Gb3/CD77, a glycolipid antigen. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 1;53(21):5314–5319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannori G., Cecconi O., Mugnai G., Ruggieri S. Role of glycolipids in the metastatic process: characteristics of neutral glycolipids in clones with different metastatic potentials isolated from a murine fibrosarcoma cell line. Int J Cancer. 1990 May 15;45(5):984–988. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musclow E., Farkas-Himsley H. Bacteriocin and flow cytometry in laboratory diagnosis of leukemic peripheral blood lymphocytes and bone marrow cells. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1983 Feb;19(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(83)90413-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naiki M., Marcus D. M. Human erythrocyte P and Pk blood group antigens: identification as glycosphingolipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 8;60(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill M. A., Agosti J., Rosen H. Hemorrhagic colitis with Escherichia coli O157:H7 preceding adult hemolytic uremic syndrome. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Dec;145(12):2215–2217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T. G., Louise C. B., Lingwood C. A., Boyd B., Barley-Maloney L., Daniel T. O. Endothelial heterogeneity in Shiga toxin receptors and responses. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15484–15488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama C., Fukushi Y., Satoh M., Saitoh S., Orikasa S., Nudelman E., Straud M., Hakomori S. Changes in glycolipid expression in human testicular tumor. Int J Cancer. 1990 Jun 15;45(6):1040–1044. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pudymaitis A., Lingwood C. A. Susceptibility to verotoxin as a function of the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):632–639. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe P. C., Orrbine E., Wells G. A., McLaine P. N. Epidemiology of hemolytic-uremic syndrome in Canadian children from 1986 to 1988. The Canadian Pediatric Kidney Disease Reference Centre. J Pediatr. 1991 Aug;119(2):218–224. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)80730-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Garred O., Prydz K., Kozlov J. V., Hansen S. H., van Deurs B. Retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin to the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):510–512. doi: 10.1038/358510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Brown J. E., Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Endocytosis from coated pits of Shiga toxin: a glycolipid-binding protein from Shigella dysenteriae 1. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., Ryd M., Garred O., Schweda E., Holm P. K., van Deurs B. Retrograde transport from the Golgi complex to the ER of both Shiga toxin and the nontoxic Shiga B-fragment is regulated by butyric acid and cAMP. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):53–64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig K., van Deurs B. Toxin-induced cell lysis: protection by 3-methyladenine and cycloheximide. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga-like toxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.695-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unravelling HUS. Lancet. 1987 Dec 19;2(8573):1437–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell T., Cohen A., Lingwood C. A. Induction of verotoxin sensitivity in receptor-deficient cell lines using the receptor glycolipid globotriosylceramide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7898–7901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenk J., Andrews P. W., Casper J., Hata J., Pera M. F., von Keitz A., Damjanov I., Fenderson B. A. Glycolipids of germ cell tumors: extended globo-series glycolipids are a hallmark of human embryonal carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jul 1;58(1):108–115. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yiu S. C., Lingwood C. A. Polyisobutylmethacrylate modifies glycolipid binding specificity of verotoxin 1 in thin-layer chromatogram overlay procedures. Anal Biochem. 1992 Apr;202(1):188–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90226-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Kar N. C., Monnens L. A., Karmali M. A., van Hinsbergh V. W. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 induce expression of the verocytotoxin receptor globotriaosylceramide on human endothelial cells: implications for the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2755–2764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]