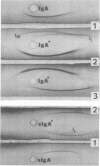
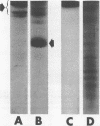
Abstract
Thirty-seven strains of the genus Haemophilus and five strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae were examined for their ability to produce extracellular enzyme that cleaves immunoglobulin molecules. All strains of H. influenzae, H. aegyptius, and S. pneumoniae elaborated enzyme that selectively cleaved human immunoglobulin A1 (IgA1) myeloma proteins but was inactive against a variety of other proteins including human IgA2, IgG, and IgM, porcine and bovine secretory IgA, human and bovine serum albumins, and ovalbumin. Although susceptible, human secretory IgA remained largely undigested. Two strains of H. pleuropneumoniae isolated from fatally infected pigs cleaved porcine secretory IgA, but had no effect on human IgA proteins. None of 16 strains that belonged to nonpathogenic Haemophilus species produced IgA protease. Analyses of the cleavage products of human IgA1 and secretory IgA proteins by immunochemical methods, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and analytical ultracentrifugation revealed that Fab and Fc fragments were produced. Since the production of IgA1 protease by Neisseria meningitidis has been reported previously, our finding that H. influenzae and S. pneumoniae produce an IgA1 protease indicates that this is a property of all three major etiological agents of bacterial meningitis. This suggests that IgA1 protease production may be an important factor in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Full text
PDF


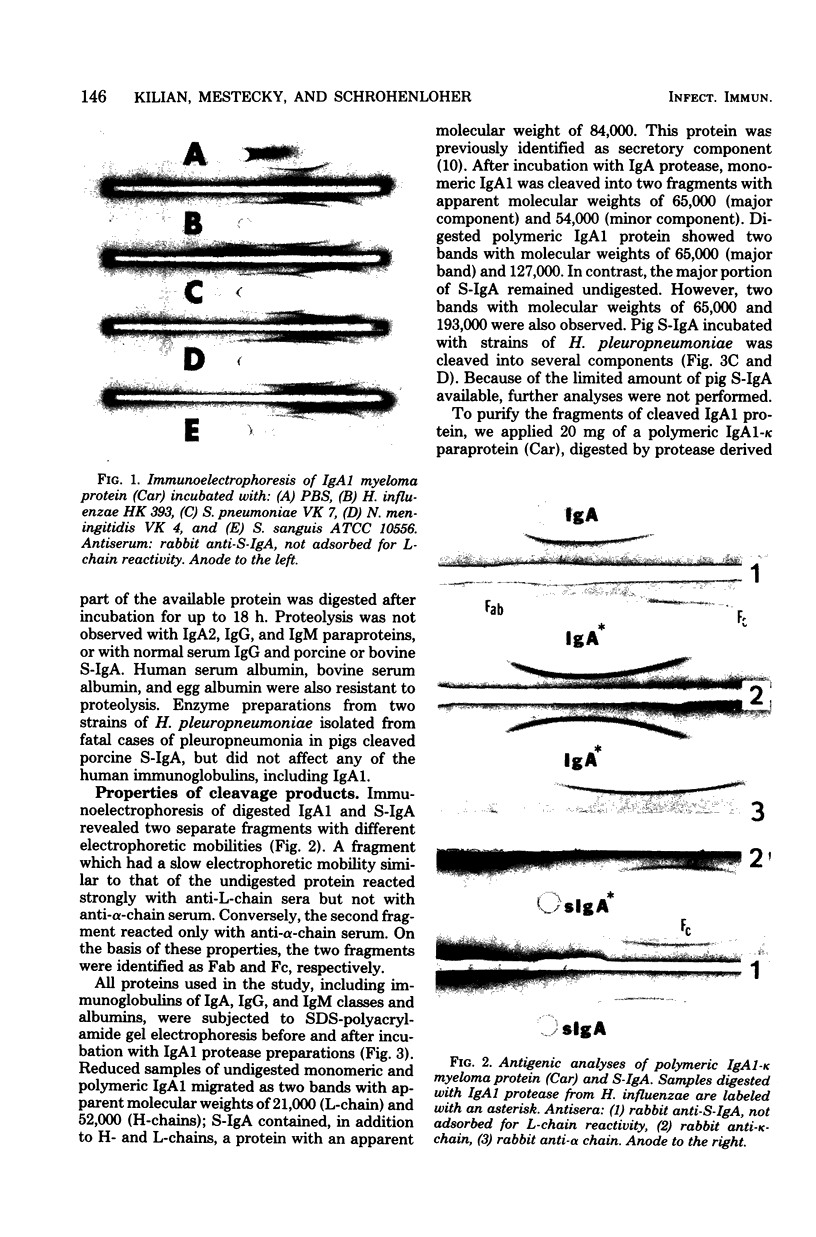



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M., Holmes K. K., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XVII. IgA1-cleaving protease in vaginal washings from women with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jan;139(1):89–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M. Bactericidal activity of meningococcal antisera. Blocking by IgA of lytic antibody in human convalescent sera. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1779–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiss J. M., Bertram M. A. Immunoepidemiology of meningococcal disease in military recruits. II. Blocking of serum bactericidal activity by circulating IgA early in the course of invasive disease. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):733–739. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higerd T. B., Virella G., Cardenas R., Koistinen J., Fett J. W. New method for obtaining IgA-specific protease. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(3-4):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Schiott C. R. Haemophili and related bacteria in the human oral cavity. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Dec;20(12):791–796. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Stjernström I., Edebo L. Reduction of phagocytosis, surface hydrophobicity and charge of Salmonella typhimurium 395 MR10 by reaction with secretory IgA (SIgA). Immunology. 1979 Mar;36(3):439–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta S. K., Plaut A. G., Calvanico N. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Human immunoglobulin A: production of an Fc fragment by an enteric microbial proteolytic enzyme. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1274–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Hammack W. J., Kulhavy R., Wright G. P., Tomana M. Properties of IgA myeloma proteins isolated rom sera of patients with the hyperviscosity syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 May;89(5):919–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Kulhavy R., Kraus F. W. Studies on human secretory immunoglobulin A. II. Subunit structure. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):738–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gilbert J. V., Artenstein M. S., Capra J. D. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and neisseria meningitidis: extracellular enzyme cleaves human immunoglobulin A. Science. 1975 Dec 12;190(4219):1103–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.810892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gilbert J. V., Wistar R., Jr Loss of antibody activity in human immunoglobulin A exposed extracellular immunoglobulin A proteases of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):130–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.130-135.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G. Microbial IgA proteases. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1459–1463. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Wistar R., Jr, Capra J. D. Differential susceptibility of human IgA immunoglobulins to streptococcal IgA protease. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1295–1300. doi: 10.1172/JCI107875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Lawrence D. A., Henson P. Cytophilic properties of IgA to human neutrophils. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):67–74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanborg-Edén C., Svennerholm A. M. Secretory immunoglobulin A and G antibodies prevent adhesion of Escherichia coli to human urinary tract epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.790-797.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Reed K., Williams R. C., Jr Suppression of human PMN bactericidal activity by human IgA paraproteins. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Suppression of leukocyte chemotaxis by human IgA myeloma components. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zikan J., Mestecky J., Schrohenloher R. E., Tomana M., Kulhavy R. Studies on human secretory immunoglobulin A. V. Trypsin hydrolysis at elevated temperatures. Immunochemistry. 1972 Dec;9(12):1185–1193. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]