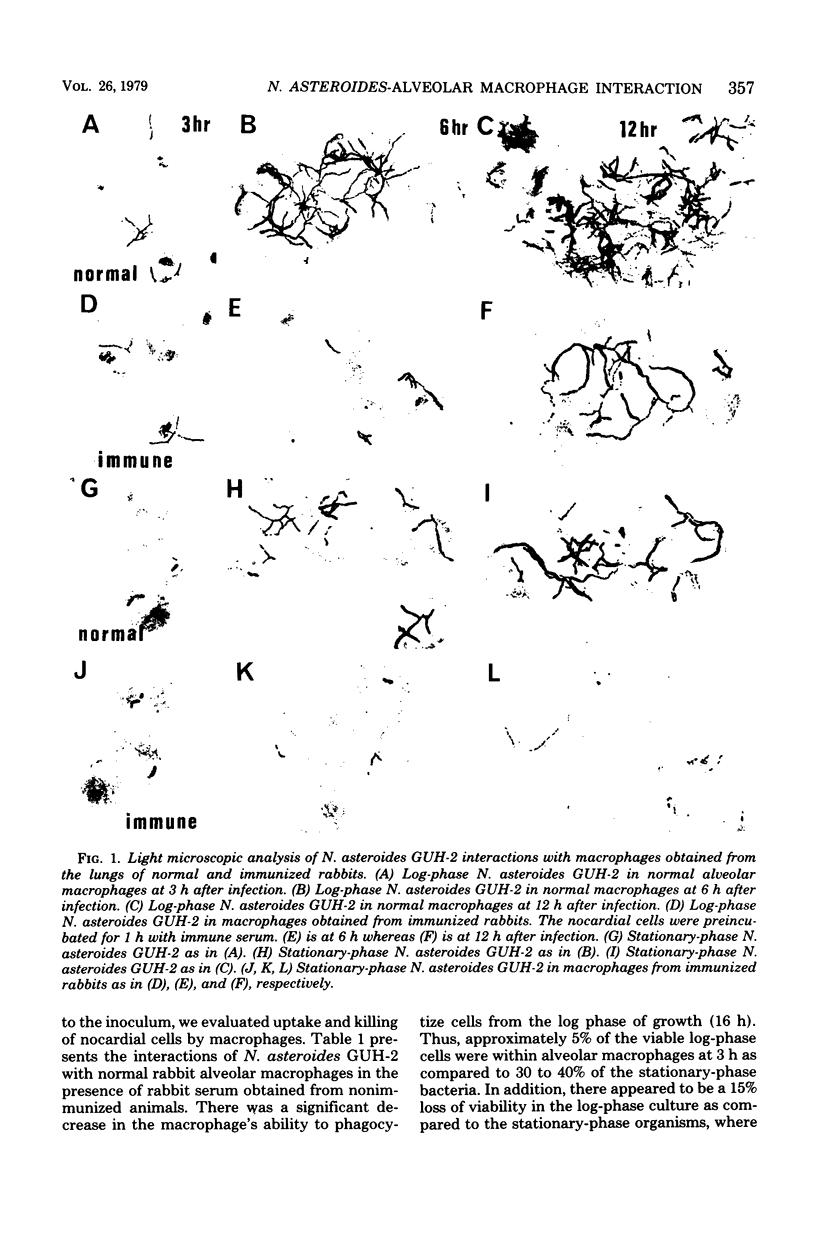
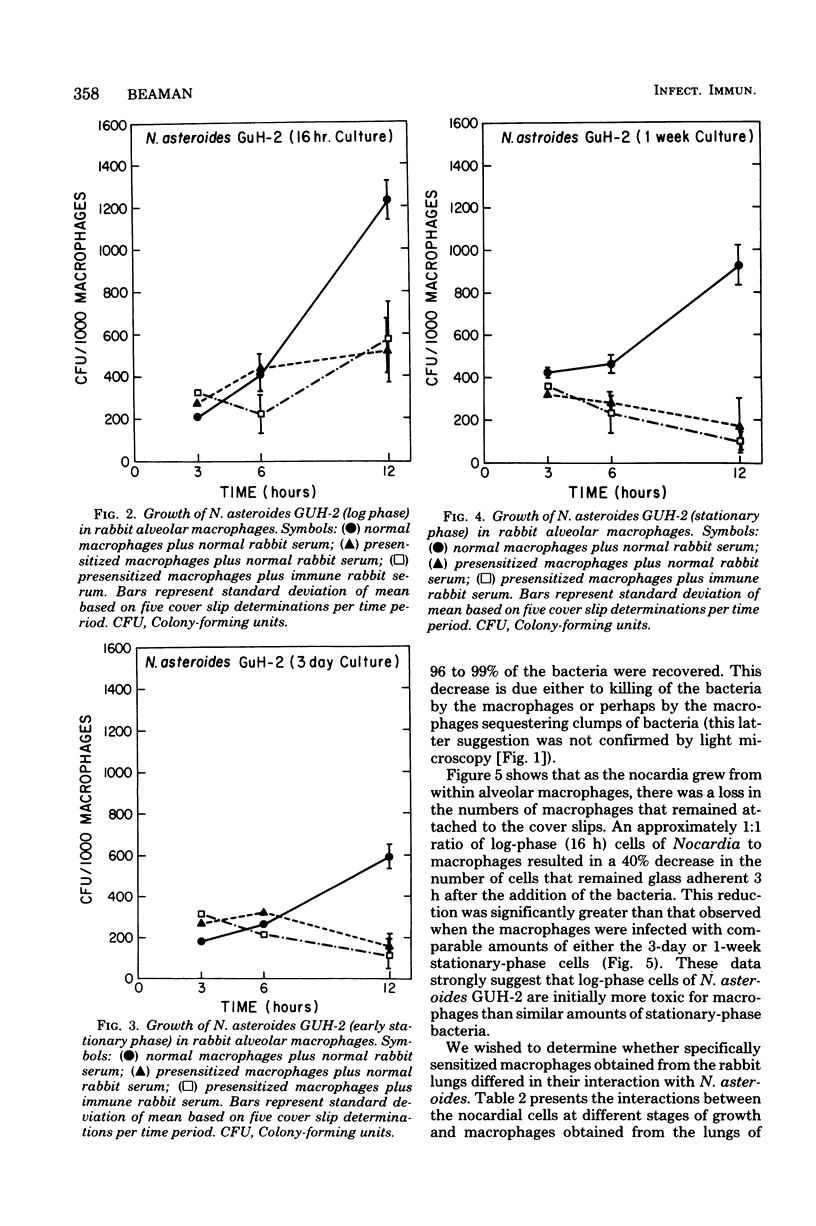
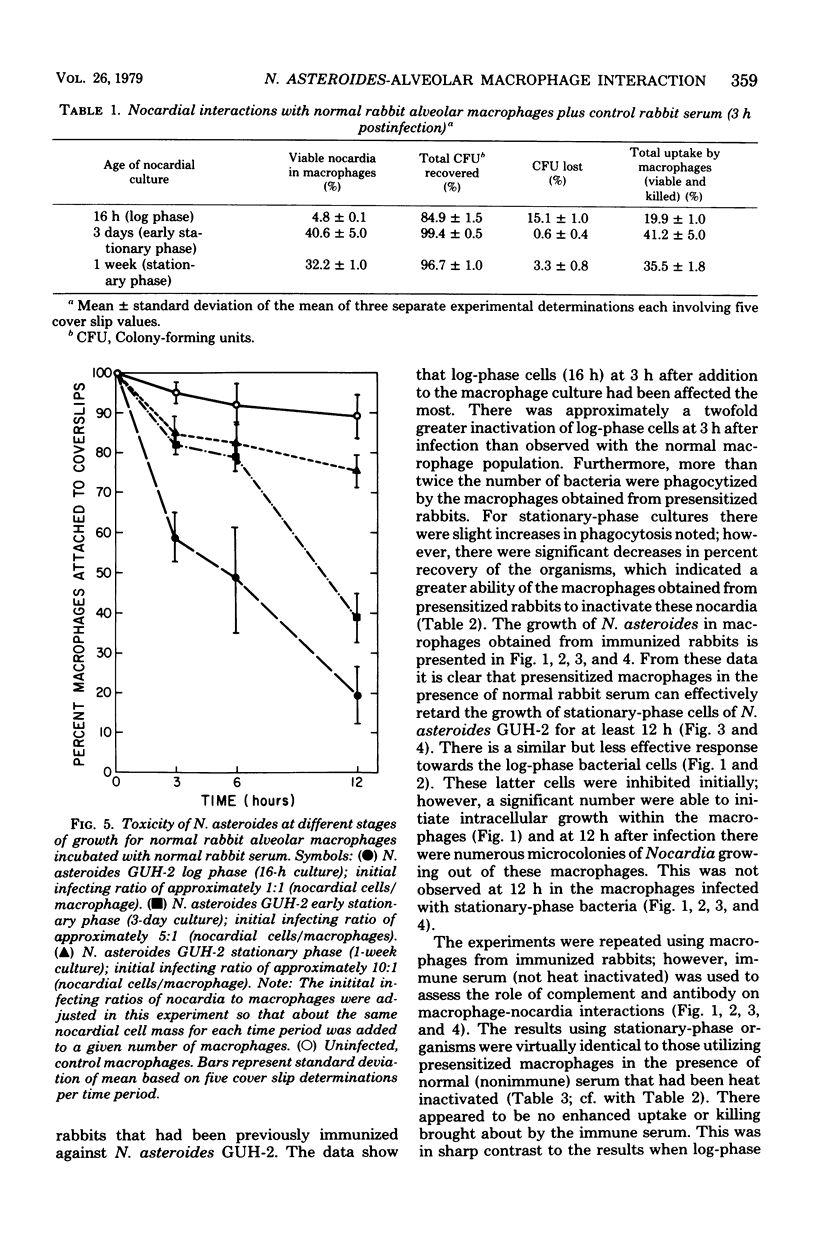
Abstract
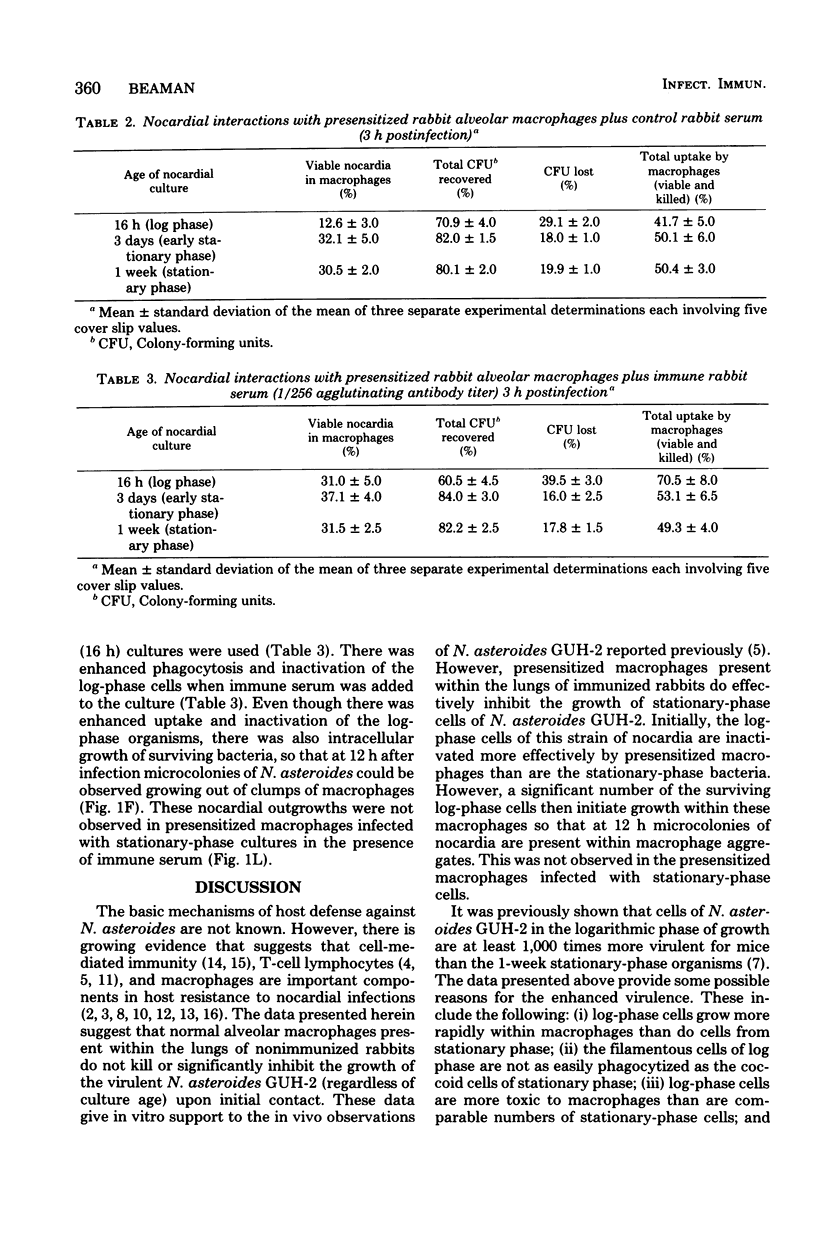
The interactions of cells of Nocardia asteroides GUH-2 during different stages of growth with cultured macrophages obtained from the lungs of nonimmunized and immunized rabbits were studied. The nocardial cells from all stages grew intracellularly in "normal" alveolar macrophages; however, log-phase cells increased in numbers more rapidly than did stationary-phase cells. Macrophages obtained from the lungs of specifically immunized rabbits effectively inhibited the growth of stationary-phase cells but only temporarily retarded the growth of log-phase organisms. Specific antiserum added to the nocardial cells before incubation with presensitized macrophages caused enhanced phagocytosis and inactivation of the log-phase cells but had no effect on the fate of the stationary-phase nocardia. In addition, it was fo-nd that log-phase cells were phagocytized less effectively by normal macrophages than were the stationary-phase cells, and log-phase cells were more toxic to the macrophage monolayer. From these data we conclude that secondarily induced macrophages play a major role in host resistance to pulmonary nocardial infections, and antibody may be important for effective host resistance to the filamentous form of N. asteroides. Since the nocardia were able, with time, to overcome these effects, it appears that additional host factors (such as T-lymphocytes) must be involved in an effective host response to N. asteroides.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaman B. L., Gershwin M. E., Maslan S. Infectious agents in immunodeficient murine models: pathogenicity of Nocardia asteroides in congenitally athymic (nude) and hereditarily asplenic (Dh/+) mice. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.381-387.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Goldstein E., Gershwin M. E., Maslan S., Lippert W. Lung response to congenitally athymic (nude), heterozygous, and Swiss Webster mice to aerogenic and intranasal infection by Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):867–877. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.867-877.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. In vitro response of rabbit alveolar macrophages to infection with Nocardia asteroides. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.925-937.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Maslan S. Effect of cyclophosphamide on experimental Nocardia asteroides infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.995-1004.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Maslan S. Virulence of Nocardia asteroides during its growth cycle. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):290–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.290-295.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L., Smathers M. Interaction of Nocardia asteroides with cultured rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1126–1131. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1126-1131.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman B. L. Structural and biochemical alterations of Nocardia asteroides cell walls during its growth cycle. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):1235–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.1235-1253.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois L., Beaman B. L. Probable L-forms of Nocardia asteroides induced in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):576–590. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.576-590.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabrowski W., Bogunowicz A., Stelmaska E., Pietkiewicz D. Fagocytarna aktywnoś makrofagów wobec Nocardia asteroides. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1976;28(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folb P. I., Timme A., Horowitz A. Nocardia infections in congenitally athymic (nude) mice and in other inbred mouse strains. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):459–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.459-466.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krick J. A., Remington J. S. Resistance to infection with Nocardia asteroides. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jun;131(6):665–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splino M., Merka V., Kyntera F. Phagozytose und intrazelluläre Proliferation von Nocardia asteroides (Stamm Weipheld) in Zellstrukturen in vitro. 2. Peritoneale Makrophagen von Meerschweinchen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(4):512–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj T., Agarwal S. C. Cell-mediated immunity in experimental Nocardia asteroides infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):370–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.370-375.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj T., Agarwal S. C. Cell-mediated immunity to Nocardia asteroides induced by its ribonucleic acid protein fraction. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):253–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.253-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj T., Agarwal S. C. Relationship of macrophages to cell-mediated immunity in experimental Nocardia asteroides infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.685-691.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]