Abstract
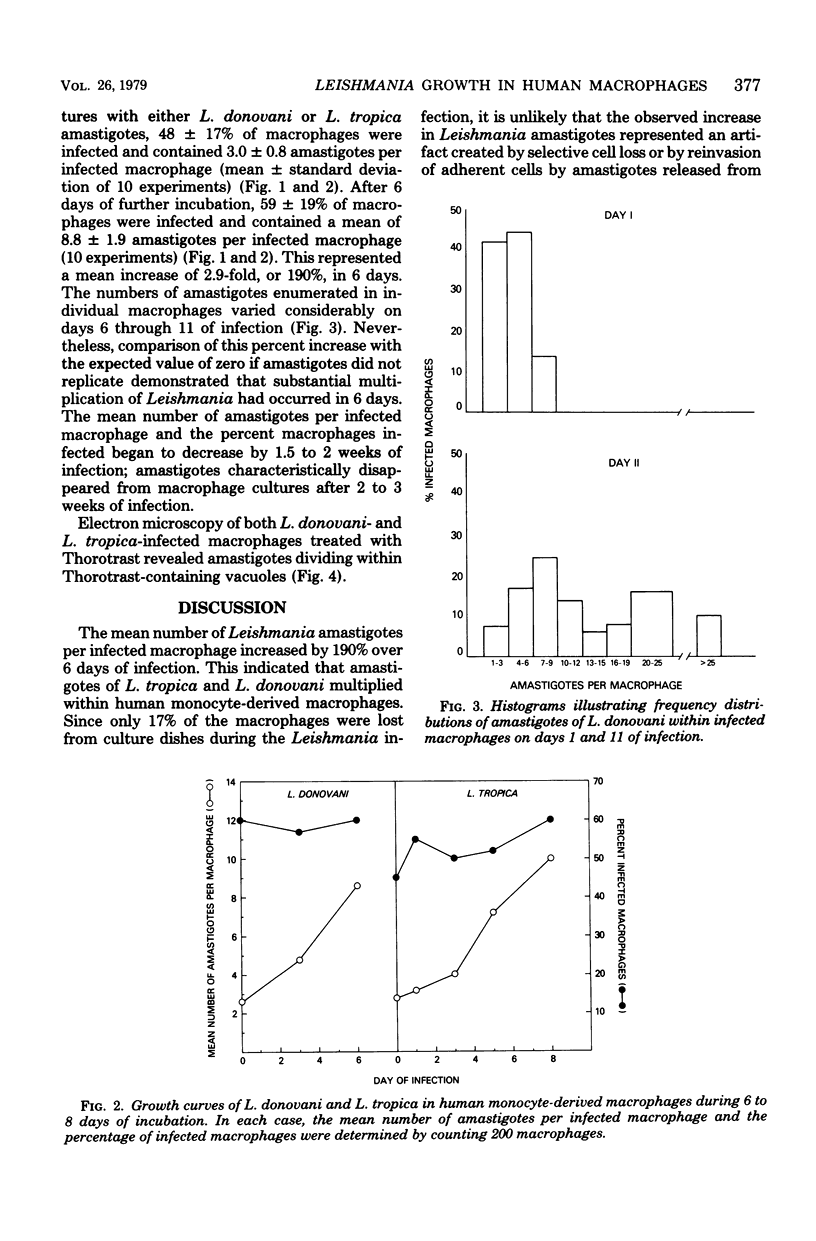
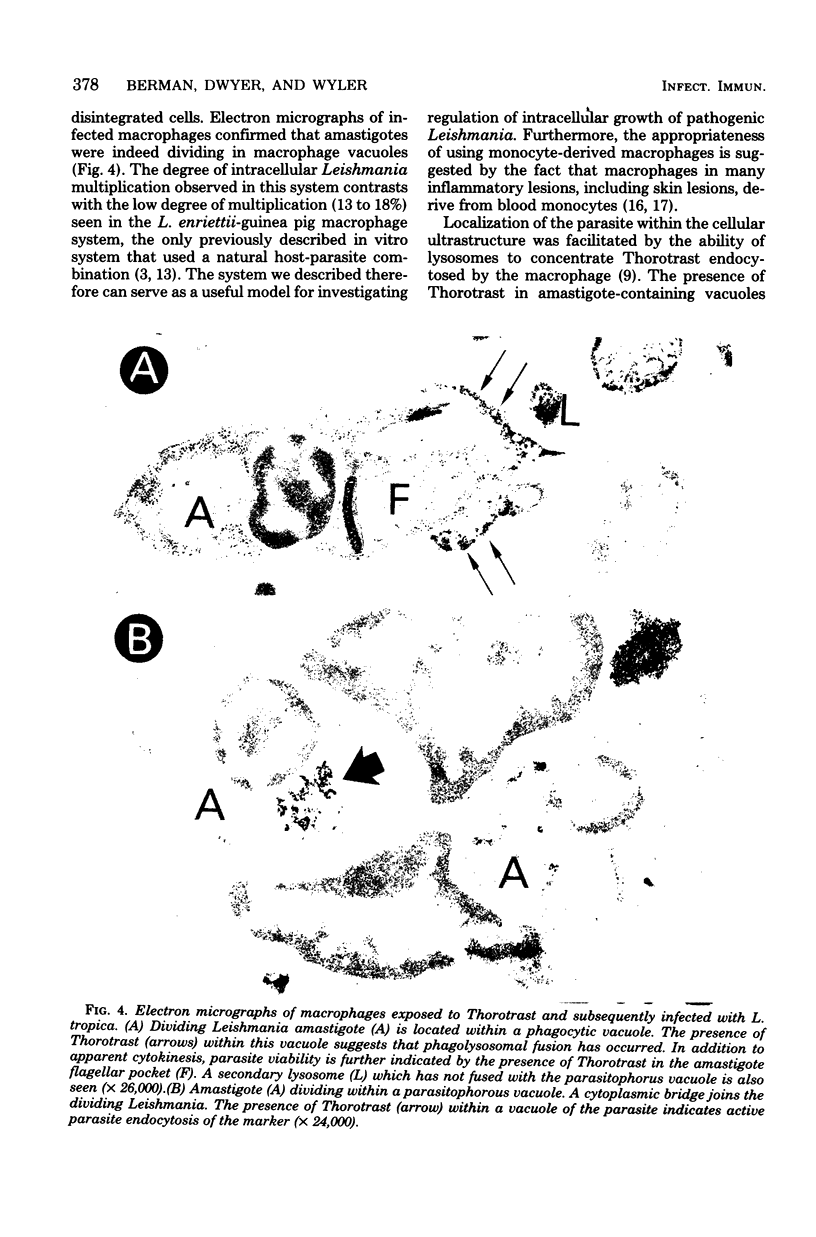
To facilitate in vitro studies of the immunology of human leishmaniasis, we developed a method of growing pathogenic Leishmania in human monocyte-derived macrophages. After 6 days of incubation, adherent mononuclear cells were infected with Leishmania donovani amastigotes obtained from infected hamster spleen cells or with L. tropica amastigotes obtained from infected BALB/c tissue mouse footpad. Forty-eight percent of the macrophages were initially infected, with a mean of 3.0 amastigotes per infected macrophage. After 6 days of incubation, 59% of macrophages were infected and contained 8.8 amastigotes per infected macrophage, representing 2.9-fold multiplication. Electron microscopy revealed the presence of dividing parasites within phagolysosomes. These observations indicate that Leishmania survive and multiply within human monocyte-derived macrophages despite fusion of secondary lysosomes with the parasitophorous vacuole.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J., Vickerman K. Fusion of host cell secondary lysosomes with the parasitophorous vacuoles of Leishmania mexicana-infected macrophages. J Protozool. 1975 Nov;22(4):502–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorvatn B., Neva F. A. A model in mice for experimental leishmaniasis with a West African strain of Leishmania tropica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):472–479. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. S. Leishmania. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):189–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D., Bray R. S., Wolstencroft R. A., Dumonde D. C. Immunity in cutaneous leishmaniasis of the guinea-pig. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Sep;7(3):301–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani. Hamster macrophage interactions in vitro: cell entry, intracellular survival, and multiplication of amastigotes. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):515–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Multiplication of a human parasite (Leishmania donovani) in phagolysosomes of hamster macrophages in vitro. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):678–680. doi: 10.1126/science.948742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frothingham T. E., Lehtimaki E. Prolonged growth of Leishmania species in cell culture. J Parasitol. 1969 Feb;55(1):196–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Spira D. T. Growth of Leishmania amastigotes in macrophages from normal and immune mice. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Aug 25;53(1):75–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00383117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. D., Jr, Mei B., Cohn Z. A. The separation, long-term cultivation, and maturation of the human monocyte. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1613–1626. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress Y., Tanowitz H., Bloom B., Wittner M. Trypanosoma cruzi: infection of normal and activated mouse macrophages. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Apr;41(2):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. H. Infection of tissue culture cells of low phagocytic ability by Leishmania mexicana mexicana. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1974 Sep;68(3):327–336. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1974.11686955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattock N. M., Peters W. The experimental chemotherapy of leishmaniasis. I: Techniques for the study of drug action in tissue culture. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1975 Sep;69(3):349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. C., Twohy D. W. Cellular immunity to Leishmania donovani in macrophages in cultures. J Parasitol. 1969 Feb;55(1):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber L. A. Characterization of strains of Leishmania donovani. Exp Parasitol. 1966 Feb;18(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(66)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKMAN A., GOWANS J. L. THE PRODUCTION OF MACROPHAGES IN THE RAT. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Feb;46:50–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman A. The origin and fate of the monocyte. Ser Haematol. 1970;3(2):62–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]