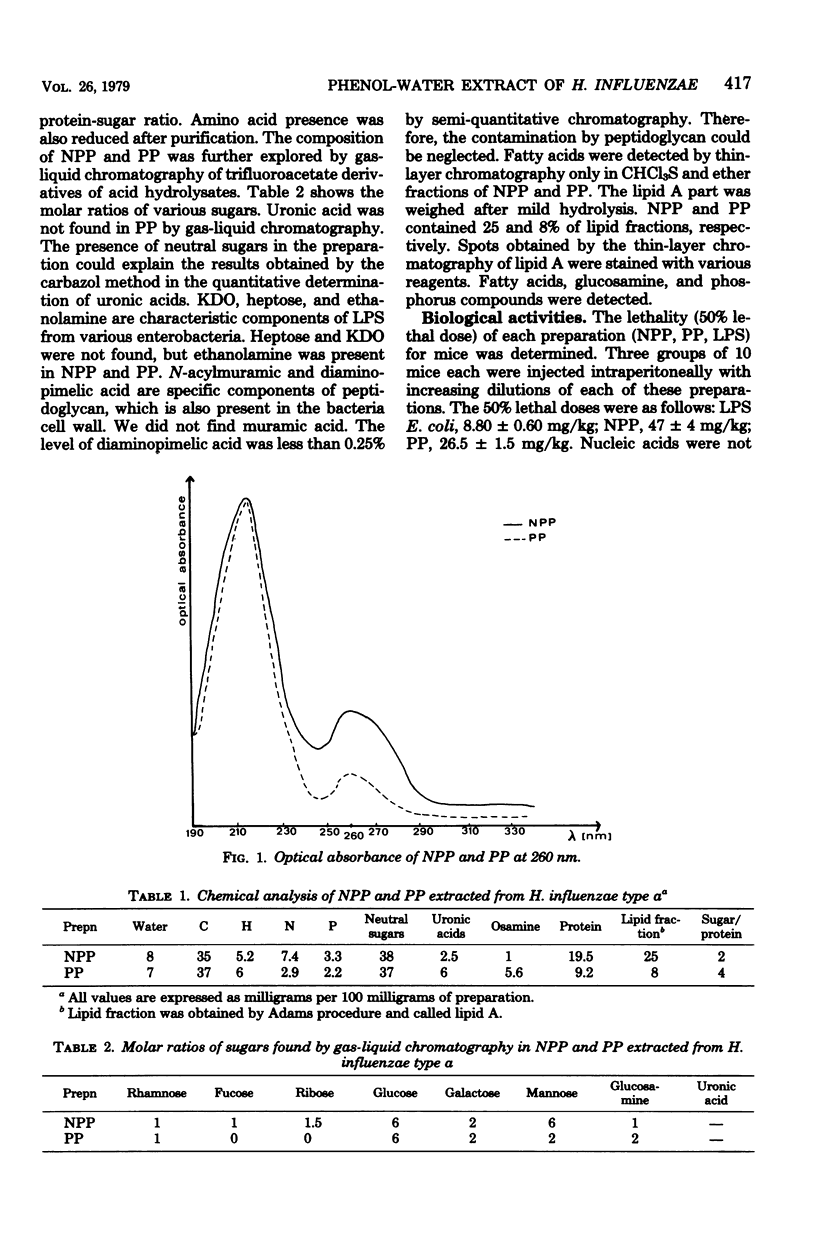
Abstract
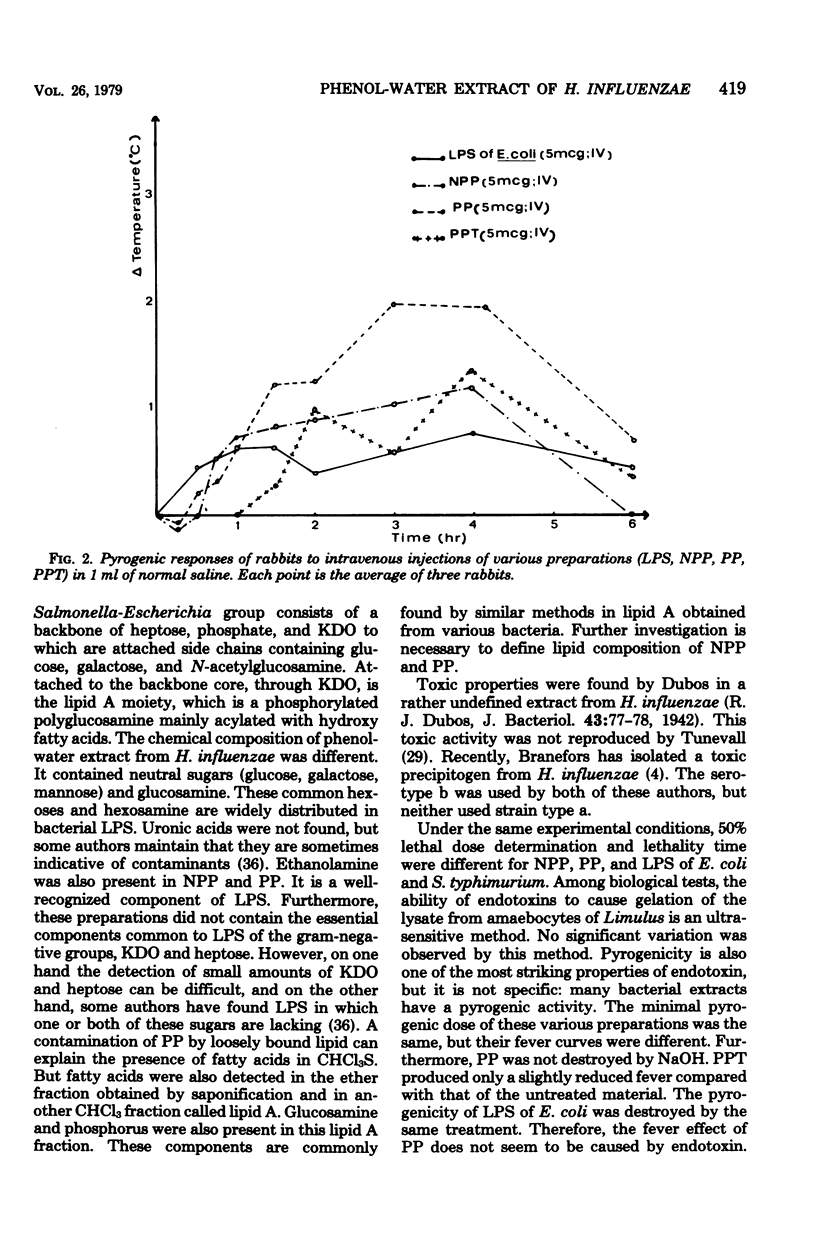
Ribonucleic acid was removed from a phenol-water extract of Haemophilus influenzae type a by streptomycin sulfate. This preparation was called purified preparation or PP. It contained neutral sugars (glucose, galactose, mannose, pentose), glucosamine, amino acids, and fatty acids. Heptose and 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonic acid were not present. The biological properties and immunogenicity were compared with the activities of lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli or Salmonella typhimurium. Higher doses were necessary to obtain lethality in mice and Sanarelli and Shwartzman reactions with our preparations than were necessary with lipopolysaccharide. The Limulus test and pyrogen assay in rabbits gave the same results with purified preparation and lipopolysaccharide, but pyrogenicity of purified preparation was not destroyed by NaOH treatment. Purified preparation was not as immunogenic at low doeses for rabbits as lipopolysaccharide. The results were different from those obtained with lipopolysaccharide but similar to those known from peptidoglycan studies. The contamination of purified preparation with peptidoglycan was negligible and cannot explain the biological activities of purified preparation. We suggest that the phenol-water extract from H. influenzae is not a classical endotoxin, but rather an endotoxin-like substance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Kates M., Shaw D. H., Yaguchi M. Studies on the chemical constitution of cell-wall lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria perflava. Can J Biochem. 1968 Oct;46(10):1175–1184. doi: 10.1139/o68-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Peter G., Johnston R. B., Jr, Wetterlow L. H., Smith D. H. Immunization of humans with polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI106794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Taudou B., Chuilon S. Glutaraldehyde, cyanuric chloride and tetrazotized O-dianisidine as coupling reagents in the passive hemagglutination test. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branefors-Helander P. Serological studies of Haemophilus influenzae. 3. The endotoxic effect of various antigen preparations and the relation between this effect and demonstrable precipitinogens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(5):585–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W. Effect of a toxin produced by Haemophilus influenzae on ciliated respiratory epithelium. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):93–100. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN A. P., OSBORN M. J. O-PHOSPHORYLETHANOLAMINE: A COMPONENT OF LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN CERTAIN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1571–1574. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori M. Biological activities of endotoxins from Yersinia enterocolitica. Jpn J Microbiol. 1976 Aug;20(4):273–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1976.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno S. Studies on the lipid components in endotoxin. I. Thin-layer chromatographic analyses and purification of lipids in acid hydrolyzed endotoxin of Salmonella typhosa. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1974 Sep;47(3):115–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Poore T. E., Zauber N. P., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in the blood of patients with sepsis due to gran-negative bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 10;283(24):1313–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012102832404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I. A., WILKINSON J. F., SWAIN R. H. The effect of Klebsiella aerogenes and Klebsiella cloacae polysaccharides on haemagglutination by and multiplication of the influenza group of viruses. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Dec;34(6):603–615. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Elson L. A. A colorimetric method for the determination of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylchrondrosamine. Biochem J. 1934;28(3):988–995. doi: 10.1042/bj0280988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J. Endotoxin-like properties of the peptidoglycan. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):230–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Schleifer K. H. Pyrogenic activity of bacterial mucopeptides. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1974;18(1):50–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROMINGER J. L., PARK J. T., THOMPSON R. E. Composition of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus: its relation to the mechanism of action of penicillin. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3263–3268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUNEVALL G. Studies on haemophilus influenzae; Haemophilus influenzae antigens studied by the gel precipitation method. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;32(1):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Jacquemin-Sablon A., Live T. R., Fareed G. C., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. VI. Further purification and properties of polynucleotide ligase from Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4543–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. H. Separation of amino acids in physiological fluids by two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;21(3):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetta J. P., Breckenridge W. C., Vincendon G. Analysis of monosaccharides by gas-liquid chromatography of the O-methyl glycosides as trifluoroacetate derivatives. Application to glycoproteins and glycolipids. J Chromatogr. 1972 Jul 5;69(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92897-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zwan J. C., Orie N. G., de Vries K. Biphasic reaction after inhalation of Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic nonspecific lung disease. Clin Allergy. 1975 Jun;5(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1975.tb01856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


