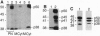Abstract
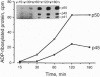
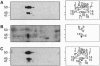
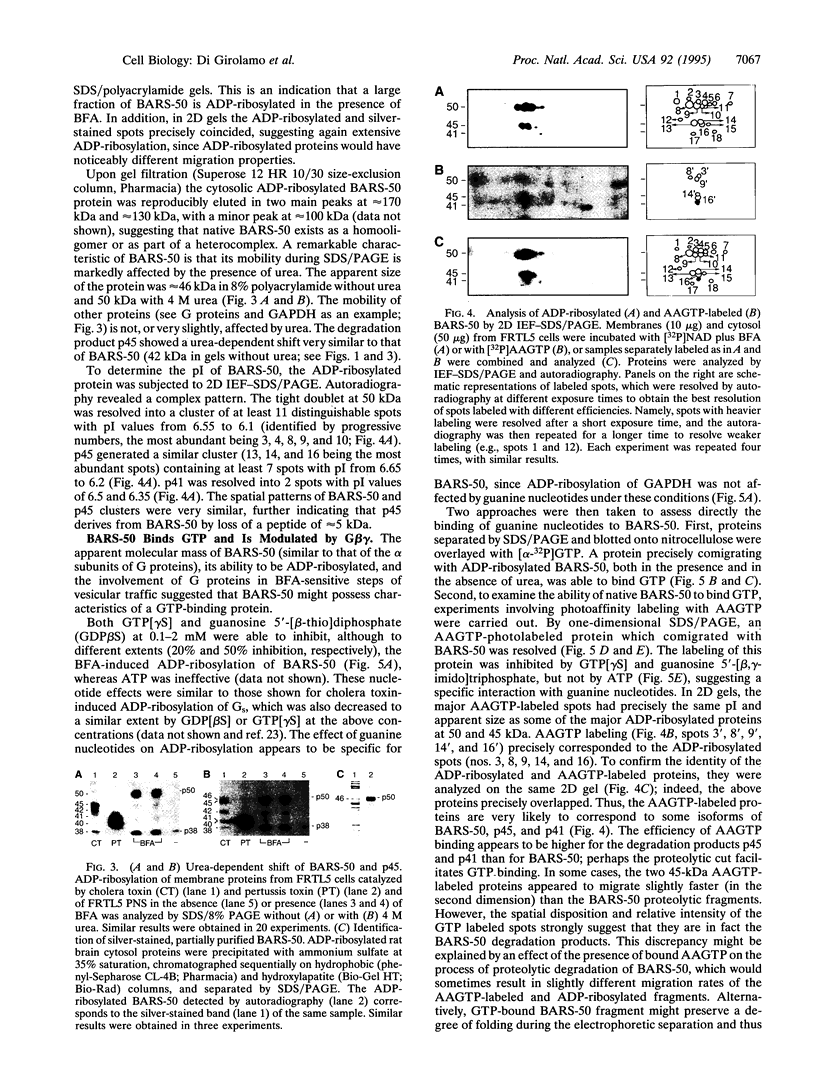
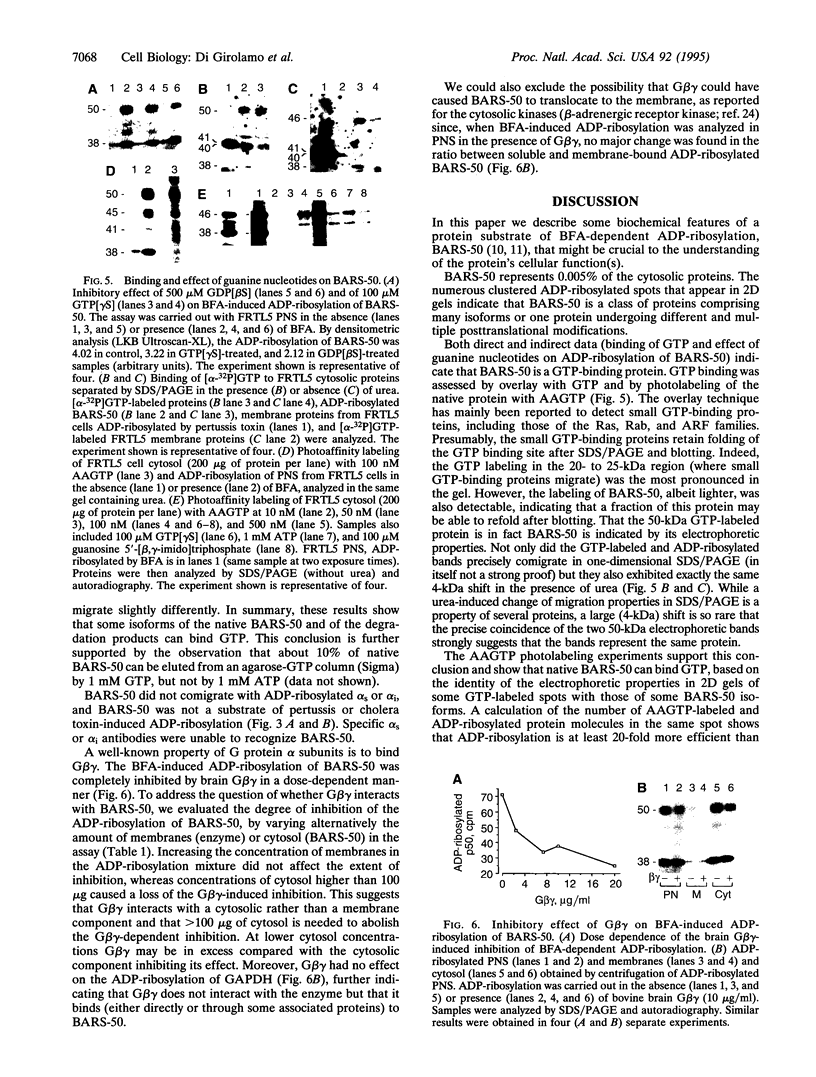
Brefeldin A, a fungal metabolite that inhibits membrane transport, induces the mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of two cytosolic proteins of 38 and 50 kDa as judged by SDS/PAGE. The 38-kDa substrate has been previously identified as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). We report that the 50-kDa BFA-induced ADP-ribosylated substrate (BARS-50) has native forms of 170 and 130 kDa, as determined by gel filtration of rat brain cytosol, indicating that BARS-50 might exist as a multimeric complex. BARS-50 can bind GTP, as indicated by blot-overlay studies with [alpha-32P]GTP and by photoaffinity labeling with guanosine 5'-[gamma-32P] [beta,gamma-(4-azidoanilido)]triphosphate. Moreover, ADP-ribosylation of BARS-50 was completely inhibited by the beta gamma subunit complex of G proteins, while the ADP-ribosylation of GAPDH was unmodified, indicating that this effect was due to an interaction of the beta gamma complex with BARS-50, rather than with the ADP-ribosylating enzyme. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analysis shows that BARS-50 is a group of closely related proteins that appear to be different from all the known GTP-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Parks L. A., Coon H. G. Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brands J. H., Maassen J. A., van Hemert F. J., Amons R., Möller W. The primary structure of the alpha subunit of human elongation factor 1. Structural aspects of guanine-nucleotide-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham D. E., Neer E. J. New roles for G-protein beta gamma-dimers in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):403–406. doi: 10.1038/365403a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. I., Mayorga L. S., Casey P. J., Stahl P. D. Evidence of a role for heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins in endosome fusion. Science. 1992 Mar 27;255(5052):1695–1697. doi: 10.1126/science.1348148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis M. A., Di Girolamo M., Colanzi A., Pallas M., Di Tullio G., McDonald L. J., Moss J., Santini G., Bannykh S., Corda D. Stimulation of endogenous ADP-ribosylation by brefeldin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1114–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., D'Arcangelo D., Cacciamani T., Gierschik P., Corda D. K-ras transformation greatly increases the toxin-dependent ADP-ribosylation of GTP binding proteins in thyroid cells. Involvement of an inhibitor of the ADP-ribosylation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17397–17403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Cassel D., Kahn R. A., Klausner R. D. ADP-ribosylation factor, a small GTP-binding protein, is required for binding of the coatomer protein beta-COP to Golgi membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6408–6412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Kahn R. A., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Binding of ARF and beta-COP to Golgi membranes: possible regulation by a trimeric G protein. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1197–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.1957170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Klausner R. D. Guanine nucleotides modulate the effects of brefeldin A in semipermeable cells: regulation of the association of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein with the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):579–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Tuana B. S. Identification of low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins and their sites of interaction in subcellular fractions from skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17613–17620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Hyvönen M., Musacchio A., Saraste M., Birney E. PH domain: the first anniversary. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Sep;19(9):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Woolkalis M. J. Cholera toxin-catalyzed [32P]ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:267–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95172-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. H., Rasenick M. M. In situ binding of a photo-affinity GTP analog to synaptic membrane G-proteins. Distribution of bound GTP analog reflects the status of adenylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. H., Casanova J. E. Gs alpha stimulates transcytosis and apical secretion in MDCK cells through cAMP and protein kinase A. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):677–687. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilz H., Koch R., Fanick W., Klapproth K., Adamietz P. Nonenzymic ADP-ribosylation of specific mitochondrial polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3929–3933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. K., Loflin P. T., Aboul-Ela N., Mingmuang M., Moss J., Jobson E. L. Modification of plasma membrane protein cysteine residues by ADP-ribose in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10825–10828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J. Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;116(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kots AYa, Skurat A. V., Sergienko E. A., Bulargina T. V., Severin E. S. Nitroprusside stimulates the cysteine-specific mono(ADP-ribosylation) of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 23;300(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyte A., Barr F. A., Kehlenbach R. H., Huttner W. B. Multiple trimeric G-proteins on the trans-Golgi network exert stimulatory and inhibitory effects on secretory vesicle formation. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4795–4804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane receptor desensitization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90139-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosylation of guanyl nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins by bacterial toxins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1988;61:303–379. doi: 10.1002/9780470123072.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi M., Huttner W. B. An elevation of cytosolic protein phosphorylation modulates trimeric G-protein regulation of secretory vesicle formation from the trans-Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24897–24905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimplikar S. W., Simons K. Regulation of apical transport in epithelial cells by a Gs class of heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1993 Apr 1;362(6419):456–458. doi: 10.1038/362456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasenick M. M., Talluri M., Dunn W. J., 3rd Photoaffinity guanosine 5'-triphosphate analogs as a tool for the study of GTP-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1994;237:100–110. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)37055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasenick M. M., Wang N. Exchange of guanine nucleotides between tubulin and GTP-binding proteins that regulate adenylate cyclase: cytoskeletal modification of neuronal signal transduction. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):300–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Yoshihara K., Kamiya T. Enzymic and nonenzymic mono ADP-ribosylation of proteins in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touhara K., Inglese J., Pitcher J. A., Shaw G., Lefkowitz R. J. Binding of G protein beta gamma-subunits to pleckstrin homology domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10217–10220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:73–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. Purification of brain microtubules and microtubule-associated protein 1 using taxol. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:104–115. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., Kuruc N. The postsynaptic density: constituent and associated proteins characterized by electrophoresis, immunoblotting, and peptide sequencing. J Neurochem. 1992 Aug;59(2):667–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]