Abstract
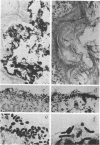
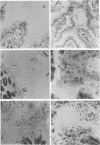
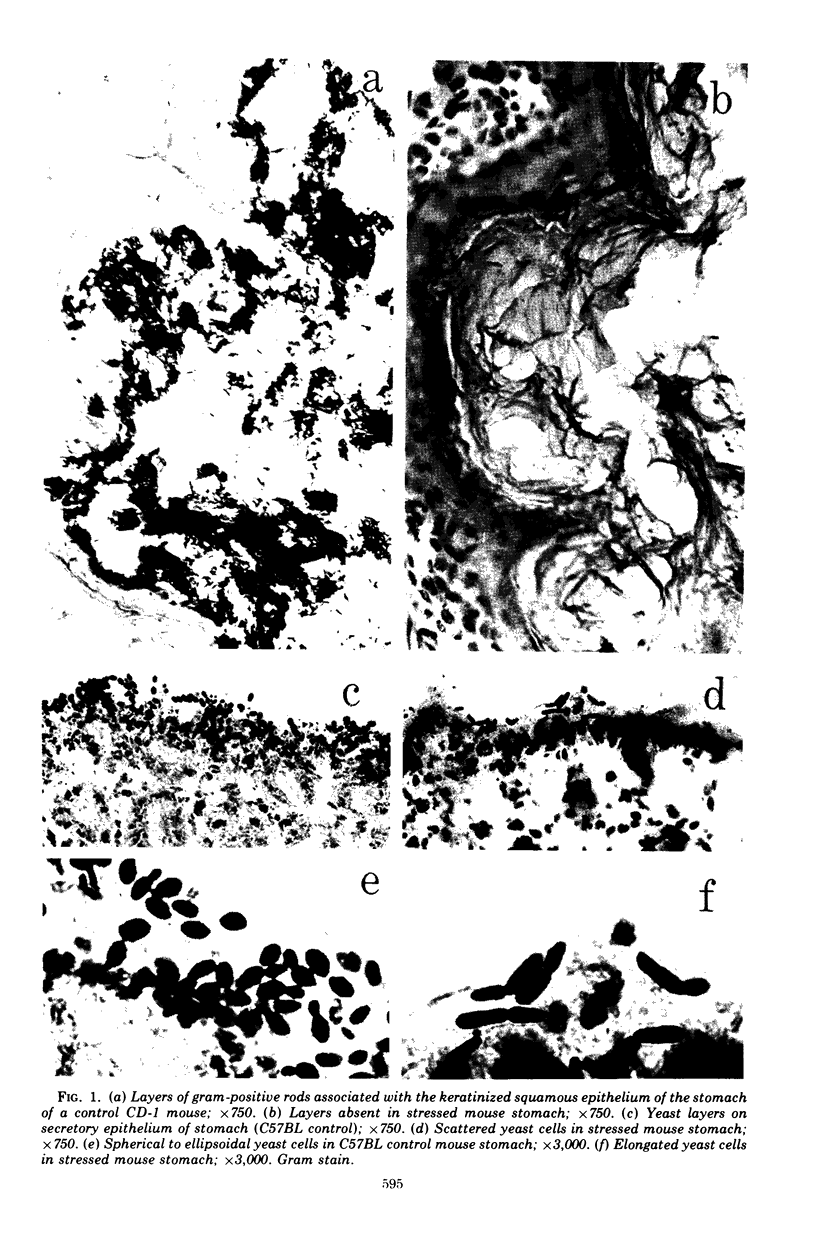
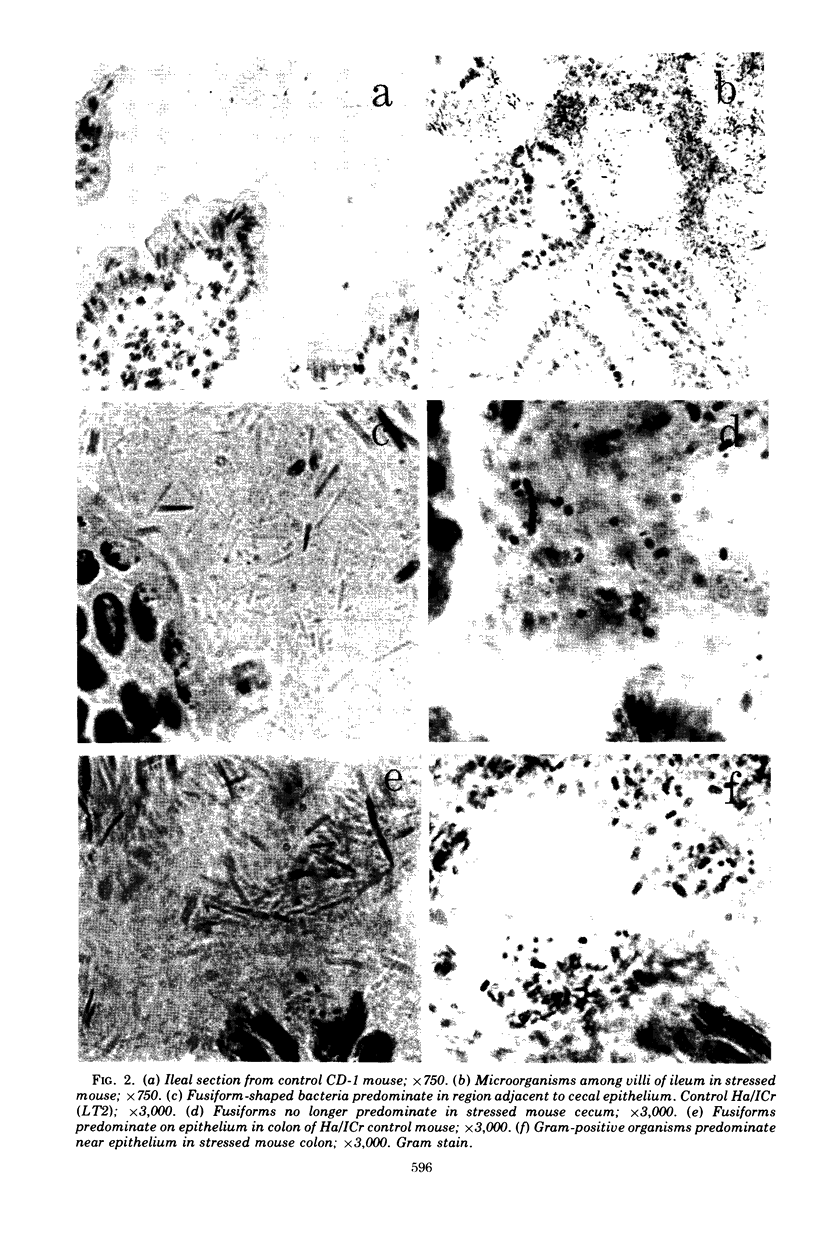
Aerobic and anaerobic cultural techniques and histological methods were used in a study of the effects of environmental and dietary stress on the indigenous microbiota of the gastrointestinal tract of mice. Mice previously inoculated with Salmonella typhimurium were examined in a similar manner. Three strains of mice (CD-1, Ha/ICr, and C57BL) were used. Control animals previously inoculated with S. typhimurium had low population levels of Salmonella bacteria in the small and large bowel. Mice previously inoculated with Salmonella and then deprived of food, water, and bedding for 48 h harbored high population levels of these bacteria in their small and large bowels. Coliforms increased in numbers in the large bowel of stressed mice inoculated with Salmonella and in the jejunum-ileum and cecum of stressed mice not previously inoculated with Salmonella. Control mice had high population levels of lactobacilli inhabiting the keratinized squamous epithelium of the stomach. Stressed mice showed dramatic reductions in these populations of lactobacilli. Populations of fusiform-shaped bacteria associated with the mucosal epithelium of the cecum and colon in control mice were reduced in stressed mice as determined by microscope examination of histological sections. Total anaerobic counts were similar, however, in both stressed and control animals. Environmental and dietary stress markedly alter the gastrointestinal microbiota in mice. Therefore, such stressful conditions profoundly affect the factors that regulate the localization and population levels of microorganisms in the stomach and intestines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on gastrointestinal motility. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):301–304. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams G. D., Bishop J. E. Effect of the normal microbial flora on the resistance of the small intestine to infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1604–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1604-1608.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnthorsson G., Johnson L., Nylander G., Wikström S. Gastric secretion of mucus related to adrenocortical activity. A histochemical study in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1971;6(1):65–70. doi: 10.3109/00365527109180672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immunological responses and microorganisms indigenous to the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1364–1371. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., McAllister J. S., Savage D. C. Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.666-672.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Zamcheck N. Bacterial degradation of gastrointestinal mucins. I. Comparison of mucus constituents in the stools of germ-free and conventional rats. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):210–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESHER S., WALBURG H. E., Jr, SACHER G. A., Jr GENERATION CYCLE IN THE DUODENAL CRYPT CELLS OF GERM-FREE AND CONVENTIONAL MICE. Nature. 1964 May 30;202:884–886. doi: 10.1038/202884a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. II. The role of Eh and volatile fatty acids in the normal gut. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:209–219. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. P., BOHNHOFF M. CHANGES IN THE MOUSE'S ENTERIC MICROFLORA ASSOCIATED WITH ENHANCED SUSCEPTIBILITY TO SALMONELLA INFECTION FOLLOWING STREPTOMYCIN TREATMENT. J Infect Dis. 1963 Jul-Aug;113:59–66. doi: 10.1093/infdis/113.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Onderdonk A. B., Baskett R. C., Hentges D. J. Shigella, indigenous flora interactions in mice. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1433–1440. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINET H. G. Relationship of host antibody to fluctuations of Escherichia coli serotypes in the human intestine. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:896–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.896-901.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R. J. The fecal flora of various strains of mice. Its bearing on their susceptibility to endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1149–1160. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R., COSTELLO R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:59–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R. Alterations in the mouse cecum and its flora produced by antibacterial drugs. J Exp Med. 1968 Jul 1;128(1):97–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., McAllister J. S., Davis C. P. Anaerobic bacteria on the mucosal epithelium of the murine large bowel. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.492-502.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial interference between indigenous yeast and lactobacilli in the rodent stomach. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1278-1283.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Horton R. E. Blood group isoantibody stimulation in man by feeding blood group-active bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1280–1291. doi: 10.1172/JCI106094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Smith J. M. A Salmonella carrier state involving the upper respiratory tract of mice. J Infect Dis. 1971 May;123(5):502–506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.5.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W., Smith J. M. The effect of food and water deprivation (stress) on Salmonella-carrier mice. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Aug;5(3):283–289. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-3-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]