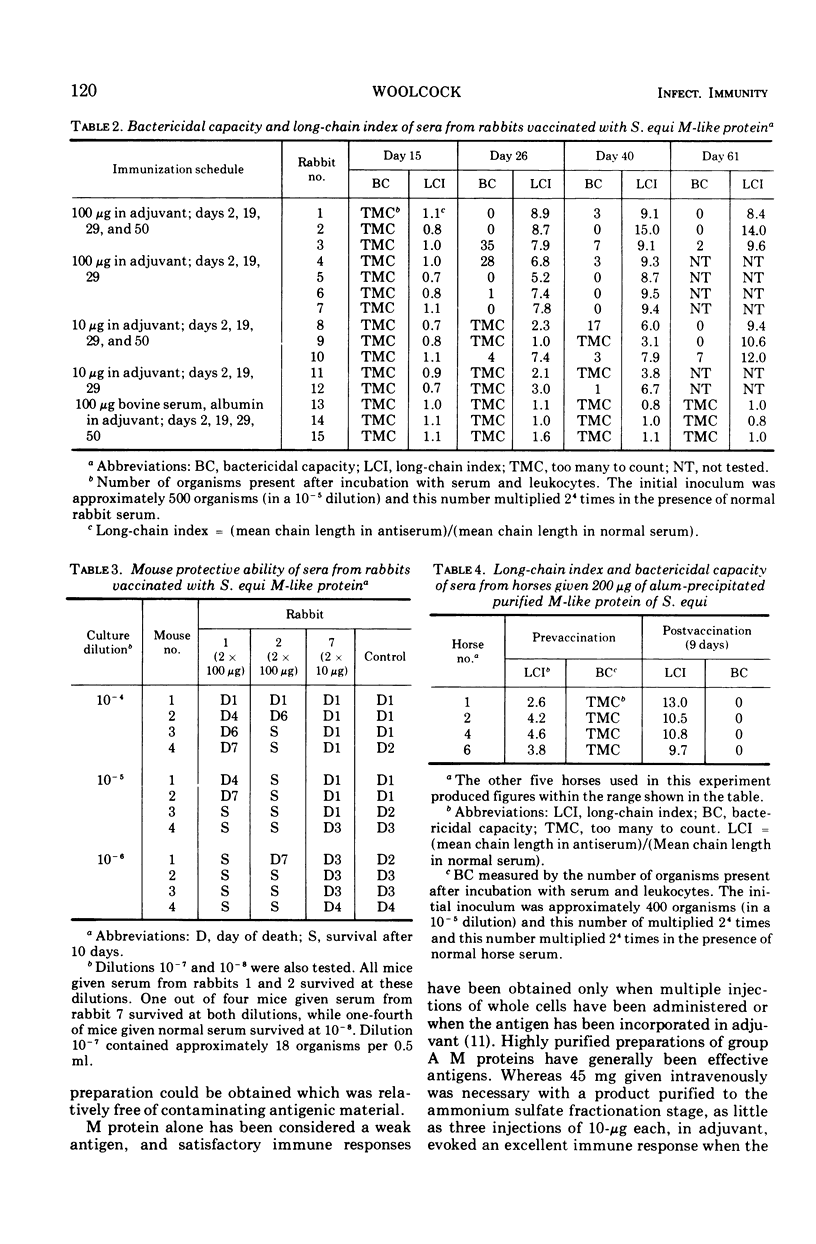
Abstract
A cell wall component of Streptococcus equi analogous to the M protein of group A streptococci has been identified and purified. A highly purified product has been obtained from cells by hot acid extraction, followed by acid precipitation, ammonium sulfate fractionation, and column chromatography. This product reacts with S. equi antiserum. The existence of this fraction in S. equi has been confirmed by the failure of trypsin-treated cells and their extracts to remove the long-chaining capacity of S. equi antiserum. The antigenicity of this M-like protein when incorporated in adjuvant has been assessed in rabbits and horses. In the rabbit, multiple doses of as low as 10 μg resulted in the production of serum capable of inducing long-chain formation and opsonizing and mouse protective antibody. Two doses of 100 μg elicited similar responses. The bactericidal capacity of this serum could be eliminated by absorption with whole S. equi cells or their extracts, but not by absorption with trypsin-treated cells or extracts therefrom. Horses vaccinated 15 months previously with a whole-cell killed vaccine and given 200 μg of the purified protein intramuscularly showed evidence of an anamnestic response to the antigen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dunlap M. B., Harvey H. S. The carrier state and type-specific immunity in streptococcal disease. Am J Dis Child. 1967 Sep;114(3):229–243. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1967.02090240043001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht H. Vaccination against strangles. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):425–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Pachman L. M., Wittner M. K., Dorfman A. Primary immunization of infants and children with group A streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1969 Nov;120(5):598–604. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N., Wittner M. K. Antigenicity of the M proteins of group A hemolytic streptococci. II. Antibody response in rabbits to vaccines prepared with oil emulsions and aluminum hydroxide. J Immunol. 1966 Jul;97(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAHN J. J., COLE R. M. STREPTOCOCCAL M ANTIGEN LOCATION AND SYNTHESIS, STUDIED BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1963 Nov 1;118:659–666. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLLERMAN G. H., EKSTEDT R. Long chain formation by strains of group A streptococci in the presence of homologous antiserum: a type-specific reaction. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):345–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent W. F., Borman E. K., Pranitis P. Chromatographic procedure for the preparation of M protein testing antigens. Health Lab Sci. 1966 Oct;3(4):225–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON A. T., WILEY G. G. THE CELLULAR ANTIGENS OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI; IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC STUDIES OF THE C, M, T, PGP, E4, F, AND E ANTIGENS OF SEROTYPE 17 STREPTOCOCCI. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:527–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]