Abstract
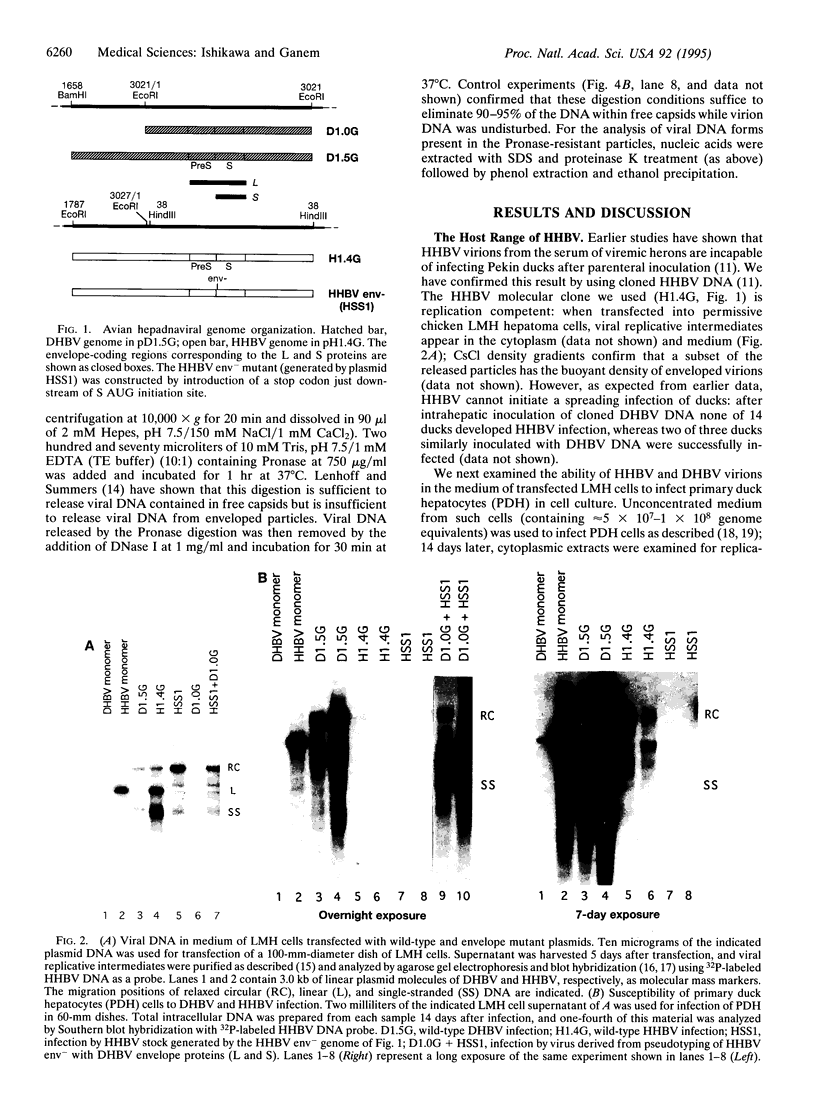
In addition to their well-recognized hepatotropism, all hepatitis B viruses (HBVs) display marked species specificity, growing poorly or not at all in species other than those closely related to their natural hosts. We have examined the molecular basis for this narrow host range, using duck HBV (DHBV) and heron HBV (HHBV) as a model system. HHBV virions will not infect ducks in vivo and infect cultured duck hepatocytes extremely inefficiently in vitro. Mutant HHBV genomes lacking all viral envelope proteins (HHBV env-) can be complemented in trans with DHBV envelope proteins; the resulting pseudotyped virions can efficiently infect duck hepatocytes. Further complementation analysis reveals that of the two viral surface proteins (L and S), it is the L protein that determines host range. Pseudotyping of HHBV env- with DHBV/HHBV chimeric envelope proteins reveals that replacement of as few as 69 amino acids of the pre-S domain of the HHBV L protein by their DHBV counterparts is sufficient to permit infection of duck hepatocytes. These studies indicate that the species-specificity of hepadnaviral infection is determined at the level of virus entry and is governed by the pre-S domain of the viral L protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker L. F., Maynard J. E., Purcell R. H., Hoofnagle J. H., Berquist K. R., London W. T. Viral hepatitis, type B, in experimental animals. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):189–195. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung R. C., Trujillo D. E., Robinson W. S., Greenberg H. B., Marion P. L. Epitope-specific antibody response to the surface antigen of duck hepatitis B virus in infected ducks. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):546–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90025-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deminie C. A., Emerman M. Incorporation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag proteins into murine leukemia virus virions. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6499–6506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6499-6506.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle P. R., Schlicht H. J., Fischer M., Schaller H. Production of infectious duck hepatitis B virus in a human hepatoma cell line. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1736–1740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1736-1740.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R., Colgrove R., Ganem D. Replication of duck hepatitis B virus in two differentiated human hepatoma cell lines after transfection with cloned viral DNA. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Kuroki K., Lenhoff R., Summers J., Ganem D. Analysis of the binding of a host cell surface glycoprotein to the preS protein of duck hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1994 Aug 1;202(2):1061–1064. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki K., Cheung R., Marion P. L., Ganem D. A cell surface protein that binds avian hepatitis B virus particles. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2091–2096. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2091-2096.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert V., Fernholz D., Sprengel R., Fourel I., Deléage G., Wildner G., Peyret C., Trépo C., Cova L., Will H. Virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibody to a conserved epitope on the duck hepatitis B virus pre-S protein. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1290–1297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1290-1297.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhoff R. J., Summers J. Coordinate regulation of replication and virus assembly by the large envelope protein of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4565–4571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4565-4571.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Simmons H. Duck hepatitis B virus infection of Muscovy duck hepatocytes and nature of virus resistance in vivo. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2487–2494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2487-2494.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Yaginuma K., Koike K., Summers J. Duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) particles produced by transient expression of DHBV DNA in a human hepatoma cell line are infectious in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3513–3516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3513-3516.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kuhn C., Will H., Schaller H. Comparative sequence analysis of duck and human hepatitis B virus genomes. J Med Virol. 1985 Apr;15(4):323–333. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S., Loeb D. D., Ganem D. Mutations affecting hepadnavirus plus-strand DNA synthesis dissociate primer cleavage from translocation and reveal the origin of linear viral DNA. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1255–1262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1255-1262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]