Abstract
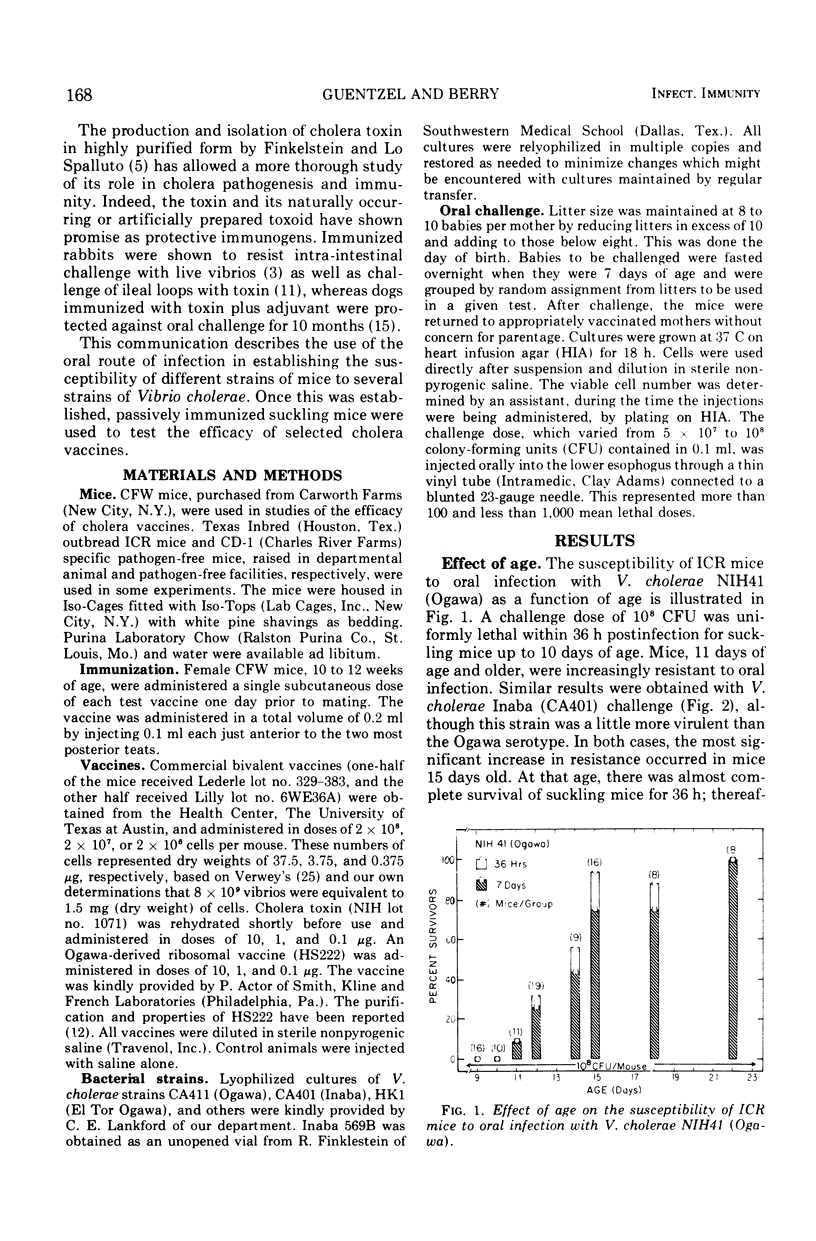
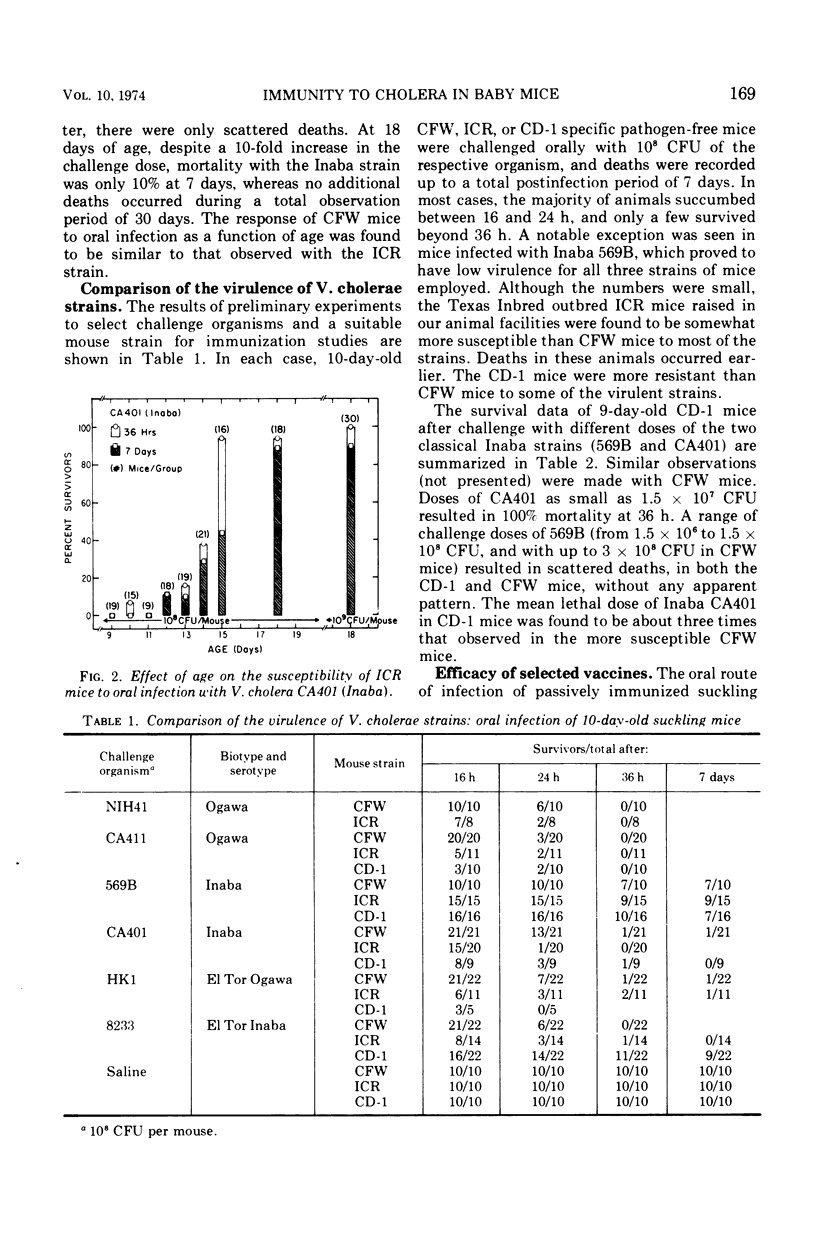
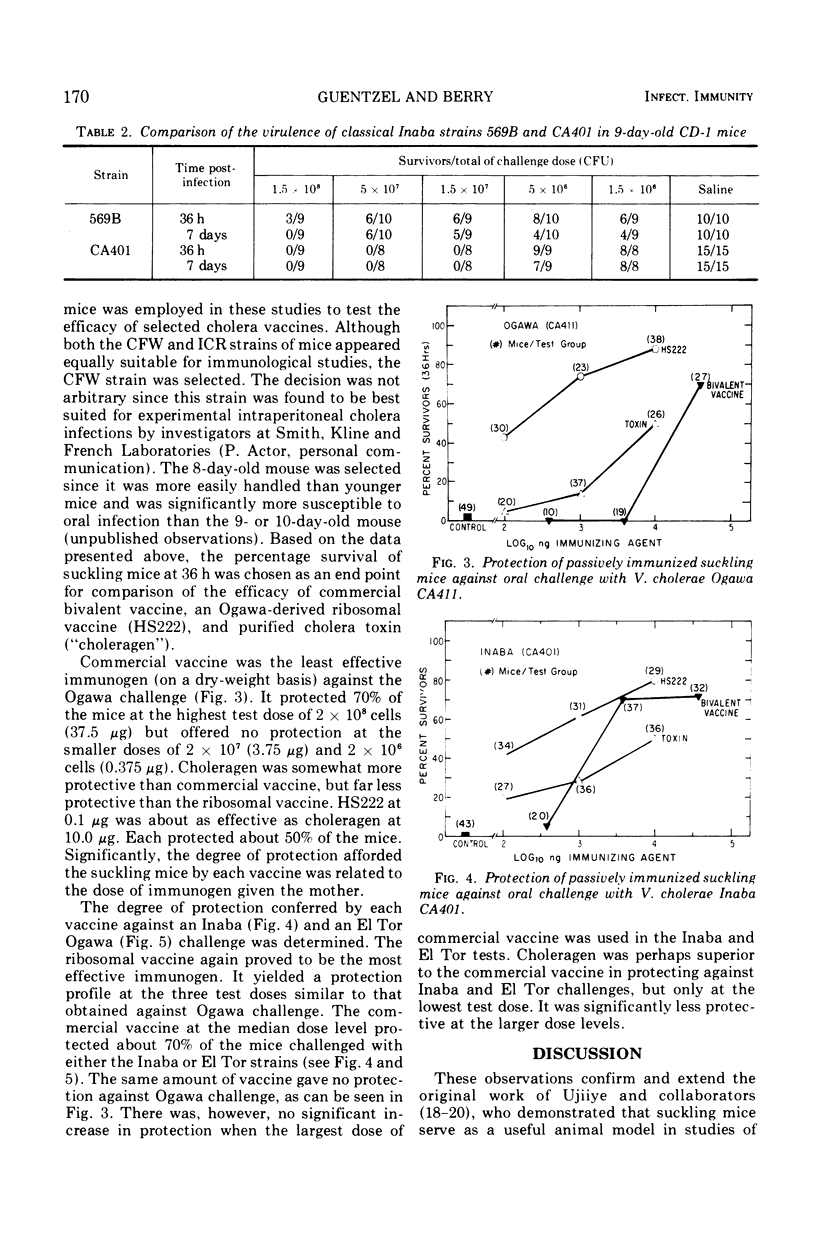
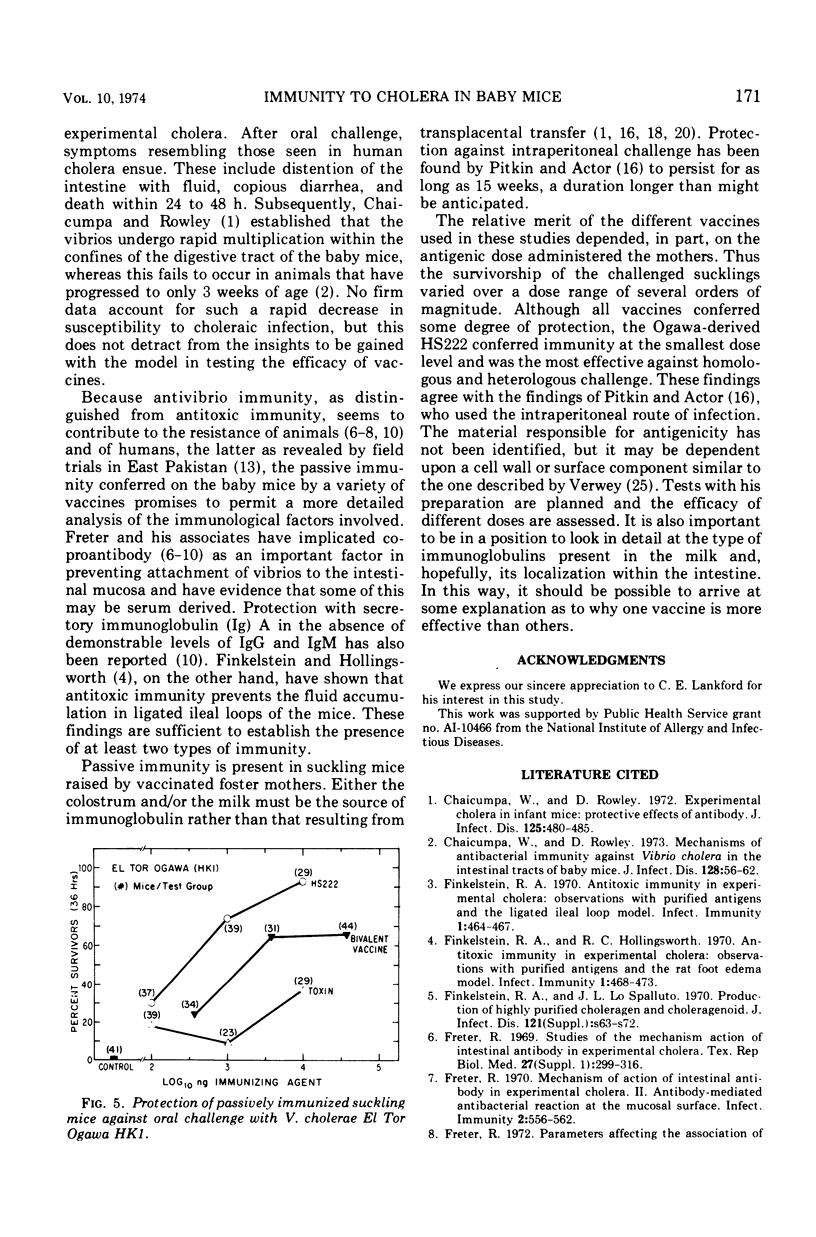
The susceptibility of suckling mice to oral infection with several different Vibrio cholerae was determined. Mice up to 10 days of age were uniformly susceptible to oral infection with 108 colony-forming units of virulent organisms. Age-dependent resistance occurred thereafter to a maximum at about 15 days of age. The efficacy of selected vaccines was compared by oral challenge of 8-day-old, passively immunized CFW mice. An Ogawa-derived ribosomal antigen was found to be superior to a commercial whole-cell vaccine or to purified cholera enterotoxin. The ribosomal antigen was 50- to 100-fold more protective than the other vaccines on a weight basis against otherwise lethal challenge with Ogawa, Inaba, or El Tor Ogawa serotypes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaicumpa W., Rowley D. Experimental cholera in infant mice: protective effects of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):480–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaicumpa W., Rowley D. Mechanisms of antibacterial immunity against Vibrio cholerae in the intestinal tracts of baby mice. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):56–62. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the ligated ileal loop model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):464–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.464-467.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Hollingsworth R. C. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the rat foot edema model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):468–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.468-473.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LoSpalluto J. J. Production of highly purified choleragen and choleragenoid. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(Suppl):63+–63+. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.supplement.s63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Mechanism of Action of Intestinal Antibody in Experimental Cholera II. Antibody-Mediated Antibacterial Reaction at the Mucosal Surface. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):556–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.556-562.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Gregory B., Naylor J., Actor P. Isolation of protective somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa) ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):156–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.156-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Kaniecki E. A., Northrup R. S. Protection against experimental cholera by antitoxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):606–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkin D., Actor P. Immunity to Vibrio cholerae in the mouse. I. Passive protection of newborn mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):428–432. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.428-432.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Serum-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):374–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.374-380.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


