Abstract
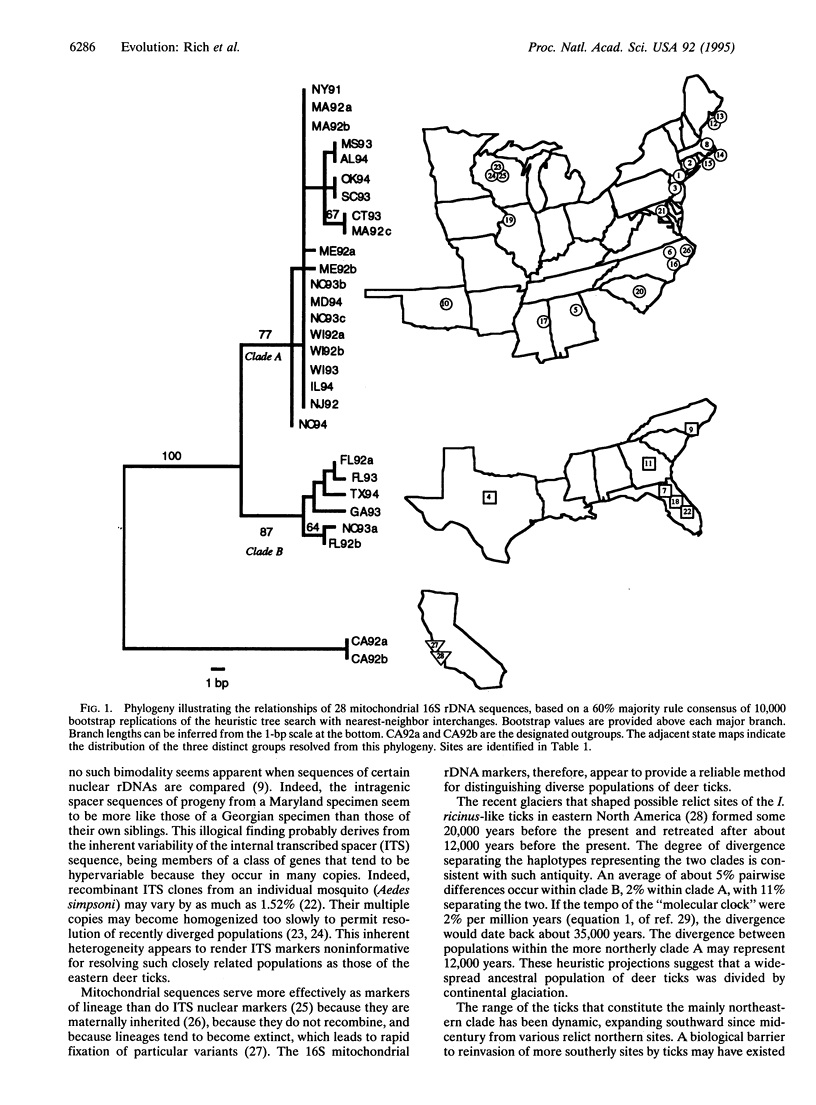
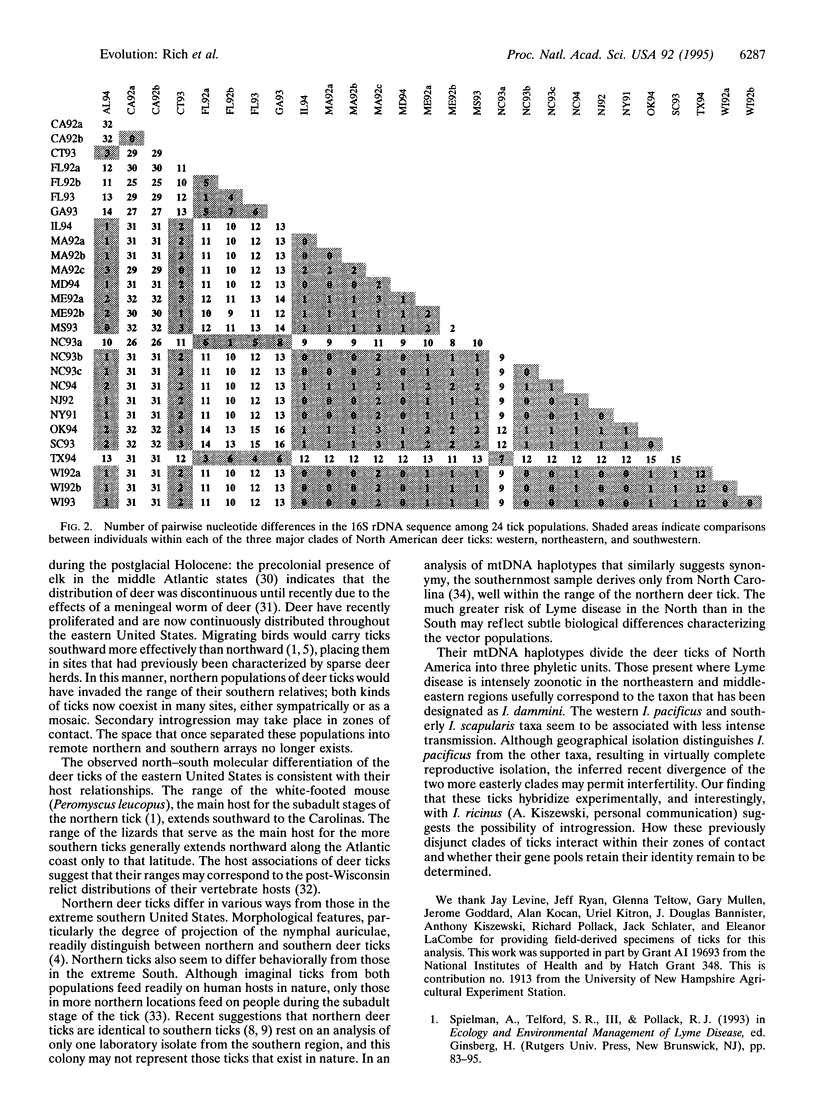
We analyzed the geographic distribution of the Ixodes ricinus-like ticks in eastern North America by comparing the mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences of specimens sampled directly from the field during the 1990s. Two distinct lineages are evident. The southern clade includes ticks from the southeastern and middle-eastern regions of the United States. The range of the northern clade, which appears to have been restricted to the northeastern region until the mid-1900s, now extends throughout the northeastern and middle-eastern regions. These phyletic units correspond to northern and southern taxa that have previously been assigned specific status as Ixodes dammini and Ixodes scapularis, respectively. The expanding range of I. dammini appears to drive the present outbreaks of zoonotic disease in eastern North America that include Lyme disease and human babesiosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avise J. C., Neigel J. E., Arnold J. Demographic influences on mitochondrial DNA lineage survivorship in animal populations. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(2):99–105. doi: 10.1007/BF02257369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. C., 4th, Piesman J. Phylogeny of hard- and soft-tick taxa (Acari: Ixodida) based on mitochondrial 16S rDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10034–10038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporale D. A., Kocher T. D. Sequence variation in the outer-surface-protein genes of Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Biol Evol. 1994 Jan;11(1):51–64. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Newbold J. E., Potter S. S., Edgell M. H. Maternal inheritance of mammalian mitochondrial DNA. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):536–538. doi: 10.1038/251536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keirans J. E., Clifford C. M. The genus Ixodes in the United States: a scanning electron microscope study and key to the adults. J Med Entomol Suppl. 1978 Jul 20;2:1–149. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/15.suppl2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher T. D., Thomas W. K., Meyer A., Edwards S. V., Päbo S., Villablanca F. X., Wilson A. C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckhart S., Mullen G. R., Durden L. A., Wright J. C. Borrelia sp. in ticks recovered from white-tailed deer in Alabama. J Wildl Dis. 1992 Jul;28(3):449–452. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-28.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Clifford C. M., Piesman J., Corwin M. D. Human babesiosis on Nantucket Island, USA: description of the vector, Ixodes (Ixodes) dammini, n. sp. (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1979 Mar 23;15(3):218–234. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/15.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesson D. M., McLain D. K., Oliver J. H., Piesman J., Collins F. H. Investigation of the validity of species status of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) using rDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10221–10225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesson D. M., Porter C. H., Collins F. H. Sequence and secondary structure comparisons of ITS rDNA in mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1992 Dec;1(4):253–269. doi: 10.1016/1055-7903(92)90001-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong B., Kocher T. D. Comparison of mitochondrial DNA sequences of seven morphospecies of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). Genome. 1991 Apr;34(2):306–311. doi: 10.1139/g91-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong B., Kocher T. D. Phylogeny of sibling species of Simulium venustum and S. verecundum (Diptera: Simuliidae) based on sequences of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1993 Dec;2(4):293–303. doi: 10.1006/mpev.1993.1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



