Abstract
The molecular drivers of thymoma are poorly understood. Outside of the identification of rarely occurring epidermal growth factor receptor and v-kit Hardy-Zuckerman 4 feline sarcoma viral oncogene homolog mutations via candidate gene sequencing, mutations in common cancer genes have yet to be observed. Only a single thymoma genome sequence has been previously reported, with no mutations in known cancer genes identified. Thus, we attempted to identify somatic driver mutations in a cytogenetically normal thymoma. A stage IVB type B3 thymoma from a 47-year-old male of Asian descent with no history of myasthenia gravis or other autoimmune condition was genomically evaluated. Exome sequencing and low-pass whole-genome sequencing was performed to identify somatic point mutations, copy number changes and structural variants. Mutations in known tumor suppressors DNMT3A (p.G728D) and ASXL1 (p.E657fs), consistent with mutations of known consequence in acute myeloid leukemia, were identified. Contrary to a previous report, this finding suggests the genetic etiology of thymomas may not be fundamentally distinct from other tumor types. Rather, these findings suggest that further sequencing of cytogenetically normal thymoma samples should reveal the specific molecular drivers of thymoma.
Introduction
Thymomas are rare tumors arising from the epithelial cells of the thymus, commonly associated with myasthenia gravis or other autoimmune disorders.1 The WHO classification system categorizes thymomas (type A, B1, B2, B3 and AB) and thymic carcinoma (type C) according to morphology, degree of atypia, histological similarity to normal thymic cells and degree of lymphocyte infiltration.2 Thymomas are staged (stage I, IIA, IIB, III, IVA and IVB) according to degree of encapsulation and anatomic extent of disease with encapsulation decreasing and dispersion from the thymus increasing with stage.3 Late stage thymomas are very rare and tend to locally recur rather than metastasize. Type B3 thymomas are the most aggressive of the thymomas.
Surgical resection is the favored treatment for thymoma. Complete surgical resection can be achieved for the vast majority of stage I and II thymomas. Stage III–IV thymomas that cannot be fully resected are generally treated with radiation and platinum-based combination chemotherapy regimens leading to substantial tumor shrinkage;4, 5, 6, 7 however, similar survival is observed with preoperative radiation therapy without chemotherapy.8, 9 Currently, there are no good biomarkers for response to therapy. Amplifications and rare activating mutations of EGFR and overexpression of HER2, KIT, BCL2 and TP53, as well as loss of CDKN2A have been previously described.7, 10 However, no strong evidence supports response of thymomas to EGFR or KIT targeted therapies.11
Thymomas and thymic carcinomas have been extensively profiled for chromosomal abnormalities, especially via comparative genomic hybridization,12, 13, 14 revealing that the vast majority of B3 thymomas display chromosomal abnormalities. However, there is no information on tumorigenic point mutations in B3 thymomas.7 Only a single genome sequence of a B3 thymoma has been reported thus far, for a tumor that displayed the typical chromosomal abnormalities for this tumor type (that is, gain of chromosome 1q, loss of chromosome 6 and 13q, and so on).15 No mutations in common cancer-associated genes were observed, leading the authors to suggest that thymomas may evolve through distinct molecular mechanisms as compared with other tumor types. In this article, we report the identification of DNMT3A and ASXL1 mutations in a cytogenetically normal stage IVB type B3 thymoma. This is the first identification of driver point mutations in B3 thymoma and suggests that further genomic profiling of cytogenetically normal B3 thymomas may reveal the specific molecular drivers of this tumor type.
Results
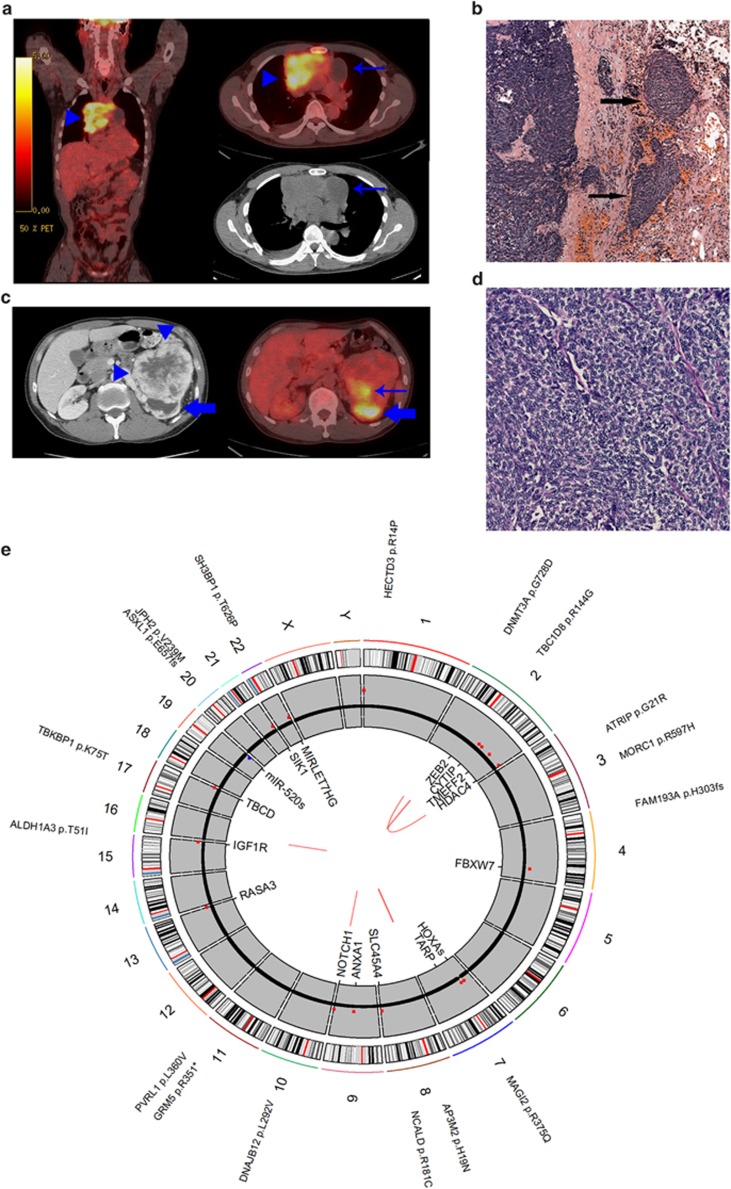
The patient presented with a 3-month history of cough. He did not have shortness of breath, hemoptysis or weight loss at presentation. He also did not have neurologic symptoms consistent with myasthenia gravis. Family history is significant for thymoma in the mother. A computed tomography of the chest showed a mediastinal mass measuring 10.5 × 7.8 × 12.1 cm and a large (12 × 9.5 × 8.3 cm) left renal mass (Figures 1a and 1b, ). The patient underwent computed tomography-guided biopsy of the mediastinal mass that revealed mildly atypical, uniform spindled cells associated with dense collagenous tissue. The tumor cells showed immunohistochemical positivity for AE1/AE3 and cytokeratin-7. Immunohistochemical markers for renal cell carcinoma were negative. The pathologic findings were consistent with thymoma. Subsequently, the patient underwent removal of mediastinal mass and right upper lobectomy as an en bloc resection. There was a separate right diaphragmatic nodule that was also excised. At the time of surgery, it was noted that the tumor was densely adherent to the pericardium and invaded the upper lobe of the right lung. Microscopic examination showed spindled to polygonal cells in varying sized lobules with accompanying fibrous bands of stroma invading the pericardium, pleura and lung (Figures 1c and d). Only occasional interspersed lymphocytes were seen. Focal lymph-vascular invasion was identified. The tumor cells showed ovoid nuclei with mild pleomorphism and scattered mitoses. The final margins were clear. The diaphragmatic nodule demonstrated tumor cells morphologically similar to the primary tumor. The final Masaoka stage of IVB was based on the finding of a separate distinct diaphragmatic tumor nodule and pleural invasion. The tumor had a WHO histologic category of B3 based on the predominance of epithelial cells and paucity of intraepithelial lymphocytes. No treatment was given before genome sequencing.
Figure 1.
(a) Thymoma imaging. fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (CT) demonstrates intensely hypermetabolic anterior mediastinal mass on fused coronal and axial images (arrowheads). Cystic tumor component on attenuation-correction CT image is non-hypermetabolic on FDG PET (arrows). (b) Renal tumor imaging. CT scan with contrast (left) demonstrates large contrast-enhancing left renal mass (arrowheads) with posterior hydronephrotic upper pole collecting system (block arrow). Fused axial FDG PET/CT (right) demonstrates mildly hypermetabolic posterior tumor component (arrow). Upper pole hydronephrosis contains excreted urinary FDG (block arrow). (c, d) Thymoma histology. (c) Lobules of thymoma tumor cells infiltrate into the adjacent lung parenchyma (arrows: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E): × 5 magnification). (d) Sheets of thymoma type B3 polygonal tumor cells with ovoid nuclei (H&E: × 20 magnification). (e) Tumor genome overview. Circos plot overview of somatic mutations identified in the thymoma. Outer text denotes location and gene impacted by somatic protein coding mutations. Middle gray ring depicts copy number variation (CNV) status (black=2 copies, red=CNV gains, blue=CNV losses). Inner text displays genes overlapping identified CNVs. Inner red lines display identified structural variants.
Tumor genome overview
An overview of the somatic variants observed is presented in Figure 1e. Overall, 14 somatic indels and 176 somatic single-nucleotide polymorphisms were identified, 17 of which impacted the amino-acid sequence of proteins (Table 1). Sixteen copy number gains, 1 copy number loss (Table 2) and 6 structural variants (Table 3) were also observed. Sequencing of the renal mass revealed no overlap in somatic mutations, confirming the tumors were of independent origin. No major interchromosomal events were present in the thymoma genome, nor were any major chromosomal aneuploidies frequently observed in B3 thymomas.12 Structural variants that were detected did not contain breakpoints within genes of known relevance to tumorigenesis (Table 3). Thus, somatic events of interest were comprised of point mutations and subchromosomal copy number variants.
Table 1. Coding mutations.
| Gene | Gene impact | Protein location | Prediction of impact | Coordinates (hg19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALDH1A3 | Missense | T51I | SIFT, Condel | chr15: 101 425 524 snp C>T |
| AP3M2 | Missense | H19N | Polyphen, SIFT, Condel | chr8: 42 012 260 snp C>A |
| ASXL1 | Frameshift | E657fs | Damaging | chr20: 31 022 486 del G>- |
| ATRIP | Missense | G21R | SIFT, Condel | chr3: 48 488 310 snp G>C |
| DNAJB12 | Missense | L292V | Neutral | chr10: 74 098 021 snp G>C |
| DNMT3A | Missense | G728D | Polyphen, SIFT, Condel | chr2: 25 463 310 snp C>T |
| FAM193A | Frameshift | H303fs | Damaging | chr4: 2 648 428 ins ->T |
| GRM5 | Nonsense | R351* | Damaging | chr11: 88 386 432 snp G>A |
| HECTD3 | Missense | R14P | SIFT, Condel | chr1: 45 476 889 snp C>G |
| JPH2 | Missense | V239M | Neutral | chr20: 42 788 712 snp C>T |
| MAGI2 | Missense | R375Q | Condel | chr7: 77 807 386 snp C>T |
| MORC1 | Missense | R597H | Neutral | chr3: 108 724 077 snp C>T |
| NCALD | Missense | R181C | Polyphen, SIFT, Condel | chr8: 102 701 578 snp G>A |
| PVRL1 | Missense | L360V | Neutral | chr11: 119 510 648 snp G>C |
| SH3BP1 | Missense | T626P | Neutral | chr22: 38 051 466 snp A>C |
| TBC1D8 | Missense | R144G | Neutral | chr2: 101 670 771 snp T>C |
| TBKBP1 | Missense | K75T | Polyphen, SIFT, Condel | chr17: 45 773 702 snp A>C |
Somatic protein coding mutations.
Table 2. Copy number variants.
| Type | Coordinates | Size (kb) | Dosage | Overlapping genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gain | chr1: 470 001–600 000 | 130 | 5 | None |
| Gain | chr2: 145 130 001–145 310 000 | 180 | 3 | ZEB2 |
| Gain | chr2: 158 260 001–158 370 000 | 110 | 3 | CYTIP |
| Gain | chr2: 192 770 001–192 940 000 | 170 | 3 | TMEFF2 |
| Gain | chr2: 240 110 001–240 240 000 | 130 | 3 | HDAC4 |
| Gain | chr4: 153 220 001–153 320 000 | 100 | 3 | FBXW7 |
| Gain | chr7: 27 120 001–27 240 000 | 120 | 3 | HOXA gene cluster, MIR196B |
| Gain | chr7: 38 290 001–38 390 000 | 100 | 3 | TARP |
| Gain | chr8: 142 200 001–142 320 000 | 120 | 3 | SLC45A4, DENND3 |
| Gain | chr9: 75 690 001–75 830 000 | 140 | 3 | ANXA1, ALDH1A1 |
| Gain | chr9: 139 420 001–139 520 000 | 100 | 3 | NOTCH1, MIR4674 |
| Gain | chr13: 114 740 001–114 920 000 | 180 | 3 | RASA3 |
| Gain | chr15: 99 410 001–99 510 000 | 100 | 3 | IGF1R |
| Gain | chr17: 80 740 001–80 920 000 | 180 | 3 | TBCD, ZNF750, B3GNTL1 |
| Loss | chr19: 54 070 001–54 200 000 | 130 | 1 | ZNF331, DPRX, MIR520 cluster |
| Gain | chr21: 44 690 001–44 900 000 | 210 | 3 | SIK1 |
| Gain | chr22: 46 380 001–46 550 000 | 170 | 3 | MIRLET7B, MIR3619, MIR4763 |
Tumor-specific copy number variants, dosage and contained genes.
Table 3. Structural variants.
|
Type |
State |
Breakpoint 1 |
Breakpoint 2 |
Overlapping genes |
| Coamplicon | Bal | chr16: 26 382 735–26 386 932 | chr16: 26 382 736–26 386 932 | None |
| Inversion | Unbal | chr2: 87 651 839–87 656 090 | chr2: 90 482 288–90 485 529 | Many |
| Inversion | Unbal | chr2: 33 141 477–33 141 679 | chr2: 242 819 853–242 820 060 | Many |
| Coamplicon | Bal | chr7: 158 706 424–158 710 034 | chr7: 158 706 425–158 710 035 | WDR60 |
| Insertion | Bal | chr7: 158 704 999–158 708 434 | chr7: 158 705 000–158 709 994 | WDR60 |
| Insertion | Bal | chr9: 139 994 967–139 997 831 | chr9: 139 994 968–139 998 202 | MAN1B1 |
Abbreviations: Bal, balanced; Unbal, unbalanced.
Tumor-specific structural variants.
Coding mutations
Fourteen nonsynonymous, 1 nonsense and 2 frameshift somatic mutations were observed in the tumor (Table 1). Of these mutations, four stood out with clear functional relevance—frameshift mutations in FAM193A and ASXL1, a nonsense mutation in GRM5, and a nonsynonymous mutation in DNMT3A. Although the mutations in FAM193A and GRM5 clearly impact protein function, the relevance of these mutations to tumorigenesis is not immediately apparent. On the other hand, the somatic mutations in DNMT3A and ASXL1 are of the type previously observed in other tumor types and expected to contribute to tumorigenesis.
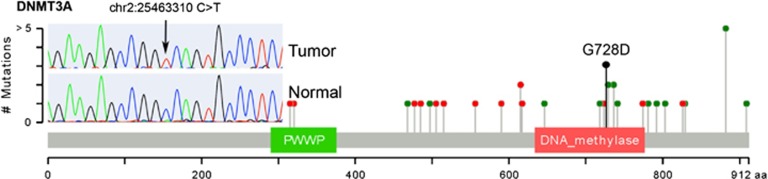
DNMT3A is a DNA methyltransferase required for de novo methylation and mammalian development.16 It is known to act as a tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and is observed mutated less frequently in other tumor types.17, 18 The nonsynonymous mutation observed in this thymoma sample leads to a nonconservative substitution of aspartate for glycine at amino-acid 728 (p.G728D) within the DNA methylase domain of DNMT3A. This region is known to be responsible for the hydrophobic interaction between DNMT3A and its regulatory subunit DNMT3L, an interaction that is required for activation of DNMT3A methyltransferase activity and previously shown to be disrupted by mutations in this region.19 Moreover, previously observed nonsynonymous mutations in AML cluster tightly within this region (shown in Figure 2)20, 21, 22. Strikingly and unusually, this somatic mutation was observed in homozygous state in the tumor: 61 of 62 (98.4%) exome sequencing reads from the tumor supported the mutation, 0 of 41 (0%) of exome sequencing reads from the normal sample supported the mutation, the homozygous state was confirmed via Sanger sequencing (Figure 2, inset), and no evidence for loss of heterozygosity was observed in the exome or low-pass whole-genome sequencing data. Moreover, no other somatic mutations were observed at >60% allelic frequency in the tumor, suggesting a specific and early gene conversion event at this locus. Finally, a previously sequenced AML, reported by Hou et al.,22 carried a mutation at this position (p.G728R) and at a nearby position (p.F731L), supporting the notion that homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations at the DNMT3A—DNMT3L interface are required to effectively disrupt methyltransferase activity.23 Thus, the type, location and unusual zygosity of this somatic mutation strongly suggest mutations in DNMT3A have a causal role in the etiology of thymoma.
Figure 2.
The DNMT3A p.G728D mutation observed in this thymoma sample is visualized in the context of other DNMT3A mutations observed in AML genome sequences from TCGA. The protein sequence and functional domains are depicted on the x axis. The number of AML mutations is depicted on the y axis. Red circles correspond to truncating mutations. Green circles correspond to missense mutations. Circle height corresponds to the number of mutations per position, however, the G728D indicator (black) is only meant to indicate position of this mutation. Note the clustering of AML nonsynonymous mutations around position 728. Mutations in this region reduce DNMT3A activity by disrupting the interaction between DNMT3L and DNMT3A. The Sanger sequencing validation trace of p.G7238D is also shown, demonstrating validation of p.G7238D as a homozygous somatic mutation.
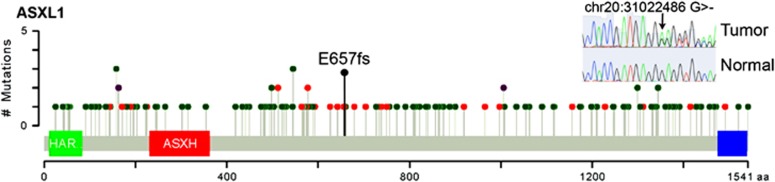
ASXL1 is a chromatin binding Polycomb group protein involved in transcriptional repression of numerous cell-type-specific systems, most likely through the recruitment of methylated histone H3 to promoters of target genes.24 ASXL1 is a known tumor suppressor in myelodysplastic syndrome and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia although it is frequently mutated in other tumor types such as lung squamous and bladder cancer.17, 18 The heterozygous deletion of a single guanine nucleotide within exon 12 of ASXL1 leads to out-of-frame translation beginning at codon 657 and premature truncation of the protein, removing >50% of the protein including the PHD domain responsible from histone interactions. This mutation was confirmed via Sanger sequencing (Figure 3, inset). Similar heterozygous C-terminal truncations are sufficient to induce myelodysplastic syndrome.25 Previously observed frameshift or nonsense mutations in ASXL1 across numerous tumor types catalogued in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) have been observed both upstream and downstream of amino-acid 657, with the highest concentration centered at position 657 (Figure 3). In fact, the majority of previously observed ASXL1 mutations occur in the same exon as this mutation, exon 12.26, 27 Thus, both the type and location of this somatic mutation strongly suggests mutations in ASXL1 have a causal role in the etiology of thymomas.
Figure 3.
The ASXL1 p.E657fs mutation observed in this thymoma sample is visualized in the context of other ASXL1 mutations observed in all tumor genome sequences catalogued in TCGA. The protein sequence and functional domains are depicted on the x axis. The number of TCGA mutations is depicted on the y axis. Red circles correspond to truncating mutations. Green circles correspond to nonsynonymous mutations. Purple circles correspond to mutations that are both nonsynonymous and truncating in different gene isoforms. Circle height corresponds to the number of mutations per position, however, the E657fs indicator (black) is only meant to indicate position of this mutation. Note the clustering of TCGA truncating mutations around position 657. The Sanger sequencing validation trace of p.E657fs is also shown, demonstrating validation of p.E657fs as a heterozygous somatic mutation.
Copy number variants
A number of focal copy number gains were observed in this tumor, the most interesting being an amplification of the HOXA cluster (see Discussion section).28 Although a number of genes are known to be involved in tumorigenic processes are observed in these focal amplifications, no significance can be confidently assigned to these events.
Discussion
Our results show that mutations in DNMT3A and ASXL1 have a role in the development of thymoma. Our findings contrast starkly with a previous genome sequence from a B3 thymoma.15 However, the previously reported thymoma displayed cytogenetic abnormalities commonly observed in B3 thymomas, whereas this tumor displayed largely normal cytogenetics. These results are reminiscent of the preferential occurrence of driver point mutations in cytogenetically normal AML and suggests further sequencing of cytogenetically normal thymomas are fertile ground for the identification of the molecular drivers of thymic cancer.29 No obvious germline variant predisposing the patient to thymoma or renal cell cancer was observed, nor was there any overlap in somatic mutations between the thymoma and renal cell cancer to suggest shared etiology of these two tumors.
The first confidently identified driver mutation was a homozygous nonsynonymous mutation in DNMT3A. DNMT3A is a DNA methyltransferase essential for development, especially for de novo DNA methylation in stem cells.16 DNMT3A is mutated in numerous tumor types, but is mutated especially frequently in AML.20, 21 DNMT3A and its binding partner, DNMT3L form a tetramer: DNMT3L:DNMT3A:DNMT3A:DNMT3L.23 The most common DNMT3A mutations in AML occur at p.R882. Mutations at this position disrupt binding at the DNMT3A:DNMT3A interface, and impact activity in dominant-negative manner,23, 30 or at least reduce the odds of proper tetramer assembly by ∼75% as a single mutated DNMT3A protein is sufficient to disrupt tetramer assembly. Alternatively, the DNMT3L:DNMT3A interface is disrupted by somatic mutations within the mutational hotspot region centered on the p.G728D mutation observed in this thymoma.23 Heterozygous mutations at this site may not be expected to influence activity as markedly as mutations at p.R882 as they likely allow for the formation of partially complete complexes, for example, DNMT3A:DNMT3A:DNMT3L complexes could form 50% of the time. Thus, it is notable that the p.G728D mutation was observed in homozygous state in this tumor. Homozygous somatic mutations are highly unusual, suggesting DNA repair via double-stranded break repair or synthesis-dependent strand annealing and/or some other gene conversion event occurred specifically at this site given we did not find any evidence for loss of heterozygosity.
The second confidently identified driver mutation was a frameshift mutation in exon 12 of ASXL1. ASXL1 is a known tumor suppressor in hematological malignancies, where the majority of frameshift and nonsense mutations are also observed in exon 12.26, 27 ASXL1 loss leads to loss of H3K27me3 and increased expression of genes repressed by these histone marks, especially the anterior HOXA gene cluster.24 HOXA genes themselves are capable of leukemogenic transformation.31 Interestingly, we also observe a concomitant and specific amplification of the HOXA gene cluster in this tumor.
It is intriguing that both DNMT3A and ASXL1 are known tumor suppressors in hematological malignancies18 and that the observed mutation characteristics are consistent with those seen in AML. However, both genes have been observed mutated, albeit at lower frequencies, in epithelial malignancies as well. Although co-occurrence of DNMT3A and ASXL1 mutations are quite rare in epithelial and hematological malignancies, sequencing of a larger number of thymomas will be required to determine whether this co-occurrence is a happenstance of our subject selection or whether it points to a specific requirement of marked epigenetic reprogramming in the neoplastic transformation of thymic cells. The extent of DNMT3A and ASXL1 mutations in thymoma should be explored, and treatments targeting epigenetic reprogramming should be considered in the future.
Materials and methods
Study consent
The study participant provided written informed consent under a protocol approved by the institutional review board of Scripps.
Tumor and normal sample
The formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded block containing the thymoma tumor was sectioned 11 times, with each section placed on a separate slide. One section, at 4-μm thick, was stained and used to assess tumor area and cellularity. The boundaries of the tumor were marked, and the tumor cellularity was estimated to be >85%. The additional 10 sections were cut at 10-μm thicknesses, and the designated (the boundaries were traced onto each slide using the stained and marked slide) tumor areas were extracted and isolated using the RecoverAll FFPE nucleic acid isolation kit (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). Freshly drawn blood was obtained for the analysis of normal DNA. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood using the QIAamp system (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). Sequence alignment and variant calling were performed against the reference human genome (NCBI 37/hg 19).
Whole-exome sequencing, variant calling and filtration
Whole-exome sequencing was pursued utilizing Agilent SureSelect exome hybridization followed by barcoding and sequencing of paired 100-bp reads on the equivalent of ∼1 lane of an Illumina HiSeq2500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) instrument (samples were barcoded and distributed across multiple lanes). Read mapping and initial variant calling and quality filtration was performed using the standard BWA-GATK32, 33 best practices variant quality score recalibration approach. A mean coverage of 157.3X and 98.7X was achieved for the tumor and normal sample with 96.1% and 98.7% of the target exome covered by >10 reads, respectively.
Somatic point mutations were detected using MUTECT.13 Somatic indels were detected using SomaticIndelDetector.32 Somatic variants were then annotated using the SG-ADVISER (genomics.scripps.edu/ADVISER/) and Cypher Genomics, Inc. (San Diego, CA, USA) systems for further filtration. Somatic variants present at >0.1% frequency in the HapMap,14 1000 Genomes,34 NHLBI GO Exome Sequencing Project,35 or 385 genomes from the Scripps Wellderly population, as well as variants present in segmental duplication regions that are prone to produce false-positive variant calls were removed. Somatic indels were stringently filtered to remove indels within simple repeats, repeats identical to the inserted/deleted sequence or adjacent to homopolymer repeats of length 5+. Nonsynonymous, in-frame, frameshift, nonsense or canonical splice-site donor/acceptor site variants were retained for further analysis.
Low-pass whole-genome sequencing, structural variant calling and filtration
Low-pass whole-genome sequencing was performed by barcoding and sequencing of paired 100-bp reads on the equivalent of ∼1 lane of an Illumina HiSeq2500. A mean coverage of 7.4X and 7.7X was achieved for the tumor and normal sample with 92.0% and 95.5% of the genome covered by >3 reads, respectively. Copy number and structural variants were identified by SVDetect.36 For copy number variants, read density was determined for 100-kb windows at 10-kb intervals. The significance of read density differences between the tumor and normal sample were determined using a binomial test with the normal sample determining the probability of read mapping per window in order to adjust for mapability and other window-specific effects. Significant windows (P-value threshold=1E–8) were stringently filtered to retain called copy number variations only where the ratio of tumor to normal reads, adjusted for the difference in total number of reads, was at least 1.5X greater for copy number gains or 0.5X lower for copy number losses. For structural variants, an initial set of raw candidate structural variants was called using SVDetect with at least seven reads supporting structural variant calls in the tumor sample and three reads supporting calls in the normal sample. Tumor sample candidate structural variants were then filtered to remove structural variants with support in the normal sample or mapping to centromeric regions.
Circos plots were generated via RCircos.37 Mutation plots were generated via adaption of cBioPortal visualization plots.38
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Scripps Genomic Medicine, an NIH-NCATS Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA; 5 UL1 RR025774) to STSI. Further support is from NIH-U01 HG006476 (AT).
Dr Belani declares an ownership interest in the Medical Oncology Associates of San Diego, intellectual property ownership with Atyr Pharma and is an adviser for Dendreon and Bayer. Dr Torkamani declares he is a co-founder and equity owner of Cypher Genomics, Inc. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thomas CR, Wright CD, Loehrer PJ. Thymoma: state of the art. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2280–2289. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.7.2280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosai J, Sobin LH. Histological Typing of Tumours of the Thymus. Springer, Berlin; New York; 1999. p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Masaoka A, Monden Y, Nakahara K, Tanioka T. Follow-up study of thymomas with special reference to their clinical stages. Cancer. 1981;48:2485–2492. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811201)48:11<2485::aid-cncr2820481123>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi K, Matsuguma H, Nakahara R, Kondo T, Kamiyama Y, Mori K, et al. Multidisciplinary treatment for advanced invasive thymoma with cisplatin, doxorubicin, and methylprednisolone. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:73–78. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31802bafc8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loehrer PJ, Sr., Kim K, Aisner SC, Livingston R, Einhorn LH, Johnson D, et al. Cisplatin plus doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide in metastatic or recurrent thymoma: final results of an intergroup trial. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Southwest Oncology Group, and Southeastern Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1994;12:1164–1168. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.6.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornasiero A, Daniele O, Ghiotto C, Piazza M, Fiore-Donati L, Calabro F, et al. Chemotherapy for invasive thymoma. A 13-year experience. Cancer. 1991;68:30–33. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910701)68:1<30::aid-cncr2820680106>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly RJ, Petrini I, Rajan A, Wang Y, Giaccone G. Thymic malignancies: from clinical management to targeted therapies. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4820–4827. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.0487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K, Hirata T, Fukuse T, Yokomise H, Inui K, Ike O, et al. Surgical treatment for invasive thymoma, especially when the superior vena cava is invaded. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996;61:521–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(95)00983-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaogi E, Ohara K, Mitsui K, Onizuka M, Ishikawa S, Mitsui T, et al. Preoperative radiotherapy and surgery for advanced thymoma with invasion to the great vessels. J Surg Oncol. 1996;63:17–22. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9098(199609)63:1<17::AID-JSO4>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoh K, Nishiwaki Y, Ishii G, Goto K, Kubota K, Ohmatsu H, et al. Mutational status of EGFR and KIT in thymoma and thymic carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2008;62:316–320. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajan A, Giaccone G. Targeted therapy for advanced thymic tumors. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5 (10 Suppl 4:S361–S364. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181f21114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly RJ. Thymoma versus thymic carcinoma: differences in biology impacting treatment. J Natl Compr Cancer Network. 2013;11:577–583. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2013.0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettl A, Strobel P, Wagner K, Katzenberger T, Ott G, Rosenwald A, et al. Recurrent genetic aberrations in thymoma and thymic carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2000;157:257–266. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64536-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M, Marx A, Zettl A, Strobel P, Muller-Hermelink HK, Starostik P. Chromosome 6 suffers frequent and multiple aberrations in thymoma. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:1507–1513. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64426-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini I, Rajan A, Pham T, Voeller D, Davis S, Gao J, et al. Whole genome and transcriptome sequencing of a B3 thymoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e60572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E. DN A methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell. 1999;99:247–257. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandoth C, McLellan MD, Vandin F, Ye K, Niu B, Lu C, et al. Mutational landscape and significance across 12 major cancer types. Nature. 2013;502:333–339. doi: 10.1038/nature12634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futreal PA, Coin L, Marshall M, Down T, Hubbard T, Wooster R, et al. A census of human cancer genes. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:177–183. doi: 10.1038/nrc1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia D, Jurkowska RZ, Zhang X, Jeltsch A, Cheng X. Structure of Dnmt3a bound to Dnmt3L suggests a model for de novo DNA methylation. Nature. 2007;449:248–251. doi: 10.1038/nature06146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research N Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. New Engl J Med. 2013;368:2059–2074. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley TJ, Ding L, Walter MJ, McLellan MD, Lamprecht T, Larson DE, et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. New Engl J Med. 2010;363:2424–2433. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1005143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou HA, Kuo YY, Liu CY, Chou WC, Lee MC, Chen CY, et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: stability during disease evolution and clinical implications. Blood. 2012;119:559–568. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-369934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz-Schietinger C, Matje DM, Reich NO. Mutations in DNA methyltransferase (DNMT3A) observed in acute myeloid leukemia patients disrupt processive methylation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:30941–30951. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.366625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Wahab O, Adli M, LaFave LM, Gao J, Hricik T, Shih AH, et al. ASXL1 mutations promote myeloid transformation through loss of PRC2-mediated gene repression. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:180–193. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.06.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue D, Kitaura J, Togami K, Nishimura K, Enomoto Y, Uchida T, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes are induced by histone methylation-altering ASXL1 mutations. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:4627–4640. doi: 10.1172/JCI70739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou WC, Huang HH, Hou HA, Chen CY, Tang JL, Yao M, et al. Distinct clinical and biological features of de novo acute myeloid leukemia with additional sex comb-like 1 (ASXL1) mutations. Blood. 2010;116:4086–4094. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-283291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittger S, Eder C, Jeromin S, Alpermann T, Fasan A, Grossmann V, et al. ASXL1 exon 12 mutations are frequent in AML with intermediate risk karyotype and are independently associated with an adverse outcome. Leukemia. 2013;27:82–91. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W. Modulating Hox gene functions during animal body patterning. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:893–904. doi: 10.1038/nrg1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrozek K, Marcucci G, Paschka P, Whitman SP, Bloomfield CD. Clinical relevance of mutations and gene-expression changes in adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics: are we ready for a prognostically prioritized molecular classification. Blood. 2007;109:431–448. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-001149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim SJ, Zhao H, Hardikar S, Singh AK, Goodell MA, Chen T. A DNMT3A mutation common in AML exhibits dominant-negative effects in murine ES cells. Blood. 2013;122:4086–4089. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-483487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach C, Buhl S, Mueller D, Garcia-Cuellar MP, Maethner E, Slany RK. Leukemogenic transformation by HOXA cluster genes. Blood. 2010;115:2910–2918. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-216606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet. 2011;43:491–498. doi: 10.1038/ng.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 2012;491:56–65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennessen JA, Bigham AW, O'Connor TD, Fu W, Kenny EE, Gravel S, et al. Evolution and functional impact of rare coding variation from deep sequencing of human exomes. Science. 2012;337:64–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1219240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitouni B, Boeva V, Janoueix-Lerosey I, Loeillet S, Legoix-ne P, Nicolas A, et al. SVDetect: a tool to identify genomic structural variations from paired-end and mate-pair sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:1895–1896. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H, Meltzer P, Davis S. RCircos: an R package for Circos 2D track plots. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:244. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013;6:pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]