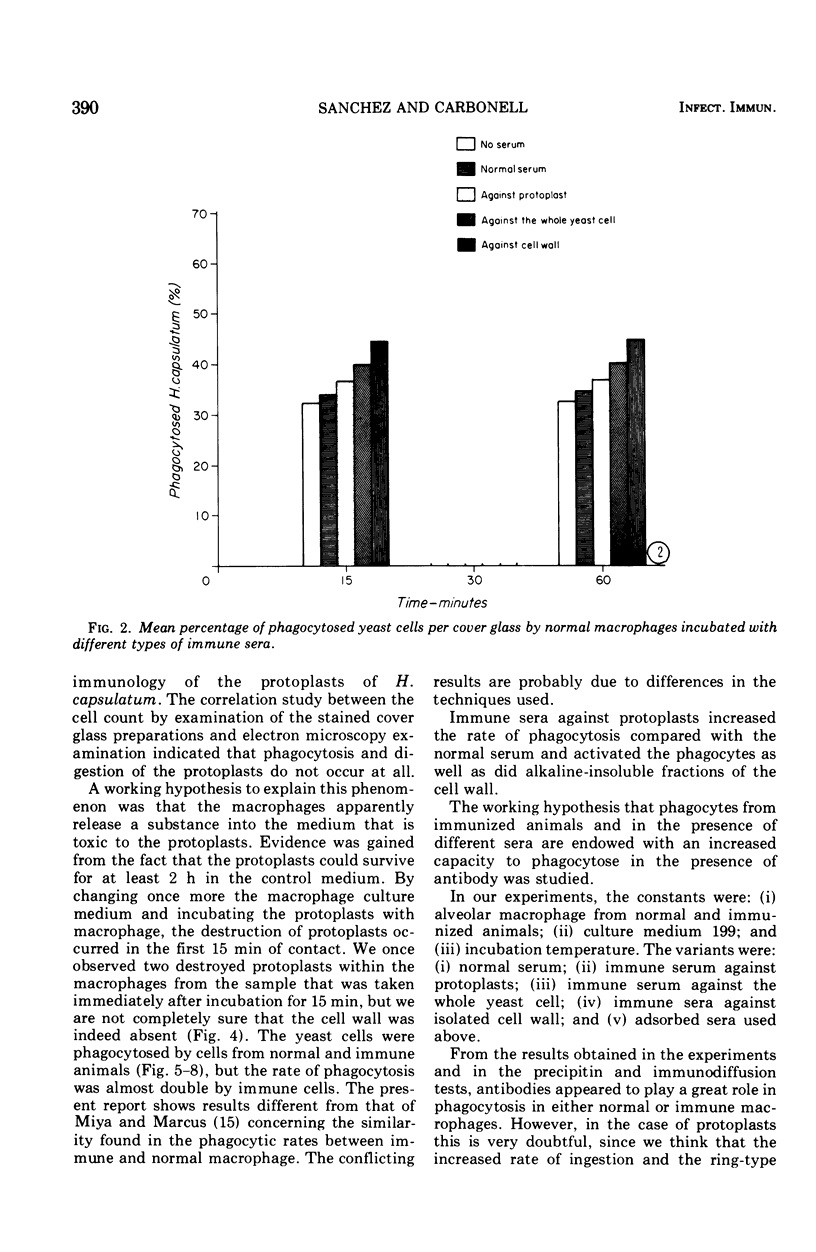
Abstract
Alveolar macrophages freshly harvested from normal and immunized rabbits were parasitized with yeast cells and protoplasts of Histoplasma capsulatum. Macrophages obtained from either normal or sensitized rabbits failed to phagocytize protoplasts, whereas, the yeast cells were actively ingested. There was no detectable intracellular killing by macrophages. A serological similarity was found between the whole yeast cell, the purified isolated cell wall, and the protoplasts of the fungus. Aprecipitin test of the protoplasts of the fungus gave a postive band, whereas immunodiffusion in agar was negative. Addition of immune sera activated phagocytosis, the immune sera against cell walls being the most active.
Full text
PDF

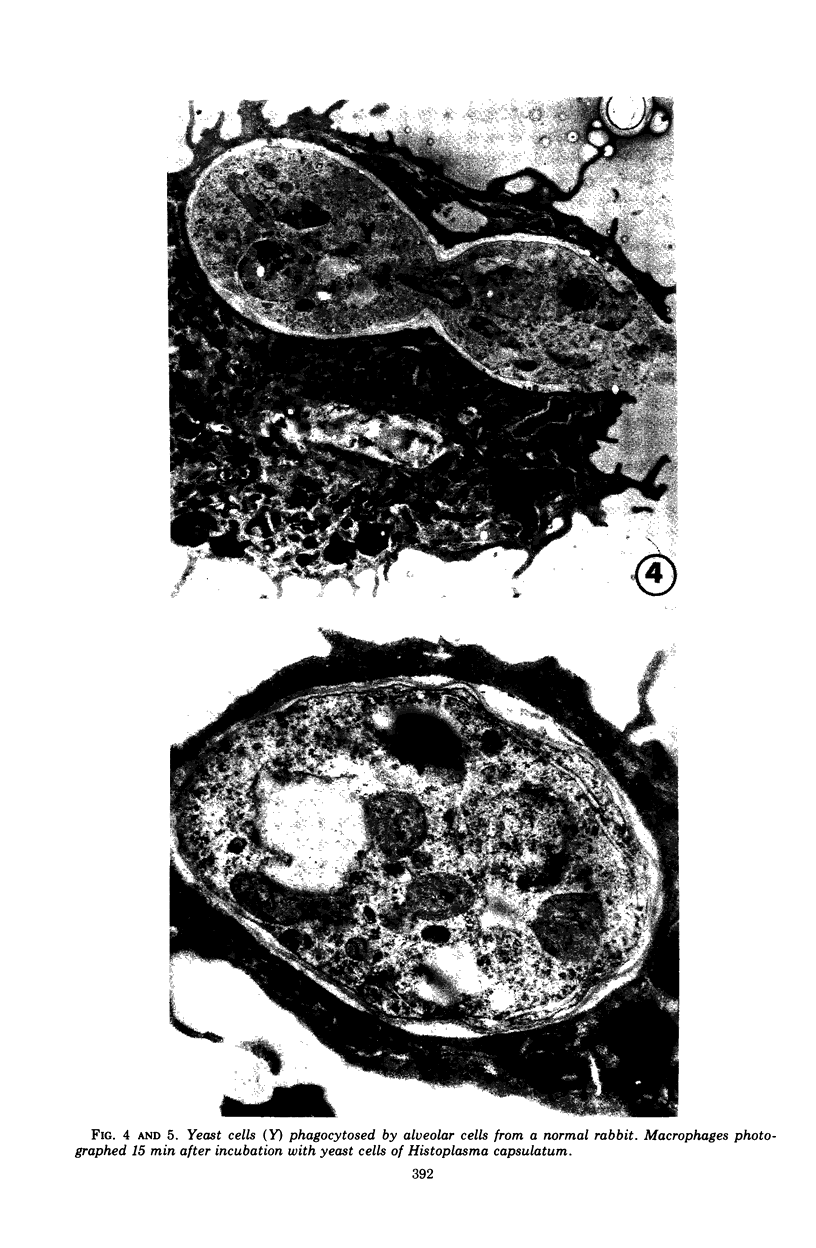
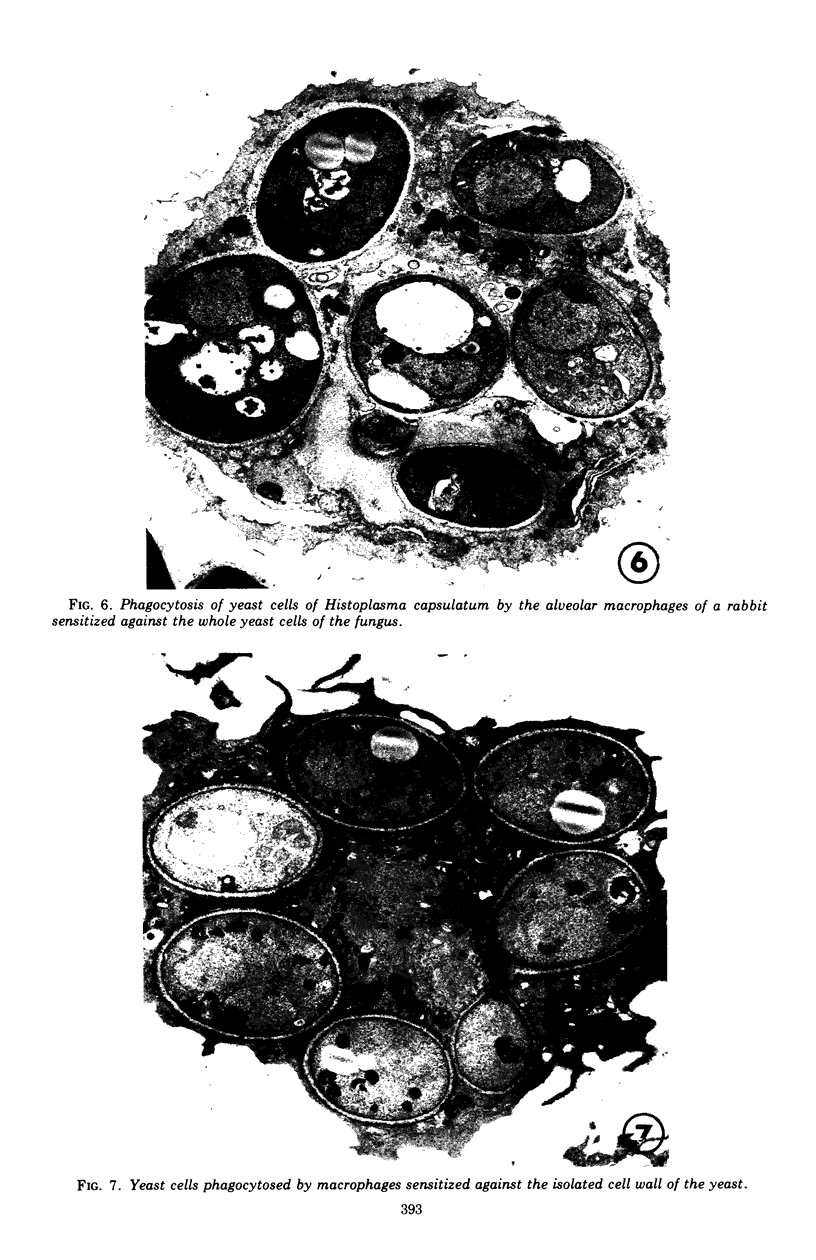
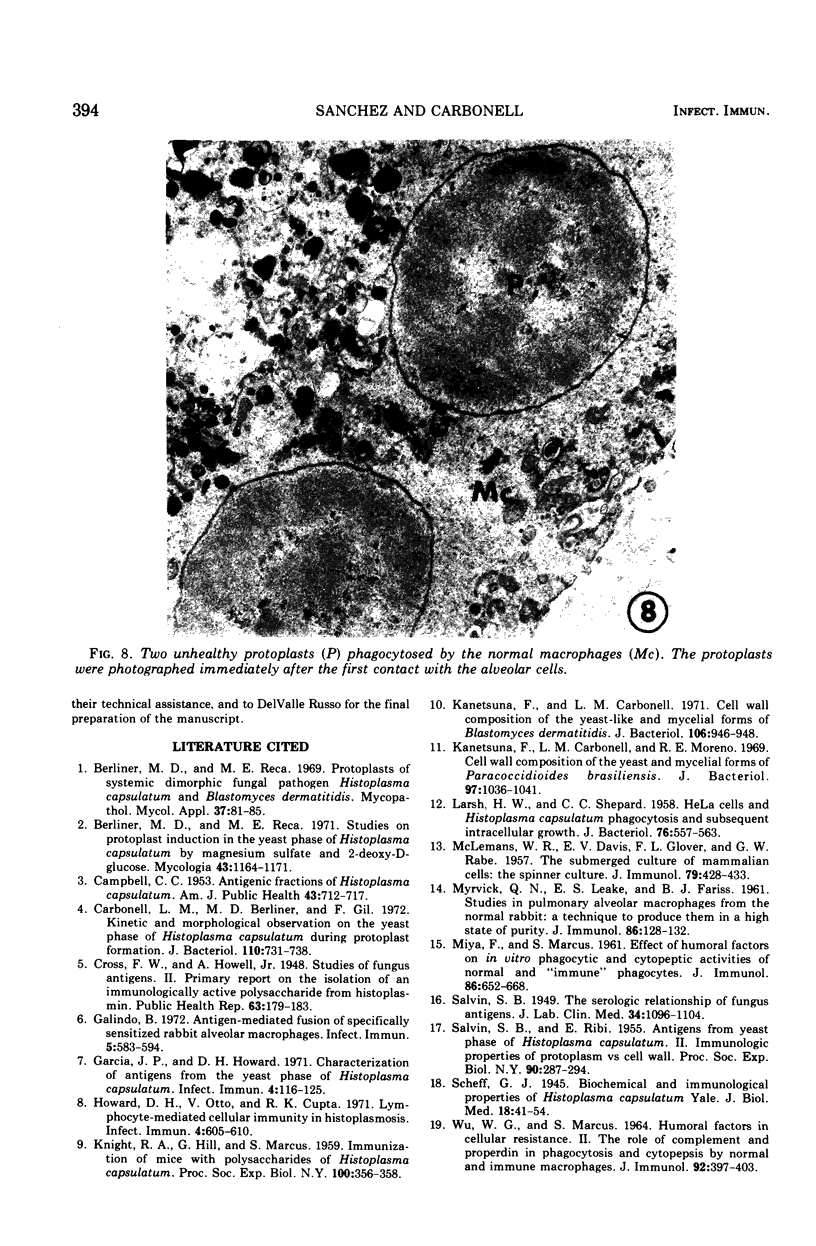
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berliner M. D., Reca M. E. Protoplasts of systemic dimorphic fungal pathogens: Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1969 Jan 29;37(1):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF02051335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner M. D., Reca M. E. Studies on protoplast induction in the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum by magnesium sulfate and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. Mycologia. 1971 Nov-Dec;63(6):1164–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL C. C. Antigenic fractions of Histoplasma capsulatum. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1953 Jun;43(6 Pt 1):712–717. doi: 10.2105/ajph.43.6_pt_1.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonell L. M., Berliner M. D., Gil F. Kinetic and morphological observations on the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum during protoplast formation. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):731–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.731-738.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo B. Antigen-mediated fusion of specifically sensitized rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):583–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.583-594.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. P., Howard D. H. Characterization of antigens from the yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1971 Aug;4(2):116–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.2.116-125.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard D. H., Otto V., Gupta R. K. Lymphocyte-mediated cellular immunity in histoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):605–610. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.605-610.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT R. A., HILL G., MARCUS S. Immunization of mice with polysaccharides of Histoplasma capsulatum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Feb;100(2):356–358. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanetsuna F., Carbonell L. M. Cell wall composition of the yeastlike and mycelial forms of Blastomyces dermatitidis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):946–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.946-948.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanetsuna F., Carbonell L. M., Moreno R. E., Rodriguez J. Cell wall composition of the yeast and mycelial forms of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1036–1041. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1036-1041.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSH H. W., SHEPARD C. C. HeLa cells and Histoplasma capsulatum; phagocytosis and subsequent intracellular growth. J Bacteriol. 1958 Nov;76(5):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.5.557-563.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYA F., MARCUS S. Effect of humoral factors in vitro phagocytic and cytopeptic activities of normal and "immune" phagocytes. J Immunol. 1961 Jun;86:652–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYRVIK Q., LEAKE E. S., FARISS B. Studies on pulmonary alveolar macrophages from the normal rabbit: a technique to procure them in a high state of purity. J Immunol. 1961 Feb;86:128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLIMANS W. F., DAVIS E. V., GLOVER F. L., RAKE G. W. The submerged culture of mammalian cells; the spinner culture. J Immunol. 1957 Nov;79(5):428–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALVIN S. B., RIBI E. Antigens from yeast phase of Histoplasma capsulatum. II. Immunologic properties of protoplasm vs. cell walls. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):287–294. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU W. G., MARCUS S. HUMORAL FACTORS IN CELLULAR RESISTANCE. II. THE ROLE OF COMPLEMENT AND PROPERDIN IN PHAGOCYTOSIS AND CYTOPEPSIS BY NORMAL AND "IMMUNE" MACROPHAGES. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:397–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]