Abstract
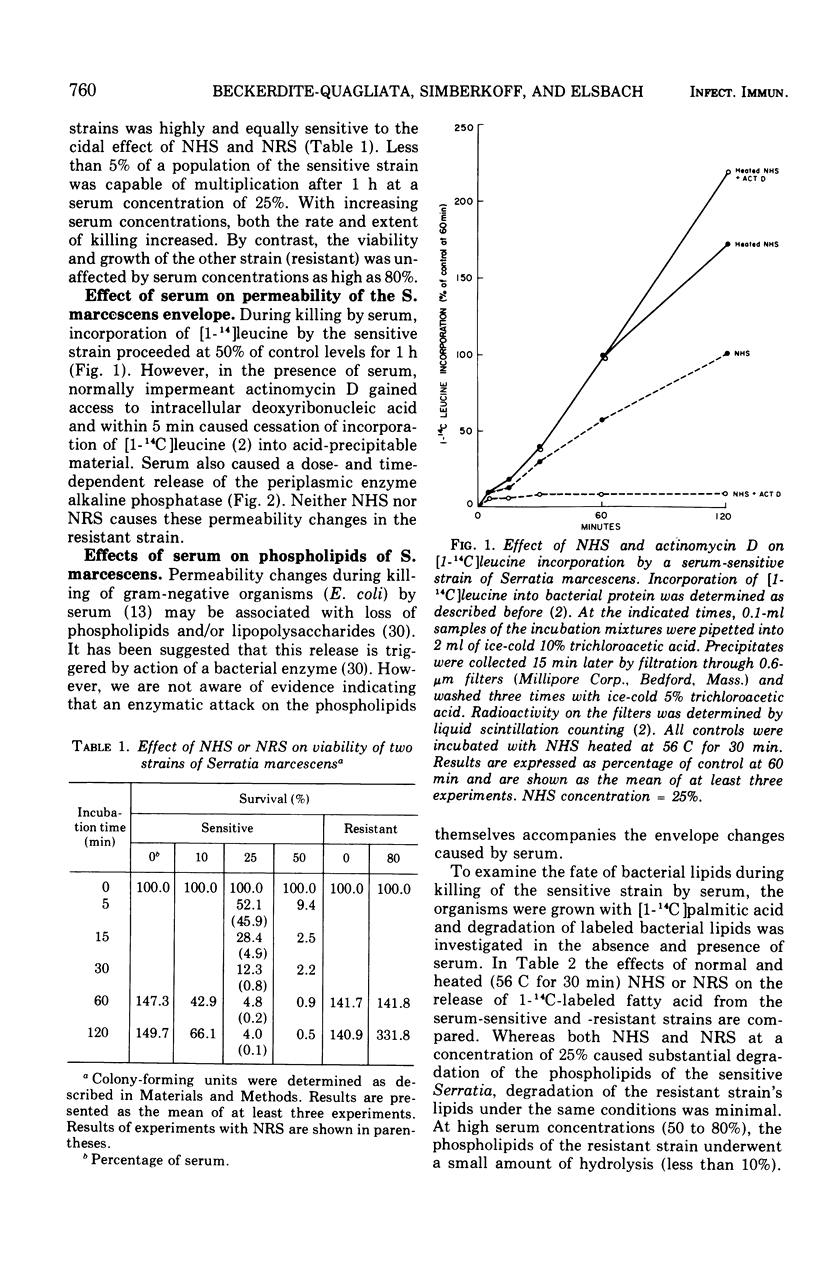
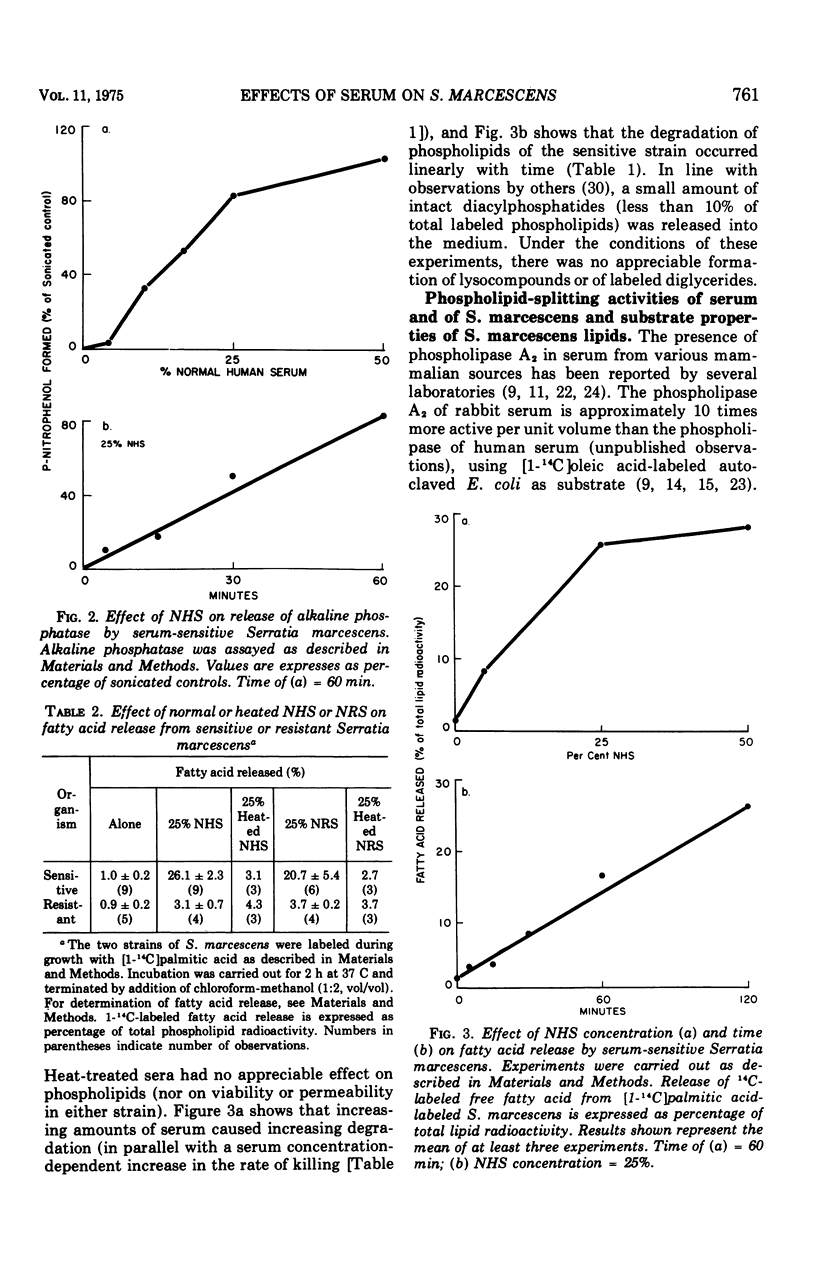
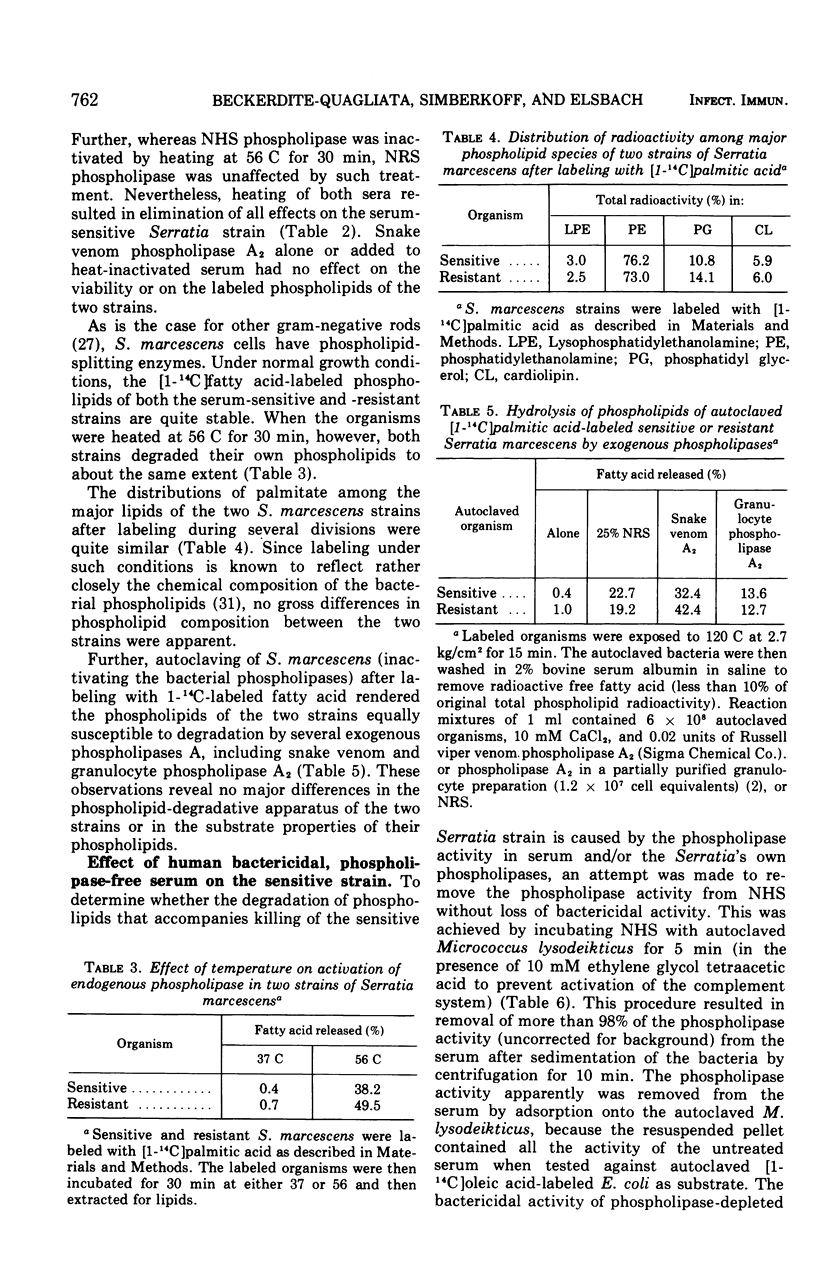
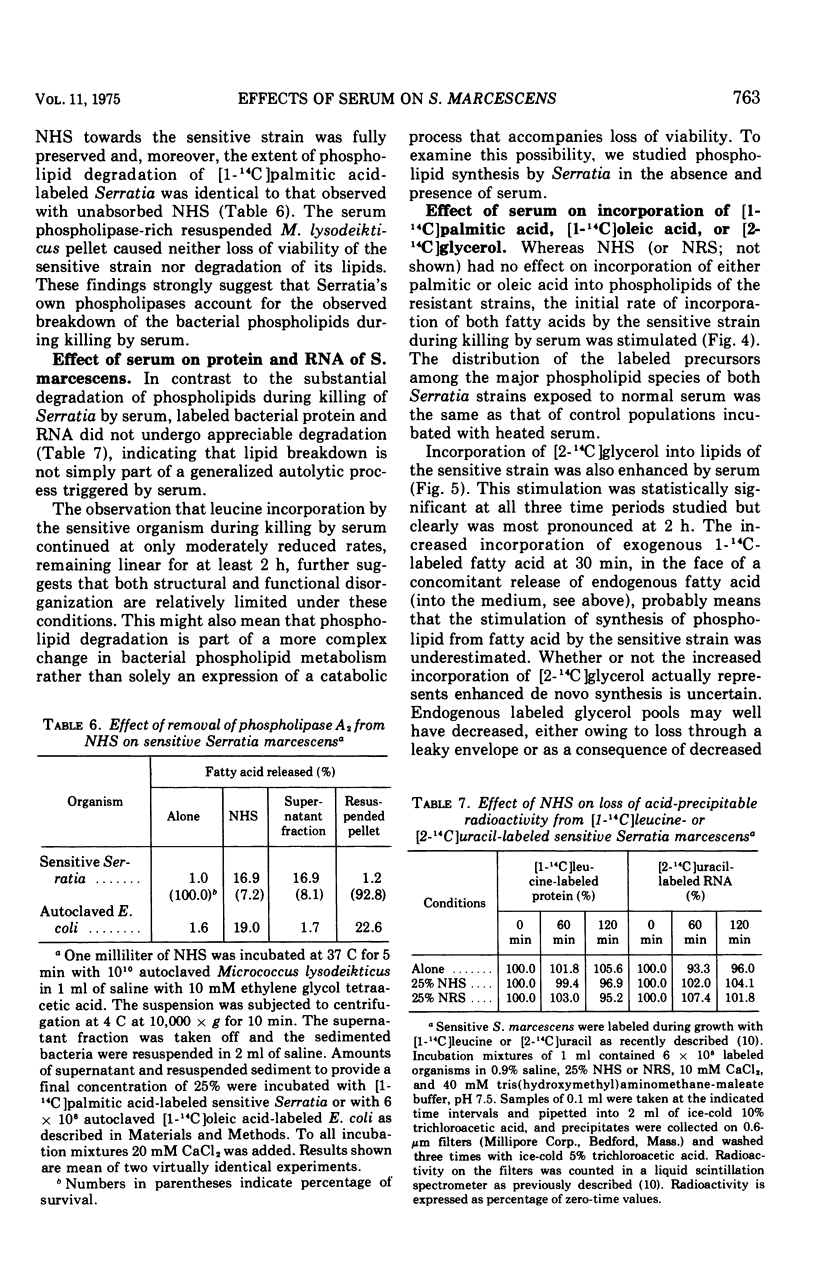
The major action of serum on gram-negative organisms is thought to be on the microbial envelope. We compared the effects of normal human and rabbit serum on the envelope lipids of two strains of Serratia marcescens, one sensitive and one resistant to the bactericidal effects of serum. During killing by either serum, the sensitive strain underwent rapid permeability changes coincident with degradation of microbial phospholipids. The resistant strain exhibited none of these effects. The phospholipid degradation that accompanies killing of the sensitive strain by serum could be caused by phospholipases present in serum or by Serratia's own phospholipid-splitting enzymes. The results indicate that phospholipid breakdown is caused by activation of bacterial of bacterial phospholipases and not by serum phospholipases. This conclusion is based upon the following findings.(i1 Although rabbit serum phospholipase A was at least 10 times more active than human serum phospholipase A, phospholipid degradation in the sensitive Serratia strain was comparable during (equally rapid) killing by human or rabbit serum. (ii) Heat treatment (56 C) of both sera eliminated bactericidal activity as well as microbial lipid degradation but abolished phospholipase activity of human serum only. (iii) Virtually complete removal of phospholipase A activity from human serum by adsorption onto autoclaved Micrococcus lysodeikticus had no effect on the extent of phospholipid hydrolysis or on bactericidal activity. Activation by serum of endogenous phospholipase activity in S. marcescens was accompanied by enhanced incorporation of lipid precursors into bacterial lipids. No evidence was found for increased turnover of protein or ribonucleic acid during killing by serum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader J., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. 1. Binding to the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Jul-Aug;28(7):422–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckerdite S., Mooney C., Weiss J., Franson R., Elsbach P. Early and discrete changes in permeability of Escherichia coli and certain other gram-negative bacteria during killing by granulocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):396–409. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Mavis R. D., Osborn M. J., Vagelos P. R. Enzymes of phospholipid metabolism: localization in the cytoplasmic and outer membrane of the cell envelope of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):628–635. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. M., Roberts R. R., Larsen H. S., Tew J. G. Interrelationship between serum beta-lysin, lysozyme, and the antibody-complement system in killing Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):657–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.657-666.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Beckerdite S., Pettis P., Franson R. Persistence of regulation of macromolecular synthesis by Escherichia coli during killing by disrupted rabbit granulocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):663–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.663-668.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Levy S. Increased synthesis of phospholipid during phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2217–2229. doi: 10.1172/JCI105907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P. On the interaction between phagocytes and micro-organisms. N Engl J Med. 1973 Oct 18;289(16):846–852. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197310182891610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Pettis P., Beckerdite S., Franson R. Effects of phagocytosis by rabbit granulocytes on macromolecular synthesis and degradation in different species of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):490–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.490-497.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Pettis P. Phospholipase activity associated with serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):89–93. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Paysant M., Grüber A., Polonovski J. Présence d'un pécurseur de phospholipase dans le sérum humain normal. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1969 Sep 18;51(4):709–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the action of serum and the role of lysozyme in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2118–2126. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2118-2126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Goldman J. N., Kuritz H. M. Locus of the lethal event in the serum bactericidal reaction. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2127-2131.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R., Beckerdite S., Wang P., Waite M., Elsbach P. Some properties of phospholipases of alveolar macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 14;296(2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson R., Patriarca P., Elsbach P. Phospholipid metabolism by phagocytic cells. Phospholipases A2 associated with rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jul;15(4):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melching L., Vas S. I. Effects of serum components on gram-negative bacteria during bactericidal reactions. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.107-115.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel L. H., Ahl L. A., Fisher M. W. Sensitivity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to normal serum and to polymyxin. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):453–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.453-457.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond D. H., Ross L. J., Holub B. J. Activity and positional specificity of a rat plasma phospholipase on phosphatidylethanolamine. Can J Biochem. 1973 Jun;51(6):855–862. doi: 10.1139/o73-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca P., Beckerdite S., Elsbach P. Phospholipases and phospholipid turnover in Escherichia coli spheroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 18;260(4):593–600. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paysant M., Bitran M., Etienne J., Polonovski J. Phospholipase A du plasma sanguin de rat. Cinétique et propriétés. Existence d'un précurseur inactif. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1969 Oct;51(5):863–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sud I. J., Feingold D. S. Mechanism of polymyxin B resistance in Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):289–294. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.289-294.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J., Franson R. C., Beckerdite S., Schmeidler K., Elsbach P. Partial characterization and purification of a rabbit granulocyte factor that increases permeability of Escherichia coli. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):33–42. doi: 10.1172/JCI107915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. A., Albright F. R., Lennarz W. J., Schnaitman C. A. Distribution of phospholipid-synthesizing enzymes in the wall and membrane subfractions of the envelope of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 3;249(2):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. A., Spitznagel J. K. Characteristics of complement-dependent release of phospholipid from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1971 Jul;4(1):23–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.1.23-28.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster N., Elsbach P., Rand J., Simon E. J. Effects of levorphanol on phospholipid metabolism and composition in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):282–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Phosphoglyceride metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):243–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


