Abstract
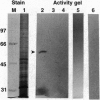
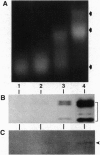
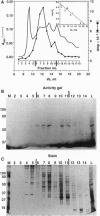
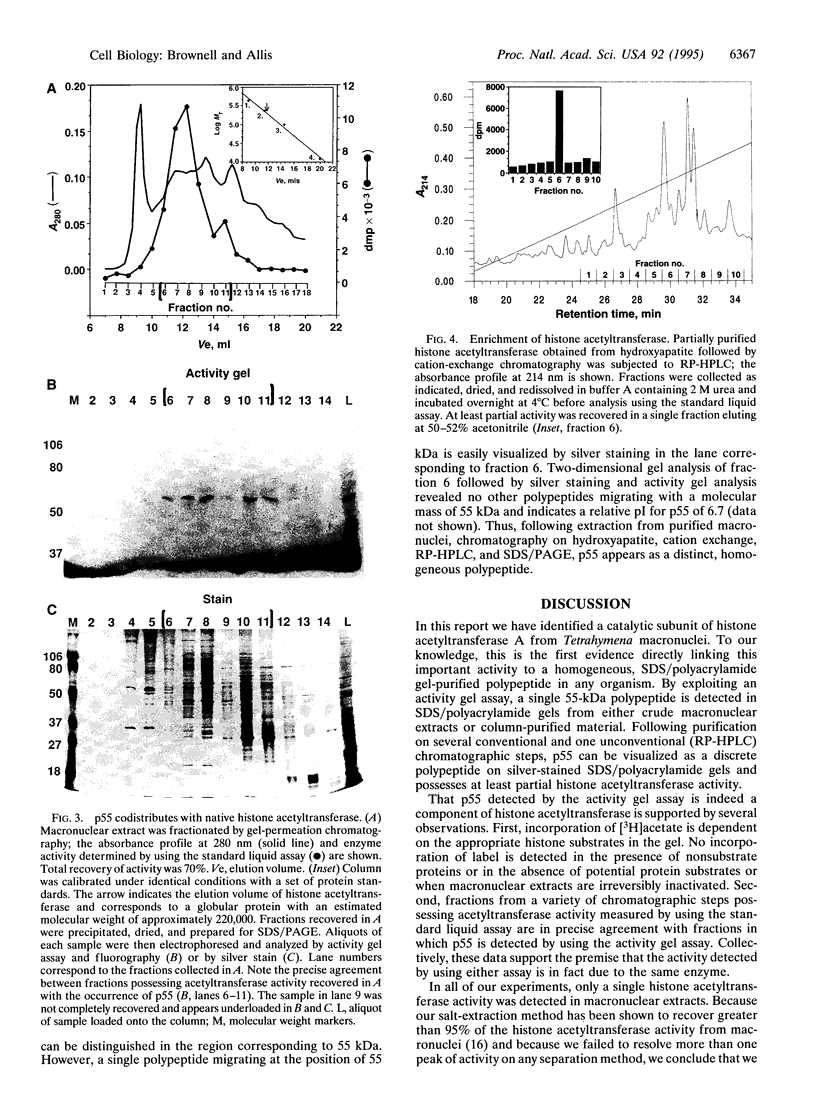
Macronuclei of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila possess a histone acetyltransferase activity closely associated with transcription-related histone acetylation. Nothing definitive is known concerning the polypeptide composition of this activity in Tetrahymena or any comparable activity from any cellular source. An acetyltransferase activity gel assay was developed which identifies a catalytically active subunit of this enzyme in Tetrahymena. This activity gel assay detects a single polypeptide of 55 kDa (p55) in crude macronuclear extracts, as well as in column-purified fractions, which incorporates [3H]acetate from [3H]acetyl-CoA into core histone substrates polymerized directly into SDS polyacrylamide gels. p55 copurifies precisely with acetyltransferase activity through all chromatographic steps examined, including reverse-phase HPLC. Gel-filtration chromatography of this activity indicates a molecular mass of 220 kDa, suggesting that the native enzyme may consist of four identical subunits of 55 kDa. Furthermore, p55 is tightly associated with di- and greater polynucleosomes and therefore may be defined as a component of histone acetyltransferase type A--i.e., chromatin associated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegra P., Sterner R., Clayton D. F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatographic purification of nucleosomes containing transcriptionally active DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attisano L., Lewis P. N. Purification and characterization of two porcine liver nuclear histone acetyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3949–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belikoff E., Wong L. J., Alberts B. M. Extensive purification of histone acetylase A, the major histone N-acetyl transferase activity detected in mammalian cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11448–11453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicoine L. G., Richman R., Cook R. G., Gorovsky M. A., Allis C. D. A single histone acetyltransferase from Tetrahymena macronuclei catalyzes deposition-related acetylation of free histones and transcription-related acetylation of nucleosomal histones. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):127–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicoine L. G., Schulman I. G., Richman R., Cook R. G., Allis C. D. Nonrandom utilization of acetylation sites in histones isolated from Tetrahymena. Evidence for functionally distinct H4 acetylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1071–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Glover C., Johmann C. A., Keevert J. B., Mathis D. J., Samuelson M. Histones and chromatin structure in Tetrahymena macro- and micronuclei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):493–503. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendzel M. J., Sun J. M., Chen H. Y., Rattner J. B., Davie J. R. Histone acetyltransferase is associated with the nuclear matrix. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22894–22901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Fujimoto D. Use of phosph-cellulose paper disks for the assay of histone acetyltransferase. Anal Biochem. 1975 Dec;69(2):491–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Fujisawa H. A sensitive method for detection of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 15;183(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loidl P. Histone acetylation: facts and questions. Chromosoma. 1994 Dec;103(7):441–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00337382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. E., Cook R. G., Allis C. D. Non-random acetylation of histone H4 by a cytoplasmic histone acetyltransferase as determined by novel methodology. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18576–18582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Extensive purification and characterization of chromatin-bound histone acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14406–14412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M., Fellows G. Specific antibodies reveal ordered and cell-cycle-related use of histone-H4 acetylation sites in mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra K. J., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Regulation of histone acetylation in Tetrahymena macro- and micronuclei. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2591–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktorowicz J. E., Bonner J. Studies on histone acetyltransferase. Partial purification and basic properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12893–12900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]