Abstract
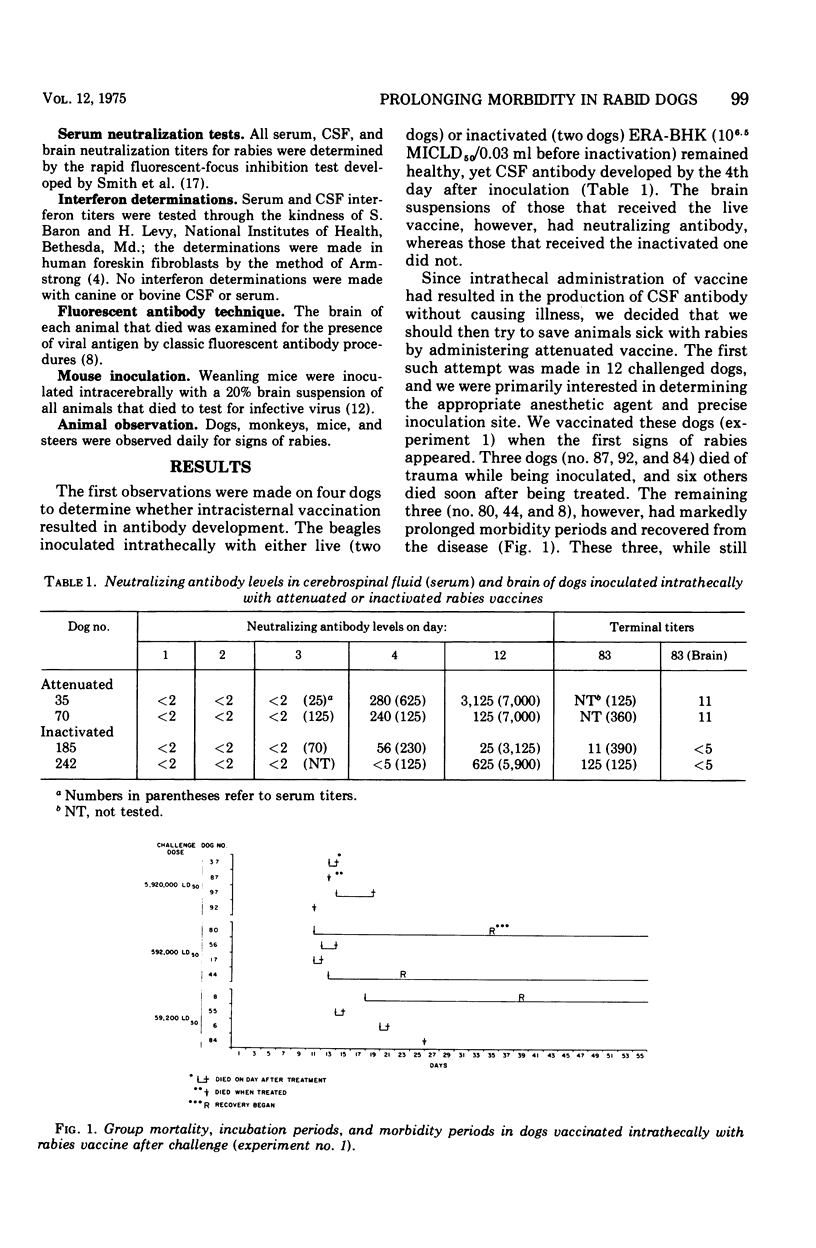
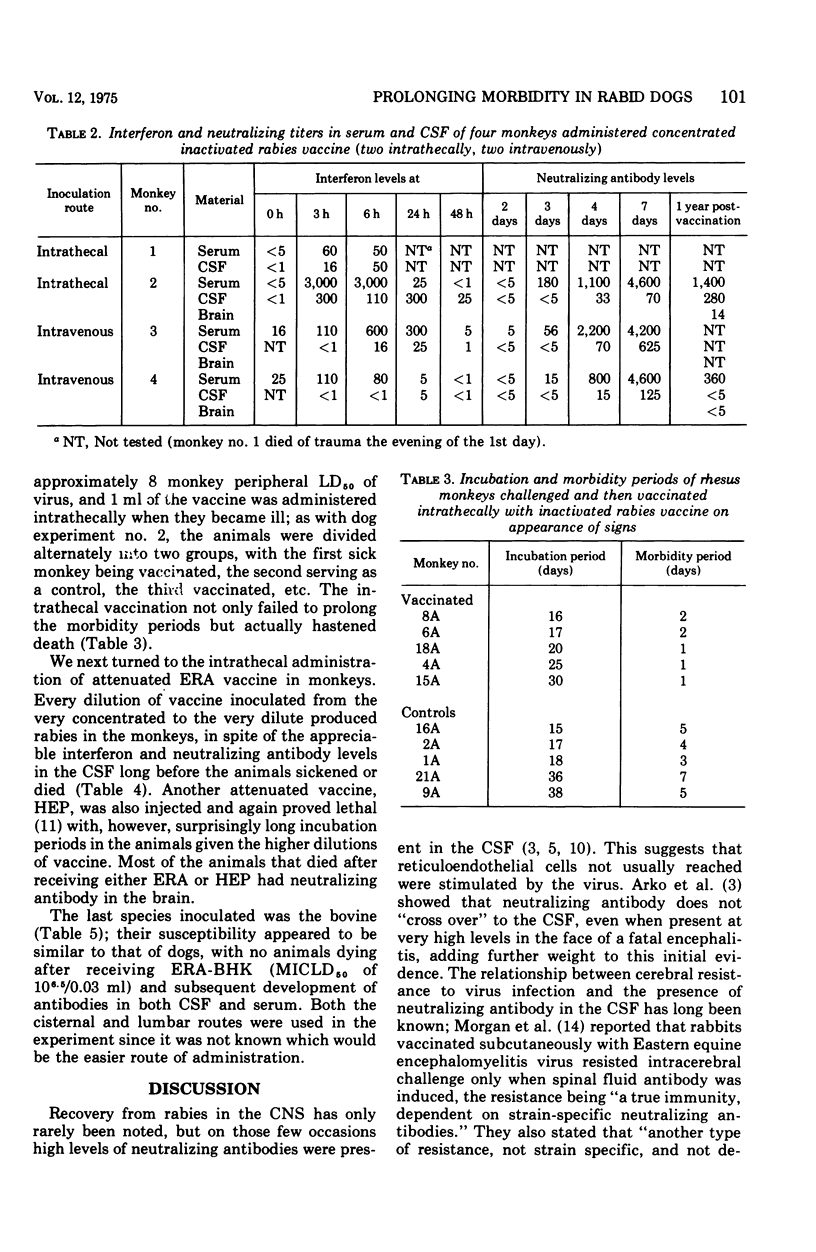
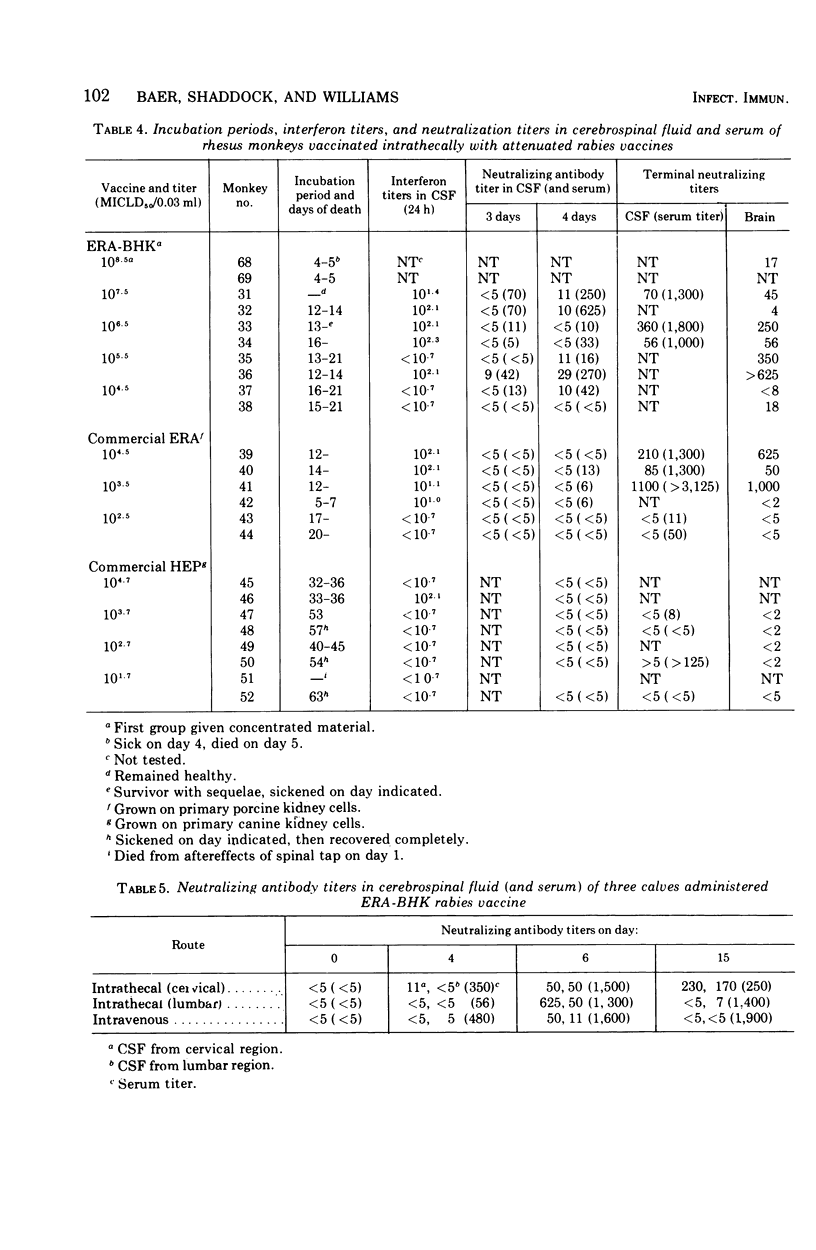
Dogs vaccinated intrathecally with attenuated rabies vaccine developed antibodies that were detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, blood, and brain; dogs similarly vaccinated but with an inactivated vaccine developed no antibodies in the brain. When the attenuated vaccine was administered to rabid dogs, a prolongation of the morbidity period was noted and, in some dogs, recovery from the disease. Rhesus monkeys died when administered any of the available attenuated vaccines intrathecally, and further studies with that species could not be undertaken.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelseth M. K. An Attenuated Rabies Vaccine for Domestic Animals Produced in Tissue Culture. Can Vet J. 1964 Nov;5(11):279–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acha P. N. Epidemiology of paralytic bovine rabies and bat rabies. Bull Off Int Epizoot. 1967 Mar-Apr;67(3):343–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J., Schneider L. G., Baer G. M. Nonfatal canine rabies. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Jul;34(7):937–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. F., Sancho M. I., Diaz A. M., Moore G. J. Nonfatal rabies in an enzootic area: results of a survey and evaluation of techniques. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Feb;95(2):190–198. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons R. W., Leonard L. L., DeGenaro F., Jr, Protas E. S., Bazeley P. L., Giammona S. T., Sturckow K. A case of human rabies with prolonged survival. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):60–72. doi: 10.1159/000148833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDWASSER R. A., KISSLING R. E. Fluorescent antibody staining of street and fixed rabies virus antigens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jun;98(2):219–223. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-23996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough P. M., Dierks R. E., Russell R. M., Archer B. G. Characterization of brain-associated rabies neutralizing substance. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):456–460. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattwick M. A., Weis T. T., Stechschulte C. J., Baer G. M., Gregg M. B. Recovery from rabies. A case report. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Jun;76(6):931–942. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-6-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H. Biological modification of rabies virus as a result of its adaptation to chicks and developing chick embryos. Bull World Health Organ. 1954;10(5):709–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H. Laboratory techniques in rabies: the mouse inoculation test. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Ogra S. S., al-Nakeeb S., Coppola P. R. Local antibody response to experimental poliovirus infection in the central nervous system of rhesus monkeys. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):931–937. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.931-937.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. Aluminium phosphate method for rabies virus purification. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):179–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid reproducible test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 May;48(5):535–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. B., Blenden D. C., Fuh T. H., Hiler L. Diagnosis of rabies by immunofluorescent staining of frozen sections of skin. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Dec 1;161(11):1495–1501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


