Abstract
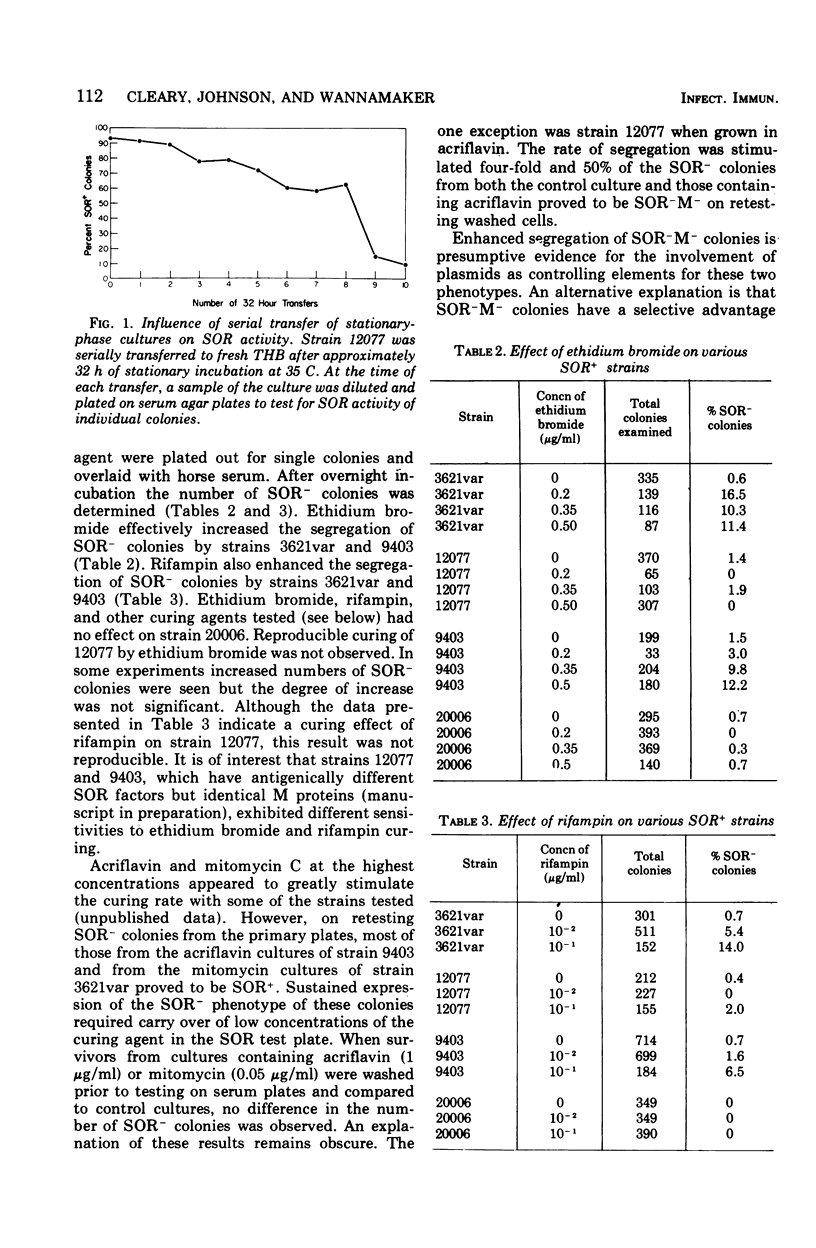
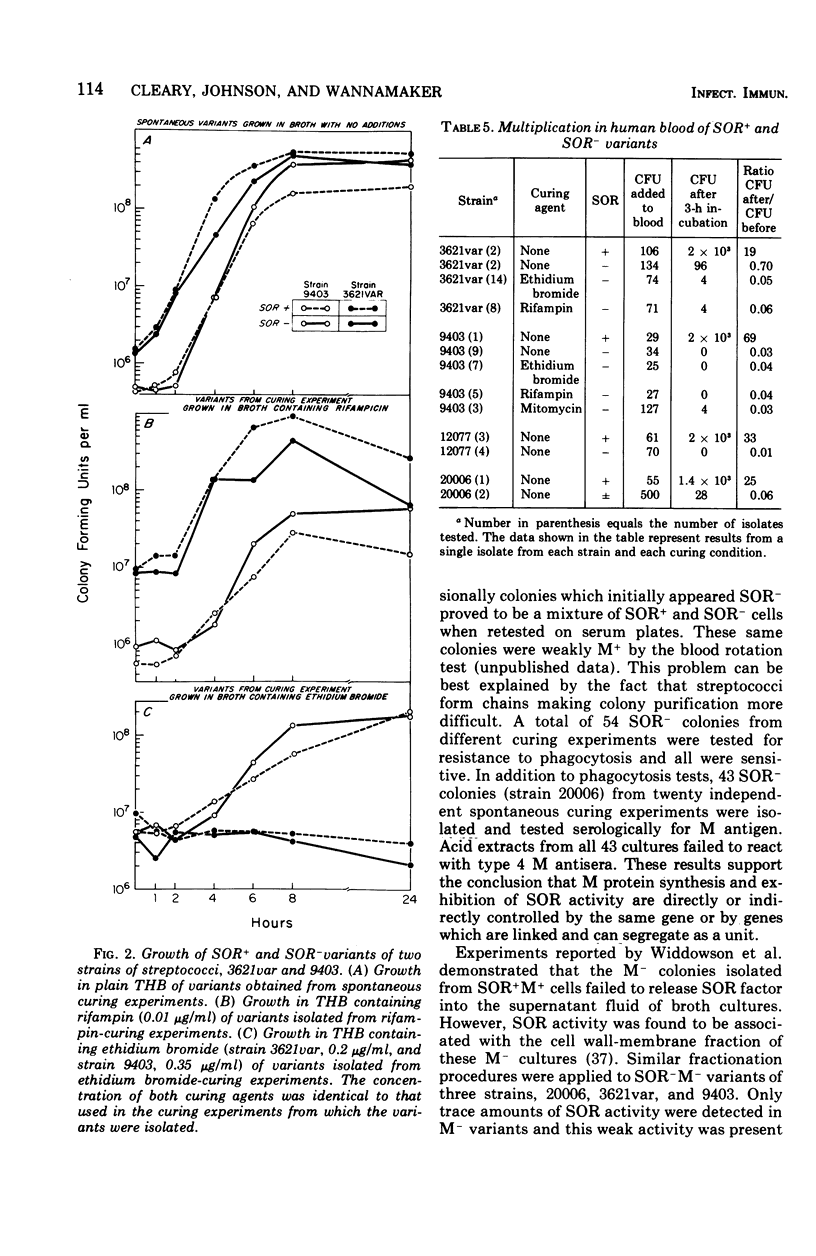
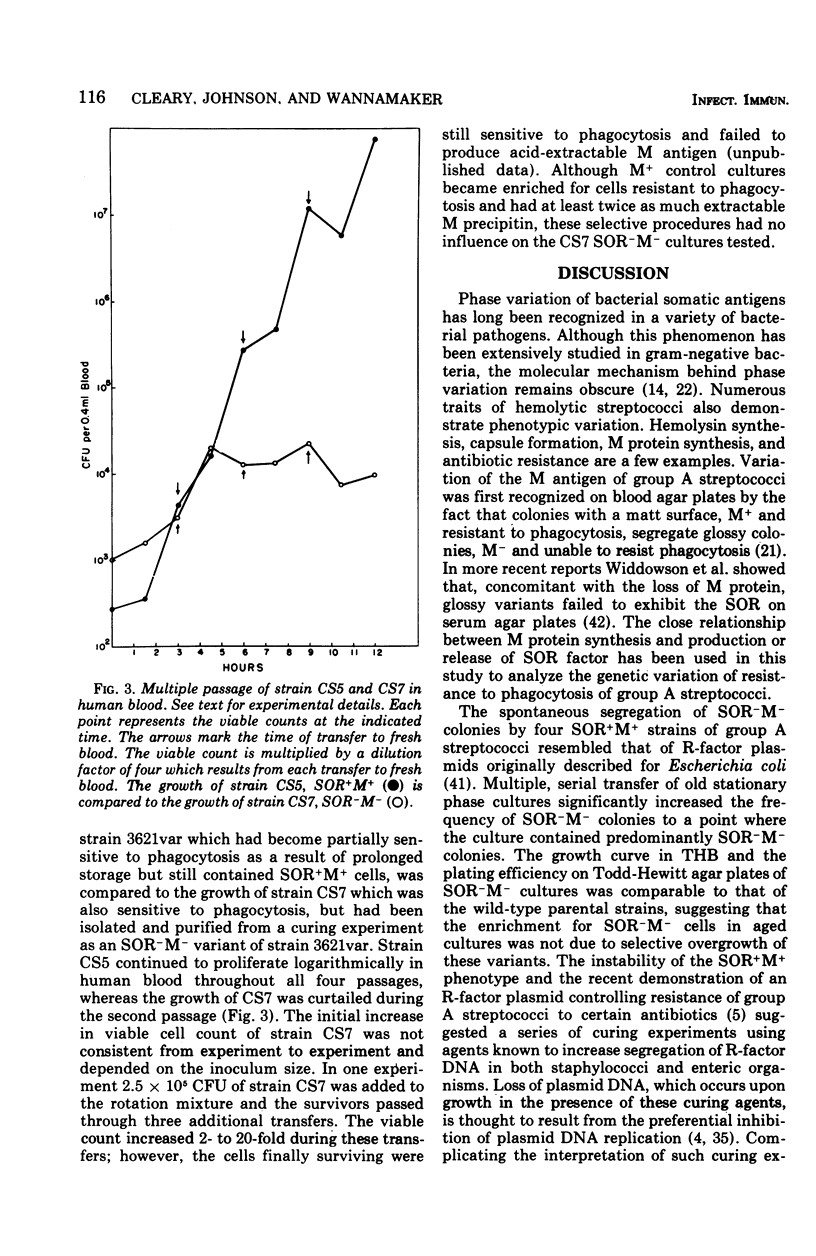
The M antigen, a primary determinant of virulence in group A streptococci that is expressed biologically as resistance to phagocytosis, is known to undergo a variety of phenotypic changes both in vivo and in vitro. These changes are nonrandom and can occur at a high frequency. Using the previously described relationship between the serum opacity reaction (associated with certain strains) and the presence of the M antigen, the phenotypic instability of the M antigen was analyzed. The results support the conclusion that M protein synthesis and the serum opacity reaction are directly or indirectly controlled by the same gene or by genes which are linked and can segregate as a unit. Moreover, growth conditions and the curing agents rifampin and ethidium bromide had a discernible influence on the segregation of clones unable to exhibit serum opacity factor and to resist phagocytosis by human leukocytes. Serial transfer of stationary-phase cultures of four strains of group A streptococci significantly increased the number of colonies negative for the serum opacity reaction and the M antigen. For two of four strains both ethidium bromide and rifampin also increased the segregation of colonies with this phenotype. In light of these experiments and the necessary controls, the possible influence of plasmids or bacteriophage in regulating M protein synthesis is discussed.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER C. G. SELECTION OF GROUP A STREPTOCOCCI RICH IN M-PROTEIN FROM POPULATIONS POOR IN M-PROTEIN. Am J Pathol. 1964 Jan;44:51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Evenchik B., Cranston J. W. Direct inhibition of Col E 1 plasmid DNA replication in Escherichia coli by rifampicin. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 3;237(70):29–31. doi: 10.1038/newbio237029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon H. C., Reeves M. S., Maxted W. R. Acute glomerulonephritis following skin infection due to streptococci of M-type 2. Lancet. 1968 Mar 16;1(7542):543–545. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92826-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT R. D., STOLLERMAN G. H. Factors affecting the chain length of group A streptococci. II. Quantative M-anti-M relationships in the long chain test. J Exp Med. 1960 Oct 1;112:687–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Benzathine penicillin in the prophylaxis of streptococcal skin infections: a pilot study. J Pediatr. 1973 Oct;83(4):572–577. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO H., KONO K., MITSUHASHI S. ELIMINATION OF PENICILLIN RESISTANCE OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BY TREATMENT WITH ACRIFLAVINE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jul;88:261–262. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.1.261-262.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. H., Richmond M. H. The increased rate of loss of penicillinase plasmids from Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of rifampicin. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):137–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. I. IDENTITY OF THE REACTANTS, AND STOICHIOMETRY OF THE REACTION. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:849–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M., RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr, DENNY F. W., Jr, WANNAMAKER L. W. Studies of the carrier state following infection with group A streptococci. 1. Effect of climate. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:568–574. doi: 10.1172/JCI104510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUMWIEDE E. Studies on a lipoproteinase of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1954 Dec 1;100(6):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.6.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. A reevaluation of the genetic mechanism governing phase variation in Salmonella. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;107(2):114–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00333627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Differentiation of group A streptococci with a common R antigen into three serological types, with special reference to the bactericidal test. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):525–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J, Iino T. Phase Variation in Salmonella. Genetics. 1956 Sep;41(5):743–757. doi: 10.1093/genetics/41.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Valkenburg H. A. Variation in the M-antigen of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):199–210. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Widdowson J. P., Fraser C. A., Ball L. C., Bassett D. C. The use of the serum opacity reaction in the typing of group-A streptococci. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):83–90. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY W. D., SIEGEL A. C., RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr, WANNAMAKER L. W., MARPLE E. C. Transmission of group A streptococci. I. The role of contaminated bedding. Am J Hyg. 1957 Jul;66(1):85–95. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. T. Streptococcal skin infection and acute glomerulonephritis. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81(Suppl):37+–37+. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb12832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. V., Ortiz J. S., Sharrett A. R., Burt E. G., Bray J. P., Finklea J. F., Poon-King T., Earle D. P. Changing types of nephritogenic streptococci in Trinidad. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1197–1205. doi: 10.1172/JCI106597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter E. V., Svartman M., Burt E. G., Finklea J. F., Poon-King T., Earle D. P. Relationship of acute rheumatic fever to acute glomerulonephritis in Trinidad. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):619–625. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMMELKAMP C. H., Jr, MORRIS A. J., CATANZARO F. J., WANNAMAKER L. W., CHAMOVITZ R., MARPLE E. C. Transmission of group A streptococci. III. The effect of drying on the infectivity of the organism for man. J Hyg (Lond) 1958 Jun;56(2):280–287. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero E., Riva S., Fietta A. M., Silvestri L. G. Effect of R factors on rifampicin resistance in E. coli. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 10;234(45):56–58. doi: 10.1038/newbio234056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotta J., Krause R. M., Lancefield R. C., Everly W., Lackland H. New approaches for the laboratory recognition of M types of group A streptococci. J Exp Med. 1971 Nov 1;134(5):1298–1315. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.5.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saedler H., Besemer J., Kemper B., Rosenwirth B., Starlinger P. Insertion mutations in the control region of the Gal operon of E. coli. I. Biological characterization of the mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(3):258–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00268889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury V., Hedges R. W., Datta N. Two modes of "curing" transmissible bacterial plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):443–452. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Top F. H., Jr, Wannamaker L. W. The serum opacity reaction of Streptococcus pyogenes. The demonstration of multiple, strain-specific lipoproteinase antigens. J Exp Med. 1968 May 1;127(5):1013–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.5.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., LYANG K. W. Episome-mediated transfer of drug resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. V. Spontaneous segregation and recombination of resistance factors in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84:422–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.422-430.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY G. G., WILSON A. T. The occurrence of two M antigens in certain group A streptococci related to type 14. J Exp Med. 1961 Feb 1;113:451–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. E. Laboratory diagnosis of streptococcal infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(1):153–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W. Differences between streptococcal infections of the throat and of the skin. I. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jan 1;282(1):23–31. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197001012820106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L., Pinney A. M. The relationship between M-antigen and opacity factor in group A streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Jan;65(1):69–80. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdowson J. P., Maxted W. R., Grant D. L. The production of opacity in serum by group A streptococci and its relationship withthe presence of M antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):343–353. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


