Abstract
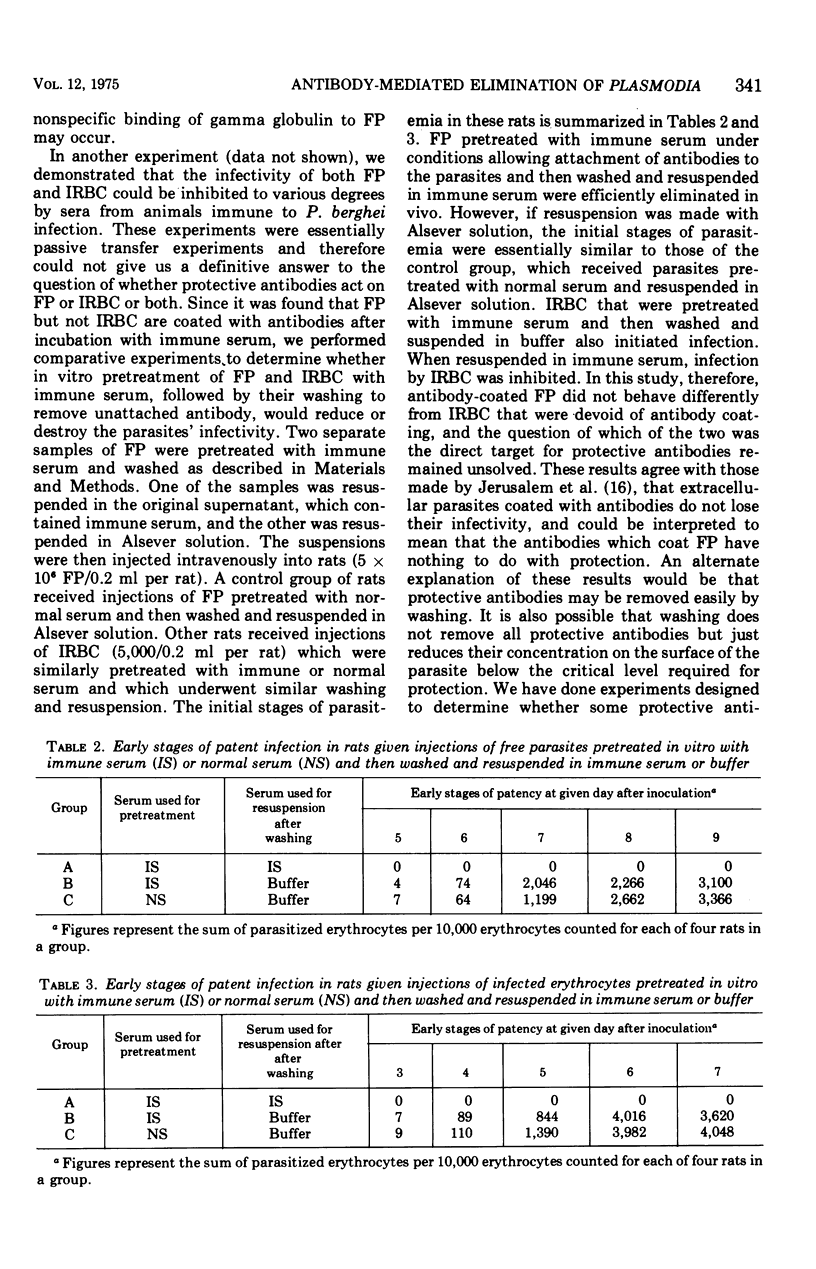
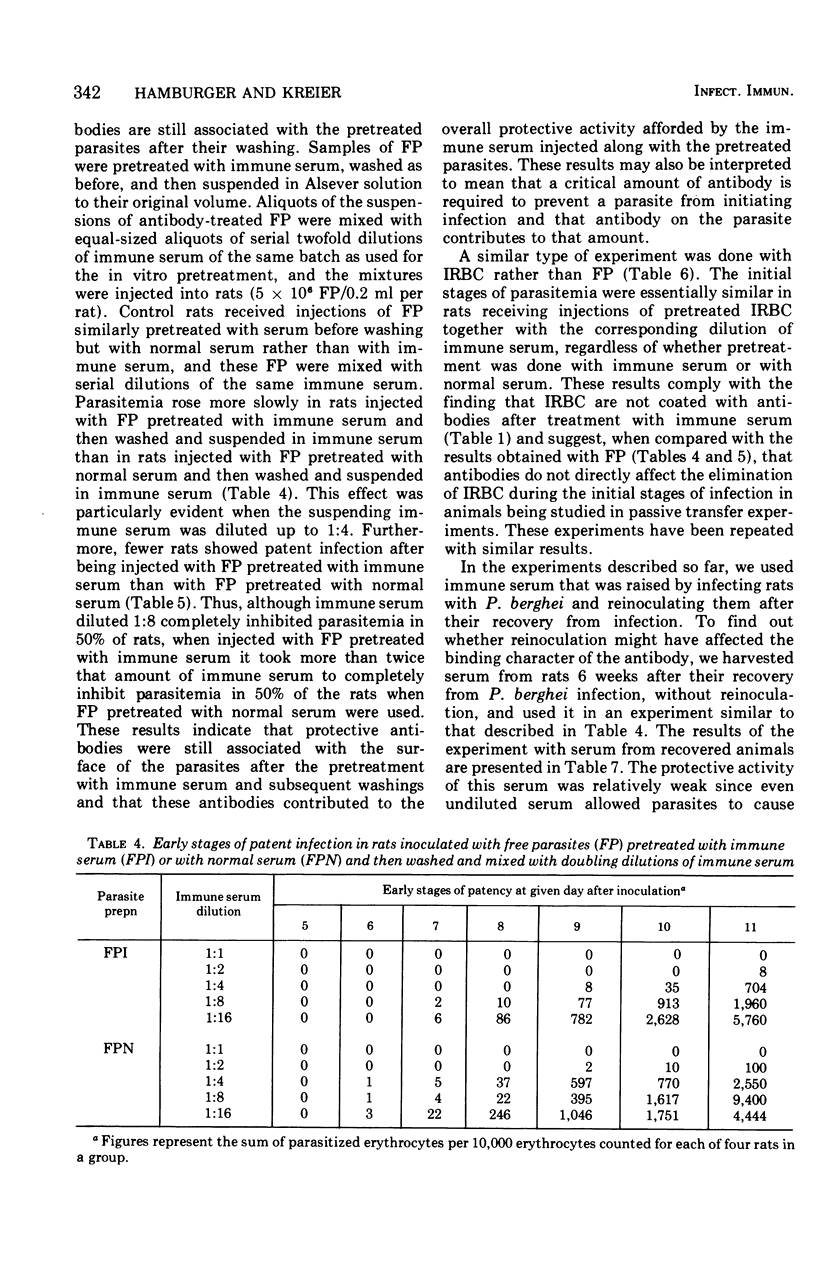
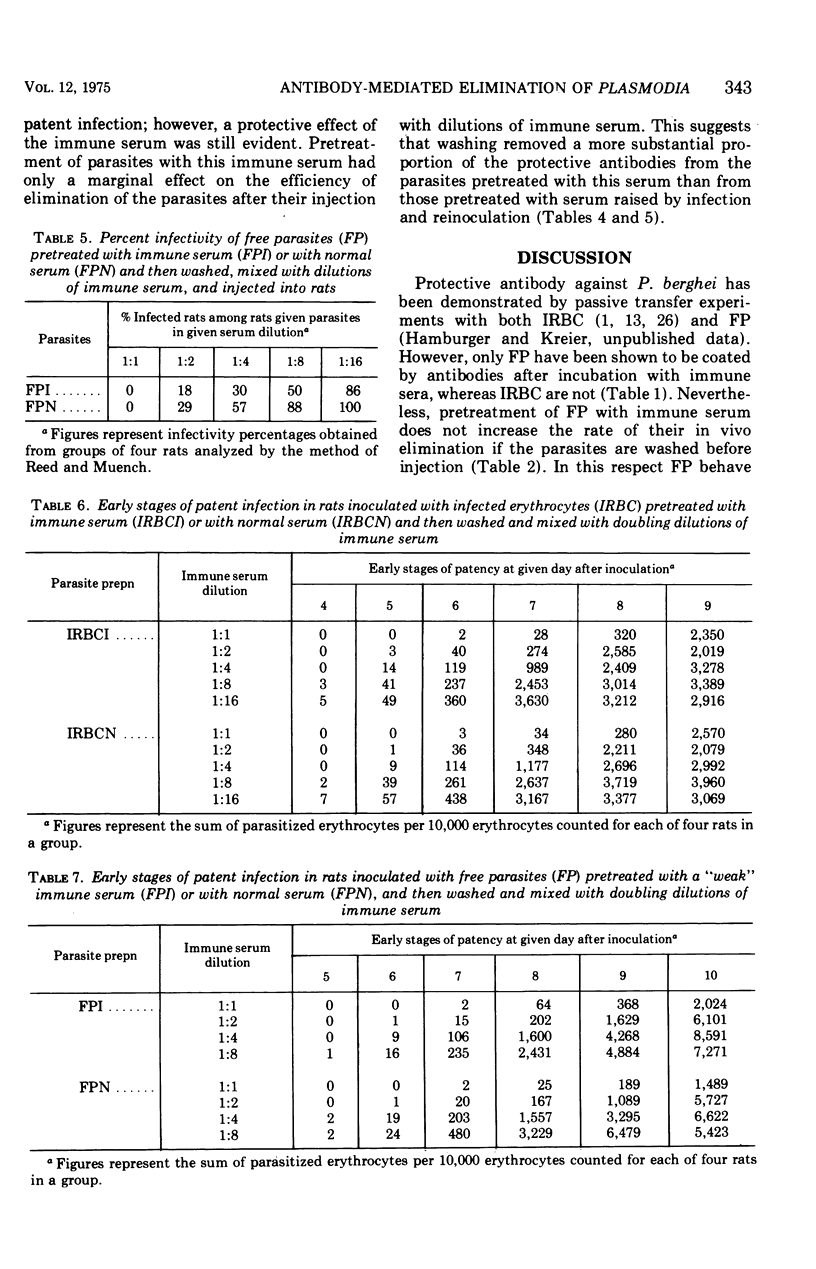
An infective preparation of extracellular blood forms (FP) of Plasmodium berghei was used to study some aspects of the interaction between protective antibodies and malaria parasites. FP but not infected erythrocytes (IRBC) were shown by the fluorescent antibody technique to be coated by antibodies after in vitro incubation with immune serum. Preincubation of both FP and IRBC with immune serum followed by their washing did not result in enhanced elimination of the parasites in vivo. However, FP preincubated with immune serum and subsequently washed were eliminated more efficiently than FP preincubated with normal serum if the preparations were injected with some immune serum. Such an increase in the efficiency of elimination was not detected with similarly pretreated IRBC. It is thus probable that protective antibodies acted in vivo against extracellular parasites rather than against parasites in erythrocytes. The interaction between parasites and antibodies may be of a highly reversible nature, and washing of the in vitro-treated parasites may cause elution of antibody from the sensitized parasites so that the amount of antibody on the parasite falls below the critical level required for in vivo elimination.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Briggs N. T., Wellde B. T., Sadun E. H. Effects of rat antiserum on the course of Plasmodium berghei infection in mice. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9 Suppl):1243–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs N. T., Wellde B. T., Sadun E. H. Variants of Plasmodium berghei resistant to passive transfer of immune serum. Exp Parasitol. 1968 Jun;22(3):338–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(68)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. N., Phillips R. S. Immunity to Plasmodium berghei in rats: passive serum transfer and role of the spleen. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1213–1218. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1213-1218.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N. Antibody induced variation in malaria parasites. Nature. 1973 Mar 2;242(5392):49–50. doi: 10.1038/242049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Brown I. N. Immunity to malaria: antigenic variation in chronic infections of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature. 1965 Dec 25;208(5017):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2081286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Cohen S. Antigenic variation and protective immunity in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):503–521. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S., McGREGOR I. A., CARRINGTON S. Gamma-globulin and acquired immunity to human malaria. Nature. 1961 Nov 25;192:733–737. doi: 10.1038/192733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX H. W. A study of relapse Plasmodium berghei infections isolated from white mice. J Immunol. 1959 Mar;82(3):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan K. M. Antibody response to viral antigens. Adv Immunol. 1973;17:195–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggs C. L., Osler A. G. Humoral immunity in rodent malaria. II. Inhibition of parasitemia by serum antibody. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggs C. L., Osler A. G. Humoral immunity in rodent malaria. III: Studies on the site of antibody action. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1243–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerusalem C., Weiss M. L., Poels L. Immunologic enhancement in malaria infection (Plasmodium berghei). J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):260–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. S., Jones V. E. Immunity to Plasmodium berghei in rats: maximum levels of protective antibody activity are associated with eradication of the infection. Parasitology. 1972 Feb;64(1):117–127. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000044693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior R. B., Kreier J. P. Plasmodium berghei freed from host erythrocytes by a continuous-flow ultrasonic system. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Oct;32(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed T. M., Aikawa M., Sterling C., Rabbege J. Surface properties of extracellular malaria parasites: morphological and cytochemical study. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):750–761. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.750-761.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Rossan R. N. Immunological studies with simian malarias. I. Antigenic variants of Plasmodium cynomolgi bastianellii. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(69)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A. Variant specific schizont agglutination antibodies in human malaria (Plasmodium falciparum) infections in Aotus. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(1):2–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhurst D. C., Folwell R. O. Measurement of the growth rate of the erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium berghei and comparisons of the potency of inocula after various treatments. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1968 Sep;62(3):349–360. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1968.11686570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


